Abstract
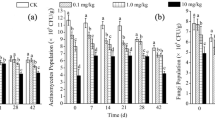
A laboratory study was conducted to evaluate the response of soil enzyme activities (namely dehydrogenase, phosphatase and urease) to different levels of trace element pollution in soil representative area. The improved ecological dose model and random-amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) were used to assess soil health. The 50% ecological dose (ED50) values modified by toxicant coefficient were calculated from the best-fit model, and determination values from the regression analysis for the three enzyme activities were studied after the incubation periods. The results showed that the elevated heavy metal concentration negatively affects the total population size of bacteria and actinomycetes and enzymatic activity; dehydrogenase (ED50 = 777) was the most sensitive soil enzyme, whereas urease activity (ED50 = 2,857) showed the lowest inhibition; combined pollution or elevated toxicant level would increase disappearing RAPD bands, and the number of denoting polymorphic bands was greater in combined polluted soils. All three mathematical modified models satisfactorily described the inhibition of soil enzyme activities caused by Cd and Pb, by giving the best fit.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen ON (1959) Experiments in soil bacteriology, 3rd edn. Burgess Publishing Co., Minneapolis, p 117
Atesiet I, Suzen HS, Aydin A (2004) The oxidative DNA base damage in tests of rats after intraperitoneal cadmium injection. Biometals 17:371–377. doi:10.1023/B:BIOM.0000029416.95488.5f
Atienzar FA, Cordi B, Evenden AJ (1999) Qualitative assessment of genotoxicity using random amplified polymorphic DNA: comparison of genomic template stability with key fitness parameters in Daphnia magna exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2275–2282. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1999)018<2275:QAOGUR>2.3.CO;2
Atienzar FA, Venier P, Jha AN (2002) Evaluation of the random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assay for the detection of DNA damage and mutations. Mutat Res 521:151–163
Bååth E (1989) Effects of heavy metals in soil on microbial processes and populations (a review). Water Air Soil Pollut 47:335–379. doi:10.1007/BF00279331
Babich H, Bewley RJF, Stotzky G (1983) Application of the ecological dose concept to the impact of heavy metals on some microbe-mediated ecological processes in soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 12:421–426
Bej AK, Perlin M, Atlas RM (1992) Effect of introducing genetically engineered microorganisms on soil microbial community diversity. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 86:169–176. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1991.tb04806.x
Belyaeva ON, Haynes RJ, Birukova OA (2005) Barley yield and soil microbial and enzyme activities as affected by contamination of two soils with lead, zinc or copper. Biol Fertil Soils 41:85–94. doi:10.1007/s00374-004-0820-9
Bowditch BM, Albright DG, Williams JGK (1993) Use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers in comparative genomic studies. Methods Enzymol 224:294–309. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(93)24022-M
Chander K, Dyckmans J, Joergensen RGJ, Meyer BG, Raubuch M (2001) Different sources of heavy metals and their long-term effects on soil microbial properties. Biol Fertil Soils 34:241–247. doi:10.1007/s003740100406
Chen X, Tang JJ, Fang ZG, Hu S (2002) Phosphate-solubilizing microbes in rhizosphere soils of 19 weeds in southeastern China. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 3:355–361
Cookson P (1999) Special variation in soil urease activity around irrigated date palms. Arid Soil Res Rehabil 13:155–169. doi:10.1080/089030699263393
Dick RP (1997) Soil enzyme activities as integrative indicators of soil health. In: Pankhurst CE, Doube BM, Gupta VVSR (eds) Biological indicators of soil health. CAB, Wallingford, pp 121–156
Dweikat I, Mackenzie S, Levy M (1993) Pedigree assessment using RAPD-DGGE in cereal crop species. Theor Appl Genet 85:497–505. doi:10.1007/BF00220905
Fliessbach A, Martens R, Reber HH (1994) Soil microbial biomass and activity in soils treated with heavy metal contaminated sewage sludge. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1201–1205. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(94)90144-9
Frostegård Å, Tunlid A, Bååth E (1996) Changes in microbial community structure during long-term incubation in two soils experimentally contaminated with metals. Soil Biol Biochem 28:55–63. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(95)00100-X
Haanstra L, Doelman P, Oude-Voshaar JH (1985) The use of sigmoidal dose response curves in soil ecotoxicological research. Plant Soil 84:293–297. doi:10.1007/BF02143194
He MC, Wang ZJ, Tang HX (1998) The chemical, toxicological and ecological studies in assessing the heavy metal pollution in Le An River, China. Wat Res 32(2):510–518. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00229-7
Hinojosa MB, Carreira JA, Rodríguez-Maroto JM, García-Ruíz R (2008) Effects of pyrite sludge pollution on soil enzyme activities: ecological dose–response model. Sci Total Environ 396:89–99. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.02.014
Hiroki M (1993) Effect of arsenic pollution on soil microbial-population. Soil Sci Plant Nutrient 39:227–235
Jensen HI (1951) Notes on the biology of Azotobacter. Proc Soc Appl Bacteriol 14:89–94
Kristensen HL, Debosz K, McCarty GW (2003) Short-term effects of tillage on mineralization of nitrogen and carbon in soil. Soil Biol Biochem. 35:979–986. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00159-7
Liu W, Li PJ, Qi XM, Zhou QX (2005) DNA changes in barley (Hordeum vulgare) seedlings induced by cadmium pollution using RAPD analysis. Chemosphere 61:158–167. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.078
Lobo MC, Sastre I, Vicente MA (2000) Enzymes as a measurement of environmental impact on soil. In: Garcia C, Hernandez MT (eds) Research and perspectives of soil enzymology in Spain. CEBAS-CSIC, Spain, pp 325–352
Lorenz N, Hintemann T, Kramarewa T, Katayama A, Yasuta T, Marschner P, Maliszewska-Kordybach B, Smreczak B (2003) Habitat function of agricultural soils as affected by heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contamination. Environ Int 28:719–728. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00117-4
Martin JP (1950) Use of acid, rose bengal and streptomycin in the plate method for estimating soil fungi. Soil Sci 69:215–232
McBride MB (1989) Reactions controlling heavy metals solubility in soils. In: Stewart BA (ed) Advances in soil science. Springer, New York, pp 1–56
Mench M, Renella G, Gelsomino A, Landi L, Nannipieri P (2006) Biochemical parameters and bacterial species richness in soils contaminated by sludge-borne metals and remediated with inorganic soil amendments. Environ Pollut 144:24–31. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.01.014
Moreno JL, Herna’ndez T, Garcı’a C (1999) Effects of a cadmium contaminated sewage sludge compost on dynamics of organic matter and microbial activity in an arid soil. Biol Fertil Soils 28:230–237. doi:10.1007/s003740050487
Moreno JL, Landi C, Garcı’a L, Falchini L, Pietramellara G, Nannipieri P (2001) The ecological dose value (ED50) for assessing Cd toxicity on ATP content and dehydrogenase and urease activities of soil. Soil Biol Biochem 33:483–489. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00189-9
Moreno JL, Garcı’a C, Herna’ndez T (2003) Toxic effect of cadmium and nickel on soil enzymes and the influence of adding sewage sludge. Eur J Soil Sci 54:377–386. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.00533.x
Nair SK, Subba-Rao NS (1977) Microbiology of the root region of coconut and cacao under mixed cropping. Plant Soil 46:511–519. doi:10.1007/BF00015910
Nannipieri P (1994) The potential use of soil enzymes as indicators of productivity, sustainability and pollution. In: Pankhurst CE, Doube BM, Gupta VVSR, Grace PR (eds) Soil biota management in sustainable farming systems. CSIRO, Melbourne, pp 238–244
Nannipieri P, Gregos S, Ceccanti B (1990) Ecological significance of the biological activity in soil. In: Bollag JM, Stotzy G (eds) Soil biochemistry, vol 6. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 293–355
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269
Nelson JR, Lawrence CW, Hinkle DC (1996) Thymine–thymine dimmer bypass by yeast DNA–polymerase–zeta. Science 272:1646–1649. doi:10.1126/science.272.5268.1646
Nguyen C (2003) Rhizo deposition of organic C by plants: mechanisms and controls. Agronomie 23:375–396. doi:10.1051/agro:2003011
Ogram A, Feng X (1997) Methods of soil microbial community analysis. In: Hurst CJ, Knudsen GR, McInerney MJ, Stetzenback LD, Walter MV (eds) Manual of environmental microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 422–430
Renella G, Ortigoza ALR, Landi L, Nannipieri P (2003) Additive effects of copper and zinc on cadmium toxicity on phosphatase activities and ATP content of soil as estimated by the ecological dose (ED50). Soil Biol Biochem 35:1203–1210. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00181-0
Renella G, Mench M, Gelsomin A, Landi L, Nannipieri P (2005) Functional activity and microbial community structure in soils amended with bimetallic sludges. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1498–1506. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.01.013
Rong ZY, Yin HW (2004) A method for genotoxicity detection using random amplified polymorphism DNA with Danio rerio. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 58:96–103. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.09.016
Smolders E, Buekers J, Oliver I, McLaughlin MJ (2004) Soil properties affecting toxicity of zinc to soil microbial properties in laboratory-spiked and field-contaminated soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2633–2640. doi:10.1897/04-27
Speir TW, Kettles HA, Parshotam A, Searle PL, Vlaar LNC (1995) A simple kinetic approach to derive the ecological dose value, ED50, for the assessment of Cr(VI) toxicity to soil biological properties. Soil Biol Biochem 27:801–810. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(94)00231-O
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1969) Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1–307
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1972) Assay of urease activity in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 4:479–487. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(72)90064-8
Viketoft M, Palmborg C, Sohlenius B, Huss-Danell K, Bengtsson J (2005) Plant species effects on soil nematode communities in experimental grasslands. Appl Soil Ecol 30:91–103. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.02.007
Waisberg M, Joseph P, Hale B (2003) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 192:95–117. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(03)00305-6
Walker C, Goodyear C, Anderson D, Titball RW (2000) Identification of Arsenic resistant bacteria in the soil of a former munitions factory at Locknitz, Germany. Land Contam Reclam 8:13–18
Wang YP, Shi JK, Wanh H, Lin Q, Chen XC, Chen YX (2007) The influence of soil heavy metals pollution on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and community composition near a copper smelter. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67:75–81. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.03.007
Welp G (1999) Inhibitory effects of the total and water-soluble concentrations of nine different metals on the dehydrogenase activity of a loess soil. Biol Fertil Soils 30:132–139. doi:10.1007/s003740050599
Wild SR, Jones KC (1995) Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in the United Kingdom environment: a preliminary source inventory and budget. Environ Pollut 88:91–108. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(95)91052-M
Yang YH, Yao J, Hu S (2000) Effects of agricultural chemicals on DNA sequence diversity of soil microbial community: a study with RAPD marker. Microb Ecol 39:72–79. doi:10.1007/s002489900180
Yang Z, Liu S, Zheng D, Feng S (2006) Effects of cadmium, zinc and lead on soil enzyme activities. J Environ Sci 18:1135–1141. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(06)60051-X
Zheng CR, Tu C, Chen HM (1999) Effect of combined heavy metal pollution on nitrogen mineralization potential, urease and phosphatase activities in a Typic Udic Ferrisol. Pedosphere 9(3):251–258
Zhou JZ, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Science Foundation of Shanghai (NO.07DZ12055, NO.07DZ19604 and NO.07JC14025), and National High-Tech Research and Development Plan (“863” Plan) (NO.2007AA10Z441).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Zhou, P., Mao, L. et al. Assessment of effects of heavy metals combined pollution on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure: modified ecological dose–response model and PCR-RAPD. Environ Earth Sci 60, 603–612 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0200-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0200-8