Abstract
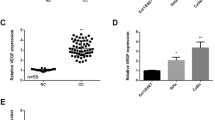
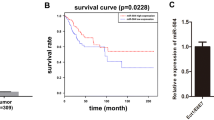
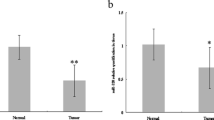
Cervical cancer is the third most common gynecologic cancer in the world. Exploration of the molecular mechanism underlying cervical cancer pathogenesis will provide new insights into the development of novel therapies. In this study, we were aimed to characterize a novel miRNA in cervical cancer tumorigenesis. First, we measured the expressional change of miR-144-3p in clinical tissues and cancer cells. Second, we employed cell proliferation, cell migration, and invasion assays to understand its functional role in cervical cancer. Then, we confirmed in vitro findings in xenograft cancer model. Last, we mapped out a downstream target of miR-144-3p and validated its functional role in cancer cells. In the results, miR-144-3p was found significantly downregulated in cervical cancer cells and tissues. Over-expressing miR-144-3p suppressed cancer cells growth and metastasis. Consistent with in vitro results, over-expressing miR-144-3p led to tumor growth inhibition in vivo. Further on, MAPK6 was identified as an endogenous target of miR-144-3p in cervical cancer. Knocking down MAPK6 inhibited cervical cancer cells proliferation, migration, and invasion potential. Our investigation was the first time to report miR-144-3p as a tumor suppressive miRNA in cervical cancer. It inhibited tumor growth by targeting MAKP6. The newly identified signalling axis may serve as novel therapeutic targets to manage cervical cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 4. doi:https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Al-Mahdi R, Babteen N, Thillai K, Holt M, Johansen B, Wetting HL, Seternes OM, Wells CM (2015) A novel role for atypical MAPK kinase ERK3 in regulating breast cancer cell morphology and migration. Cell Adhes Migr 9:483–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336918.2015.1112485
Banno K, Iida M, Yanokura M, Kisu I, Iwata T, Tominaga E, Tanaka K, Aoki D (2014) MicroRNA in cervical cancer: OncomiRs and tumor suppressor miRs in diagnosis and treatment. TheScientificWorldJournal 2014:178075. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/178075
Boulton TG, Nye SH, Robbins DJ, Ip NY, Radziejewska E, Morgenbesser SD, DePinho RA, Panayotatos N, Cobb MH, Yancopoulos GD (1991) ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell 65:663–675
Burd EM (2003) Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Clin Microbiol Rev 16:1–17
Duenas-Gonzalez A, Lizano M, Candelaria M, Cetina L, Arce C, Cervera E (2005) Epigenetics of cervical cancer. An overview and therapeutic perspectives. Mol Cancer 4:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-4-38
Fan Z, Cui H, Xu X, Lin Z, Zhang X, Kang L, Han B, Meng J, Yan Z, Yan X, Jiao S (2015) MiR-125a suppresses tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in cervical cancer by targeting STAT3. Oncotarget 6:25266–25280. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4457
Fan D, Wang Y, Qi P, Chen Y, Xu P, Yang X, Jin X, Tian X (2016) MicroRNA-183 functions as the tumor suppressor via inhibiting cellular invasion and metastasis by targeting MMP-9 in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol 141:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.02.006
Fang J, Zhang H, Jin S (2014) Epigenetics and cervical cancer: from pathogenesis to therapy. Tumour Biol 35:5083–5093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1737-z
Gao C, Zhou C, Zhuang J, Liu L, Liu C, Li H, Liu G, Wei J, Sun C (2018) MicroRNA expression in cervical cancer: novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. J Cell Biochem 119:7080–7090. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27029
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP, Lawler S (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol Med 20:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2014.06.005
Hillemanns P, Soergel P, Hertel H, Jentschke M (2016) Epidemiology and early detection of cervical cancer. Oncol Res Treat 39:501–506. https://doi.org/10.1159/000448385
Hou T, Ou J, Zhao X, Huang X, Huang Y, Zhang Y (2014) MicroRNA-196a promotes cervical cancer proliferation through the regulation of FOXO1 and p27Kip1. Br J Cancer 110:1260–1268. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.829
Hu X, Schwarz JK, Lewis JS Jr, Huettner PC, Rader JS, Deasy JO, Grigsby PW, Wang X (2010) A microRNA expression signature for cervical cancer prognosis. Cancer Res 70:1441–1448. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3289
Lee JW, Choi CH, Choi JJ, Park YA, Kim SJ, Hwang SY, Kim WY, Kim TJ, Lee JH, Kim BG, Bae DS (2008) Altered MicroRNA expression in cervical carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 14:2535–2542. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1231
Li B, Zhang S, Shen H, Li C (2017) MicroRNA-144-3p suppresses gastric cancer progression by inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through targeting PBX3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 484:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.084
Liu C, Su C, Chen Y, Li G (2018) MiR-144-3p promotes the tumor growth and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting paired box gene 8. Cancer Cell Int 18:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0550-y
Long MJ, Wu FX, Li P, Liu M, Li X, Tang H (2012a) MicroRNA-10a targets CHL1 and promotes cell growth, migration and invasion in human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Lett 324:186–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.05.022
Long W, Foulds CE, Qin J, Liu J, Ding C, Lonard DM, Solis LM, Wistuba II, Qin J, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW (2012b) ERK3 signals through SRC-3 coactivator to promote human lung cancer cell invasion. J Clin Invest 122:1869–1880. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI61492
Pimple S, Mishra G, Shastri S (2016) Global strategies for cervical cancer prevention. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 28:4–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/GCO.0000000000000241
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16:203–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246
Shishodia G, Verma G, Das BC, Bharti AC (2018) miRNA as viral transcription tuners in HPV-mediated cervical carcinogenesis. Front Biosci 10:21–47
Small W Jr, Bacon MA, Bajaj A, Chuang LT, Fisher BJ, Harkenrider MM, Jhingran A, Kitchener HC, Mileshkin LR, Viswanathan AN, Gaffney DK (2017) Cervical cancer: a global health crisis. Cancer 123:2404–2412. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30667
Tang T, Wong HK, Gu W, Yu MY, To KF, Wang CC, Wong YF, Cheung TH, Chung TK, Choy KW (2013) MicroRNA-182 plays an onco-miRNA role in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol 129:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.12.043
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS, Meyers C, Zheng ZM (2008) Aberrant expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS One 3:e2557. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002557
Xiao W, Lou N, Ruan H, Bao L, Xiong Z, Yuan C, Tong J, Xu G, Zhou Y, Qu Y, Hu W, Gao Y, Ru Z, Liu L, Xiao H, Chen K, Yang H, Zhang X (2017) Mir-144-3p promotes cell proliferation, metastasis, sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by downregulating ARID1A. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:2420–2433. https://doi.org/10.1159/000484395
Yao Q, Xu H, Zhang QQ, Zhou H, Qu LH (2009) MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation and down-regulates the expression of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.044
Zhang P, Cao L, Fan P, Mei Y, Wu M (2016) LncRNA-MIF, a c-Myc-activated long non-coding RNA, suppresses glycolysis by promoting Fbxw7-mediated c-Myc degradation. EMBO Rep 17:1204–1220. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201642067
Zheng H, Guo Z, Zheng X, Cheng W, Huang X (2018) MicroRNA-144-3p inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in prostate cancer by targeting CEP55. Am J Transl Res 10:2457–2468
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Clinical evaluation of miR-144-3p expression in human cervical tumor tissues was approved by the Ethical Committee of Heze Municipal Hospital. The animal studies complied with Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (8th edition, NIH) and was approved by the Animal Study Ethics Committee of Heze Municipal Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Zhao, Y., Li, F. et al. MiR-144-3p: a novel tumor suppressor targeting MAPK6 in cervical cancer. J Physiol Biochem 75, 143–152 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00681-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00681-9