Abstract
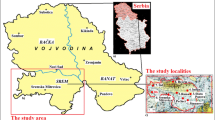
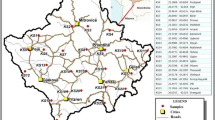
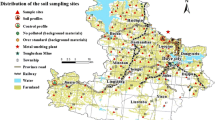
In order to investigate the factors influencing the distribution of 32 potentially toxic elements in the Ptolemais–Kozani basin, northwestern Greece, 38 soil samples were collected and analyzed. Concentrations of Al, Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na, P, Ti, Ba, Co, Cr, Cu, La, Li, Ni, Pb, Sc, Sr, V, Y, and Zn were determined by ICP-AES and concentrations of As, Bi, Cd, Cs, Mo, Rb, Sb, Th, Tl, and U by ICP-MS. Bivariate analysis, principal component analysis, and geostatistical analysis were employed to investigate the factors influencing the distribution of the elements determined in the study area. The results indicate that the distribution of the majority of elements determined, especially for Cr, Ni, and associated elements, is greatly influenced by the geology and geomorphology of the study area. Principal component analysis has yielded four factors that explain over 77% of the total variance in the data. These factors are as follows: lithophilic elements that are associated with Al silicates minerals of K (factor I: 29.4%), ultramafic rocks (factor II: 20.5%), elements that are coprecipitated with Fe and Mn oxides (factor III: 18.0%), and anthropogenic activities (factor IV: 9.3%). The anthropogenic activities that influence the distribution of several potentially toxic elements (i.e., Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn) are agricultural practices and the deposition of fly ash in the vicinity of the local power stations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett RJ (1986) Soil redox behavior. In: Sparks DJ (ed) Soil Physical chemistry. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Bölviken B, Bogen J, Demetriades A, De Vos W, Ebbing J, Hindel R, Langedal M, Locutura J, O’Connor P, Ottesen RT, Pulkkinen E, Salminen R, Schermann O, Swennen R, Van der Sluys J, Volden T (1996) Regional geochemical mapping of western Europe towards the year 2000. J Geochem Explor 56:141–166
Chen M, Ma QL, Harris WG (1999) Baseline concentrations in Florida surface soils. J Environ Qual 28:1173–1181
Chen M, Ma QL, Hoogeweg G, Harris WG (2001) Arsenic background concentrations in Florida, U.S.A. surface soils: determination and interpretation. Environ Forensics 2:117–126
Christanis K, Georgakopoulos A, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Bouzinos A (1998) Geological factors influencing the concentration of trace elements in the Philippi peatland, eastern Macedonia, Greece. Int J Coal Geol 36:295–313
Cui YJ, Zhai RΗ, Huang YZ, Qiu Y, Liang JZ (2005) Exposure to metal mixtures and human health impacts in a contaminated area in Nanning, China. Environ Int 31:784–790
Diamantopoulos A (2005) Semi-brittle asymmetric shear planes controlling the Cenozoic kinematics of Internal Hellenides (northern Greece): field evidence from Askion and Vermio mountain ranges. In: International earth Sciences Colloquium on the Aegean Regions, IESCA 2005, October 4–7, 2005, Abstract book, 31, Izmir-Turkey
Diamantopoulos A (2006) Plio-Quaternary geometry and kinematics of Ptolemais basin, northern Greece: implications for the intra-plate tectonics in western Macedonia. Geol Croat 59:85–96
Fernandez-Turiel JL, Aceñolaza P, Medina ME, Llorens JF, Sardi F (2001) Assessment of a smelter impact area using surface soils and plants. Environ Geochem Health 23:65–78
Fernandez-Turiel JL, Georgakopoulos A, Gimeno D, Papastergios G, Kolovos N (2004) Ash deposition in a pulverized coal-fired power plant after high-calcium lignite combustion. Energy Fuels 18:1512–1518
Filippidis A, Georgakopoulos A, Kassoli-Fournaraki A, Misaelides P, Yiakkoupis P, Broussoulis J (1996) Trace element contents in composite samples of three lignite seams from the central part of the Drama lignite deposit, Macedonia, Greece. Int J Coal Geol 29:219–234
FOREGS (Forum of European Geological Surveys) (2005) FOREGS geochemical baseline mapping program. http://www.gsf.fi/foregs/geo-chem/index.htm. Accessed March 2009
Georgakopoulos A, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Filippidis A, Llorens JF, Kassoli-Fournaraki A, Querol X, Lopez-Soler A (1995) Trace element contents of the Lava Xylite/Lignite and Ptolemais lignite deposits, Macedonia County, Greece. In: Pajares JA, Tascon JMD (eds) Coal science. Coal Science and Technology, vol 24. Elsevier, New York, pp 163–166
Georgakopoulos A, Filippidis A, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Kassoli-Fournaraki A, Iordanidis A (2002a) Lithogenic and anthropogenic origin of trace elements in surface soils from Amynteo-Ptolemais-Kozani lignite basin. In: 6th Pan-Helenic geographical conference, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2002 (in Greek, with English abstract), pp 335–342
Georgakopoulos A, Filippidis A, Kassoli-Fournaraki A, Iordanidis A, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Llorens JF, Gimeno D (2002b) Environmentally important elements in fly ashes and their leachates of the power stations of Greece. Energy Source 24:83–91
Georgakopoulos A, Filippidis A, Kassoli-Fournaraki A, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Llorens JF, Mousty F (2002c) Leachability of major and trace elements of fly ash from Ptolemais power station, northern Greece. Energy Source 24:103–113
Gikas GD, Tsihrintzis VA, Akratos CS, Haralambidis G (2009) Water quality trends in Polyphytos reservoir, Aliakmon River, Greece. Environ Monit Assess 149:163–181
Hesterberg D (1998) Biochemical cycles and processes leading to changes in mobility of chemicals in soils. Agric Ecosyst Environ 67:121–133
Iordanidis A, Buckman J, Triantafyllou AG, Asvesta A (2008a) ESEM–EDX characterization of airborne particles from an industrialized area of northern Greece. Environ Geochem Health 30:391–405
Iordanidis A, Buckman J, Triantafyllou AG, Asvesta A (2008b) Fly ash–airborne particles from Ptolemais–Kozani area, northern Greece, as determined by ESEM-EDX. Int J Coal Geol 73:63–73
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press, New York
Kaldellis JK, Zafirakis D, Kondili E (2009) Contribution of lignite in the Greek electricity generation: review and future prospects. Fuel 88:75–489
Karamanis D, Ioannides K, Stamoulis K (2009) Environmental assessment of natural radionuclides and heavy metals in waters discharged from a lignite-fired power plant. Fuel 88:2046–2052
Kavouridis K (2008) Lignite industry in Greece within a world context: mining, energy supply and environment. Energy Policy 36:1257–1272
Kavouridis K, Koukouzas N (2008) Coal and sustainable energy supply challenges and barriers. Energy Policy 36:693–703
Kelepertsis A, Argyraki A, Alexakis D (2006) Multivariate statistics and spatial interpretation of geochemical data for assessing soil contamination by potentially toxic elements in the mining area of Stratoni, north Greece. Geochem Explor Env A 6:349–355
Kolovos N, Georgakopoulos A, Filippidis A, Kavouridis C (2002a) Utilization of lignite reserves and simultaneous improvement of dust emissions and operation efficiency of a power plant by controlling the calcium (total and free) content of the fed lignite. Application on the Agios Dimitrios power plant, Ptolemais, Greece. Energy Fuel 16:1516–1522
Kolovos N, Georgakopoulos A, Filippidis A, Kavouridis C (2002b) Environmental effects of lignite and intermediate steriles coexcavation in the southern lignite field mine of Ptolemais, northern Greece. Energy Source 24:561–573
Kolovos N, Georgakopoulos A, Filippidis A, Kavouridis C (2002c) The effects on the mined lignite quality characteristics by the intercalated thin layers of carbonates in Ptolemais mines, northern Greece. Energy Source 24:761–772
Koufos GD, Pavlides SB (1988) Correlation between the continental deposits of the lower Axios valley and Ptolemais basin. Bull Geol Soc Greece 20:9–19
Megremi I (2010) Distribution and bioavailability of Cr in central Euboea, Greece. Cent Eur J Geosci 2:103–123
Mountrakis D (1983) The geological structure of the north Pelagonian Zone and the geotectonic evolution of the Internal Hellenides. Dissertation, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece (in Greek)
Owen RB, Renaut RW, Stamatakis MG (2010) Diatomaceous sedimentation in late Neogene lacustrine basins of western Macedonia, Greece. J Paleolimnol. doi:10.1007/s10933-010-9409-5
Papadopoulos A, Prochaska C, Papadopoulos F, Gantidis N, Metaxa E (2007) Determination and evaluation of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in agricultural soils of western Macedonia, Greece. Environ Manag 40:719–726
Papastergios G, Georgakopoulos A, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Gimeno D, Kapetanios C (2005) Leachability of environmentally hazardous elements from ashes produced after lignite combustion in Agios Dimitrios power plant, northern Greece. In: Proceedings of the 5th international scientific conference of modern management of mine producing, geology and environmental protection (SGEM), Albena Complex, Bulgaria, 13–17 June 2005, pp 299–306
Papastergios G, Fernandez–Turiel JL, Georgakopoulos A, Gimeno D (2007) Slag and ash chemistry after high-calcium lignite combustion in a pulverized coal-fired power plant. Glob NEST J 9:77–82
Papastergios G, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Georgakopoulos A, Gimeno D (2009) Natural and anthropogenic effects on the sediment geochemistry of Nestos River, northern Greece. Environ Geol 58:1361–1370
Papastergios G, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Georgakopoulos A, Gimeno D (2010a) Arsenic background concentrations in surface soils of Kavala area, northern Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut 209:323–331
Papastergios G, Filippidis A, Fernandez–Turiel JL, Gimeno D, Sikalidis C (2010b) Natural and anthropogenic effects on the soil geochemistry of Kavala area, northern Greece. Bull Geol Soc Greece 43:2373–2382
Papastergios G, Filippidis A, Fernandez–Turiel JL, Gimeno D, Sikalidis C (2011) Surface soil geochemistry for environmental assessment in Kavala area, northern Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut 216:141–152
Pavlides SB (1985) Neotectonic evolution of the Florina-Vegoritis-Ptolemais basin (W. Macedonia. Greece). Dissertation, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece (in Greek, with English summary)
Pavlides SB, Mountrakis DM (1987) Extensional tectonics of northwestern Macedonia, Greece, since the late Miocene. J Struct Geol 9:385–392
Petaloti C, Triantafyllou A, Kouimtzis T, Samara C (2006) Trace elements in atmospheric particulate matter over a coal burning power production area of western Macedonia, Greece. Chemosphere 65:2233–2243
Petrotou A, Skordas K, Papastergios G, Filippidis A (2010) Concentrations and bioavailability of potentially toxic elements in soils of an industrialised area of northwestern Greece. Fresen Environ Bull 19:2769–2776
Querol X, Alastuey AS, Lopez-Soler A, Mantillai E, Plana F (1996) Mineral composition of atmospheric particulates around a large coal-fired power station. Atmos Environ 30:3557–3572
Salminen R (2007) Geochemical Atlas of Europe. http://www.gtk.fi/publ/foregsatlas/. Accessed March 2009
Samara C (2005) Chemical mass balance source apportionment of TSP in a lignite-burning area of western Macedonia, Greece. Atmos Environ 39:6430–6443
Skordas K, Kelepertsis A (2005) Soil contamination by toxic metals in the cultivated region of Agia, Thessaly, Greece. Identification of sources of contamination. Environ Geol 48:615–624
Skordas K, Alexakis D, Kelepertsis E, Kelepertsis A (2007) Environmental geochemical research for the levels and the sources of toxic metals in the agricultural soils of Dimitra-Eleftherion and Platycampos region, Thessaly, Greece. Res J Chem Environ 11:7–18
Skordas K, Pateras D, Papastergios G, Lolas A, Filippidis A (2010) Spatial distribution and concentrations of Fe, Mg, Co, Cr and Ni in surface soils of central Greece as affected by parent rocks. Geochem Mineral Petrol, Sofia 48:95–102
Sotiropoulos D, Georgakopoulos A, Kolovos N (2005) Impact of free-calcium oxide content of the fly ash on dust and sulfur dioxide emissions in a lignite-fired power plant. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 55:1042–1049
Stalikas DC, Chaidou IC, Pilidis AG (1997) Enrichment of PAHs and heavy metals in soils in the vicinity of the lignite-fired power plants of west Macedonia (Greece). Sci Total Environ 204:134–146
Triantafyllou AG (2003) Levels and trend of suspended particles around large lignite power stations. Environ Monit Assess 89:15–34
Triantafyllou AG, Zoras S, Evagelopoulos V (2006) Particulate matter over a seven year period in urban and rural areas within, proximal and far from mining and power station operations in Greece. Environ Monit Assess 122:41–60
Tsikritzis LI (2005) Chemometrics of the distribution and origin of 226Ra, 228Ra, 40K and 137Cs in plants near the west Macedonia lignite center (Greece). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 264:651–656
van Hinsbergen DJJ, van der Meer DG, Zachariasse WJ, Meulenkamp JE (2006) Deformation of western Greece during Neogene clockwise rotation and collision with Apulia. Int J Earth Sci 95:463–490
Vatalis KI, Kaliampakos DC (2006) An overall index of environmental quality in coal mining areas and energy facilities. Environ Manag 38:1031–1045
Acknowledgments
The first author gratefully acknowledges the assistance of Dr Kevin Clemitshaw and, lab technician, Sue Hall of the Royal Holloway University of London, as well as the assistance of Dr Christos Sachanidis of the Public Power Corporation of Greece SA. The constructive comments of the anonymous reviewers that helped improve the original manuscript are gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrotou, A., Skordas, K., Papastergios, G. et al. Factors affecting the distribution of potentially toxic elements in surface soils around an industrialized area of northwestern Greece. Environ Earth Sci 65, 823–833 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1127-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1127-4