Abstract
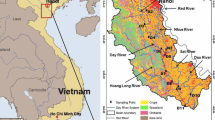
Water samples were collected from three streams flowing through the metropolitan city of Daejeon in South Korea to identify controls on the composition of dissolved ions in stream waters. The seasonal and spatial variations in the concentrations of the dissolved ions were examined and the major contaminant sources were identified using multiple isotopes. All streams exhibited gradual increases in Cl, NO3, and SO4 concentrations as water flowed downstream; the water types were changed from Ca–HCO3 to Ca–(Cl, NO3, SO4). Combined δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 data revealed that the dissolved NO3 was mainly derived from manure or sewage, with partial contributions from NH4 fertilizer in summer. The δ34SSO4 and SO4 concentrations in the stream waters indicated that the dissolved sulfates were derived from contaminants, such as sewage, detergent, and chemical fertilizer supplied discriminately to each stream along its course. The 87Sr/86Sr ratios combined with the Sr and Cl concentrations suggest that sewage associated with chemical fertilizer rather than detergent contributed significantly to the dissolved Sr in all the streams.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson KK, Hooper AB (1983) O2 and H2O are each the source of one O in NO2 − produced from NH3 by Nitrosomonas: 15N-NMR evidence. FEBS Lett 164:236–240
Balci N, Shanks WC, Mayer B, Mandernack KW (2007) Oxygen and sulfur isotope systematic of sulfate produced by bacterial and abiotic oxidation of pyrite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:3796–3811
Böhlke JK, Horan M (2000) Strontium isotope geochemistry of groundwaters and streams affected by agriculture, Locust Grove, MD. Appl Geochem 15:599–609
Bottrell S, Tellam J, Bartlett R, Hughes A (2008) Isotopic composition of sulfate as a tracer of natural and anthropogenic influences on groundwater geochemistry in an urban sandstone aquifer, Birmingham, UK. Appl Geochem 23:2382–2394
Brunner B, Bernasconi SM, Kleikemper J, Schroth MH (2005) A model for oxygen and sulfur isotope fractionation in sulfate during bacterial sulfate reduction processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:4773–4785
Chapman PJ, Edwards AC, Cresser MS (2001) The nitrogen composition of streams in upland Scotland: some regional and seasonal differences. Sci Total Environ 265:65–83
Cheong CS, Jeong GY, Kim H, Choi MS, Lee SH, Cho M (2002) Early Permian peak metamorphism recorded in U-Pb system of black slates from the Ogcheon metamorphic belt, South Korea, and its tectonic implication. Chem Geol 193:81–92
Christian LN, Banner JL, Mack LE (2011) Sr isotopes as tracers of anthropogenic influences on stream water in the Austin, Texas, area. Chem Geol 282:84–97
Church TM, Sommerfield CK, Velinsky DJ, Point D, Benoit C, Amouroux D, Plaa D, Donard OFX (2006) Marsh sediments as records of sedimentation, eutrophication and metal pollution in the urban Delaware Estuary. Mar Chem 102:72–95
Clark MJ, Cresser MS, Smart R, Chapman PJ, Edwards AC (2004) The influence of catchment characteristics on the seasonality of carbon and nitrogen species concentrations in upland rivers of Northern Scotland. Biogeochemistry 68:1–19
Daejeon Metropolitan City (2007) Three major streams in Daejeon. http://www.daejeon.go.kr/life/policy/stream/stream1/index.html. Accessed 4 Feb 2007
Douglas TA, Chamberlain CP, Blum JD (2002) Land use and geologic controls on the major elemental and isotopic (δ15N and 87Sr/86Sr) geochemistry of the Connecticut River watershed, USA. Chem Geol 189:19–34
Faure G (1986) Principles of isotope geology. Wiley, New York
Fritz SJ (1994) A survey of charge-balance errors on published analyses of potable ground and surface waters. Ground Water 32:539–546
Geological Society of Korea (1999) Geology of Korea. Sigma press, Seoul (in Korean)
Hindshaw RS, Tipper ET, Reynolds BC, Lemarchand E, Wiederhold JG, Magnusson J, Bernasconi SM, Kretzschmar R, Bourdon B (2011) Hydrological control of stream water chemistry in a glacial catchment (Damma Glacier, Switzerland). Chem Geol 285:215–230
Hollocher TC (1984) Source of the oxygen atoms of nitrate in the oxidation of nitrite by Nitrobacter agilis and evidence against a P-O-N anhydride mechanism in oxidative phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys 233:721–727
Hosono T, Nakano T, Igeta A, Tayasu I, Tanaka T, Yachi S (2007) Impact of fertilizer on a small watershed of Lake Biwa: use of sulfur and strontium isotopes in environmental diagnosis. Sci Total Environ 384:342–354
Hosono T, Delinom R, Nakano T, Kagabu M, Shimada J (2011a) Evolution model of δ34S and δ18O in dissolved sulfate in volcanic fan aquifers from recharge to coastal zone and through the Jakarta urban area, Indonesia. Sci Total Environ 409:2541–2554
Hosono T, Wang CH, Umezawa Y, Nakano T, Onodera SI, Nagata T, Yoshimizu C, Tayasu I, Taniguchi M (2011b) Multiple isotope (H, O, N, S and Sr) approach elucidates complex pollution causes in the shallow groundwaters of the Taipei urban area. J Hydrol 397:23–36
Karr JD, Showers WJ, Jennings GD (2003) Low-level nitrate export from confined dairy farming detected in North Carolina streams using δ15N. Agric Ecosyst Environ 95:103–110
Kendall C, Elliott EM, Wankel SD (2007) Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. In: Michener R, Lajtha K (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 375–449
Kim KH, Park SS, Na CK (1996) Nd and Sr isotopic signatures of Mesozoic granitoids in South Korea. Resour Geol 46:215–226 (in Korean with English abstract)
Knoepp JD, Swank WT (2002) Using soil temperature and moisture to predict forest soil nitrogen mineralization. Biol Fertility Soils 36:177–182
Korea Meteorological Administration (2008) Data of meteorological elements. http://www.kma.go.kr/weather/observation/past_table.jsp. Accessed 7 Apr 2008
Krouse HR, Mayer B (2000) Sulphur and oxygen isotopes in sulfate. In: Cook PG, Herczeg AL (eds) Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 195–231
Lang YC, Liu CQ, Li SL, Zhao ZQ, Zhou ZH (2011) Tracing natural and anthropogenic sources of dissolved sulfate in a karst region by using major ion chemistry and stable sulfur isotopes. Appl Geochem 26:S202–S205
Lee SM, Kim HS, Na KC (1980) Explanatory text of the geological map of Daejeon sheet. Korea Research Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources, Daejeon (in Korean)
Marsden MW, Mackay DW (2001) Water quality in Scotland: the view of the regulator. Sci Total Environ 265:369–386
Mayer B, Boyer EW, Goodale C, Jaworski NA, Breemen NV, Howarth RW (2002) Sources of nitrate in rivers draining sixteen watersheds in the northeastern US.: isotopic constraints. Biogeochemistry 57(58):171–197
Miller EK, Blum JD, Friedland AJ (1993) Determination of soil exchangeable-cation loss and weathering rates using Sr isotopes. Nature 362:438–441
Nakano T, Tayasu I, Yamada Y, Hosono T, Igeta A, Hyodo F, Ando A, Saitoh Y, Tanaka T, Wada E, Yachi S (2008) Effect of agriculture on water quality of Lake Biwa tributaries, Japan. Sci Total Environ 389:132–148
Nisi B, Buccianti A, Vaselli O, Perini G, Tassi F, Minissale A, Montegrossi G (2008) Hydrogeochemistry and strontium isotopes in the Arno River Basin (Tuscany, Italy): constraints on natural controls by statistical modeling. J Hydrol 360:166–183
Novák M, Kirchner JW, Groscheová H, Havel M, Černý J, Krejčí R, Buzek F (2000) Sulfur isotope dynamics in two Central European watersheds affected by high atmospheric deposition of SOx. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:367–383
Novák M, Vile MA, Bottrell SH, Štĕpánová M, Jačková I, Buzek F, Přechová E, Newton RJ (2005) Isotope systematic of sulfate-oxygen and sulfate-sulfur in six European peatlands. Biogeochemistry 76:187–213
Novák M, Mitchell MJ, Jačková I, Buzek F, Schweigstillová J, Erbanová L, Přikryl R, Fottová D (2007) Processes affecting oxygen isotope ratios of atmospheric and ecosystem sulfate in two contrasting forest catchments in Central Europe. Environ Sci Technol 41:703–709
Ogrinc N, Markovics R, Kanduč T, Walter LM, Hamilton SK (2008) Sources and transport of carbon and nitrogen in the River Sava watershed, a major tributary of the River Danube. Appl Geochem 23:3685–3698
Otero N, Canals À, Soler A (2007) Using dual-isotope data to trace the origin and processes of dissolved sulphate: a case study in Calders stream (Llobregat basin, Spain). Aquat Geochem 13:109–126
Otero N, Soler A, Canals À (2008) Controls of δ34S and δ18O in dissolved sulphate: learning from a detailed survey in the Llobregat River (Spain). Appl Geochem 23:1166–1185
Panno SV, Hackley KC, Hwang HH, Kelly WR (2001) Determination of the sources of nitrate contamination in karst springs using isotopic and chemical indicators. Chem Geol 179:113–128
Pardo LH, Kendall C, Pett-Ridge J, Chang CCY (2004) Evaluating the source of streamwater nitrate using and δ15N and δ18O in nitrate in two watersheds in New Hampshire, USA. Hydrol Process 18:2699–2712
Park HI, Lee JD, Cheong JG (1977) Explanatory text of the geological map of Yuseong sheet. Korea Research Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources, Daejeon (in Korean)
Pawellek F, Frauenstein F, Veizer J (2002) Hydrochemistry and isotope geochemistry of the upper Danube River. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:3839–3853
Perrin AS, Probst A, Probst JL (2008) Impact of nitrogenous fertilizers on carbonate dissolution in small agricultural catchments: implications for weathering CO2 uptake at regional and global scales. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:3105–3123
Poor CJ, McDonnell JJ (2007) The effects of land use on stream nitrate dynamics. J Hydrol 332:54–68
Ryu JS, Lee KS, Chang HW (2007) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic investigations of the Han River basin, South Korea. J Hydrol 345:50–60
Ryu JS, Lee KS, Chang HW, Shin HS (2008) Chemical weathering of carbonates and silicates in the Han River basin, South Korea. Chem Geol 247:66–80
Shin WJ, Ryu JS, Mayer B, Lee KS, Lee SW (2014) Natural and anthropogenic sources and processes affecting water chemistry in two South Korean streams. Sci Total Environ 485–486:270–280
Stögbauer A, Strauss H, Arndt J, Marek V, Einsiedl F, van Geldern R (2008) Rivers of North-Rhine Westphalia revisited: tracing changes in river chemistry. Appl Geochem 23:3290–3304
Thevenon F, Graham ND, Herbez A, Wildi W, Poté J (2011) Spatio-temporal distribution of organic and inorganic pollutants from Lake Geneva (Switzerland) reveals strong interacting effects of sewage treatment plant and eutrophication on microbial abundance. Chemosphere 84:609–617
Umezawa Y, Hosono T, Onodera S, Siringan F, Buapeng S, Delinom R, Yoshimizu C, Tayasu I, Nagata T, Taniguchi M (2008) Sources of nitrate and ammonium contamination in groundwater under developing Asian megacities. Sci Total Environ 404:361–376
White AF, Bullen TD, Vivit DV, Schulz MS, Clow DW (1999) The role of disseminated calcite in the chemical weathering of granitoid rocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1939–1953
Yanagisawa F, Sakai H (1983) Thermal decomposition of barium sulfate-vanadium pentaoxcide-silica glass mixtures for preparation of sulfur dioxide in sulfur isotope ratio measurements. Anal Chem 55:985–987
Yu JY, Park Y (2004) Sulfur isotope and chemical compositions of the natural waters in the Chuncheon area, Korea. Appl Geochem 19:843–853
Yu JY, Park Y, Mielke RE, Coleman ML (2007) Sulfur and oxygen isotopic compositions of the dissolved sulphate in the meteoric water in Chuncheon, Korea. Geosci J 11:357–367
Acknowledgments
We thank H.S. Shin and D.C. Koh for analyzing the water samples. This work was supported by a national agenda program (NAP) of the Korea Research Council of Fundamental Science and Technology and by a KBSI grant (C34701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W.-J. Shin and J.-S. Ryu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, WJ., Ryu, JS., Lee, KS. et al. Identification of anthropogenic contaminant sources in urbanized streams using multiple isotopes. Environ Earth Sci 73, 8311–8324 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3992-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3992-0