Abstract
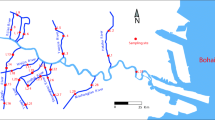
Zn, Cu, Cr and Pb concentrations of the sediment collected from three tidal flat sites of Yangtze estuary were investigated in October 2003. Results showed that the average concentrations of heavy metals in the sediments were two to three times to the environment background values of Yangtze estuary tidal flat sediment. The heavy metal concentrations in the sediments near the Bailonggang (BLG) and Laogang (LG) sewage outfalls were obviously higher than those of Chaoyang (CY) tidal flat where there are no sewage outfalls near the coast. And the concentrations of heavy metals in the surface sediments of LG tidal flat decreased with the increasing of the distance to the sewage outfalls. The heavy metal concentration profile in the sediment core changed with the depth, and generally reached maximum values at the depth of plant roots. The assessment results showed that the sediments of LG, BLG and CY tidal flat had been polluted by heavy metals in different level. The pollution degree of heavy metals in the sediments was as follows: Zn > Cu > Pb > Cr. The potential ecological risks of the four heavy metals in three tidal flat sites sediment were all at a middle level, and Cu and Pb made the main contributions. The adverse ecological effects caused by the four heavy metals did not occur frequently.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Lack of data point between 18 and 20 cm in core sediments of middle tidal flat of LG and CY is because only 18 cm long sediment cores was obtained by using PVC pipes. Concentrations of Cr in the core sediments of the low tidal flat of CY were absent due to the failure in the laboratory analysis.
References
Aston SR, Thornton I (1977) Regional geochemical data in relation to seasonal variations in water quality. Sci Total Environ 7(3):247–260
Batley G (1997) ANZWCC interim sediment quality guidelines. Prepared for Environmental research Institute of the Supervising Scientist (Draft)
Bi C, Chen Z, Xu S (2003a) Chemical association of heavy metals in the sediments near Bailonggang sewage discharge outlet of Shanghai. Mar Sci Bull 5(1):52–58
Bi C, Chen Z, Xu S et al (2003b) Seasonal variation and chemical species distribution of rhizosphere heavy metals on tidal flat in Shanghai. Oceanol Limnol Sin 34(2):194–200
Brack K, Johannesson LT, Stevens RL (2001) Accumulation rates and mass calculations of Zn and Hg in recent sediments, Göta älv estuary, Sweden. Environ Geol 40:1232–1241
Chatterjee M, Silva Filho EV, Sarkar SK et al (2007) Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance. Environ Int 33:346–356
Chen Z, Xu S, Liu L et al (2000) Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in tidal flat sediments of Shanghai coastal zone. Acta Geogr Sin 55(6):641–651
Ding X, Ye S, Gao Z (2005) Methods of heavy metal pollution evaluation for off-shore sediments. Mar Geol Lett 21(8):31–36
Feng H, Han X, Zhang W et al (2004) A preliminary study of heavy metal contamination in Yangtze River intertidal zone due to urbanization. Mar Pollut Bull 49:910–915
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
He M (1998) Bioavailability of heavy metals in aquatic environment and sediment quality assessment approaches. Adv Environ Sci 6(5):9–19
Hu Q (2001) Pollution and evaluation of heavy metal in the siliqua minima and the intertidal sediment at Fengting Bay. Fujian Environ 18(3):20–22
Lee SV, Cundy AB (2001) Heavy metal contamination and mixing processes in sediments from the Humber Estuary, Eastern England. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 53:619–636
Macdonald DD, Carr RS, Calder FD et al (1996) Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 5(4):253–278
Mæhlum T (1995) Treatment of landfill leachate in on-site lagoons and constructed wetlands. Water Sci Technol 32(3):129–135
Peter MC, Pcitrick JA, Gary AV (1999) Development of sediment quality values for Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: a possible model for other jurisdictions. Mar Pollut Bull 38(3):161–169
Roach AC (2005) Assessment of metals in sediments from Lake Macquarie, New South Wales, Australia, using normalization models and sediment quality guidelines. Mar Environ Res 59:453–472
Shen H, He S, Pan D et al (1992) A study on turbidity maximum in the Changjiang estuary. Acta Geogr Sin 47(5):272–279
Smith SL (1996) The development and implementation of Canadian sediment quality guidelines Development and progress in sediment quality assessment: rational, challenge, techniques & strategies. SPB academic, Amsterdam, pp 233–249
Wang L, Chen J, Hong S et al (2001) The new advances of sediment quality criteria for heavy metals, the biological effect database-based approach. Environ Sci Technol 2:4–8
Xu S, Tao J, Chen Z et al (1997) Dynamic accumulation of heavy metals in tidal flat sediments of Shanghai. Oceanol Limnol Sin 28(5):509–515
Zhang W, Yu L, Hutchinson SM et al (2001) China’s Yangtze Estuary: I. Geomorphic influence on heavy metal accumulation in intertidal sediments. Geomorphology 41:195–205
Zhou J, Ma D, Pan J et al (2008) Application of multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in sediments and waters: a case study in Yangzhong, China. Environ Geol 54:373–380
Acknowledgments
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40730526, 40701164), the Science and Technology Department of Shanghai (Grant No. 07DZ12037). The authors also would like to thank the anonymous reviewers aided in the development and improvement of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, HG., Zhang, J., Wang, DQ. et al. Heavy metal pollution and assessment of the tidal flat sediments near the coastal sewage outfalls of shanghai, China. Environ Earth Sci 60, 57–63 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0169-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0169-3