Abstract
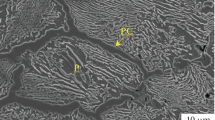
Dry sliding wear characteristics, mechanical properties and microstructural behavior of powder-chip based reinforcement silicon rich LM6 aluminum alloy, fabricated by semi-solid casting were investigated. Wear tests were conducted on powder-chip reinforced cast samples using the pin on disc apparatus under 5, 10 and 15 N with 0.4, 0.8 and 1.2 m/s sliding speeds for 250, 500 and 750 m sliding distances versus EN31 tool steel hardened to 62 HRC. An observation from the microstructure images indicated that the porosity of the cast composite reduces due to the distribution of un-melted chips inside the short cavities by the addition of reinforcement and confirmed with the obtained results of density. The fracture in cast specimens indicates that the micro-cracks were prevalently propagated along the broken eutectic silicon particles. Additionally, wear resistance was increased reasonably due to the inclusion of reinforcement under metallic wear environment. Worn surfaces SEM, EDS, XRD and, AFM analysis suggests that surfaces plastically deformed along with silicon brittle asperities which stuck on the softer surface of the contact layers, while dominant wear mechanisms were found from these surfaces and wear debris.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu B, Raju GB, Suri AK (2006) Int Mater Reviews 51:352
Poria S, Sahoo P, Sutradhar G (2016) Silicon 8(4):591
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2013) Trans Non Met Soc China 23(7):1905
Mousavian RT, Khosroshahi RA, Yazdani S, Brabazon D (2016) Mat Des 89:58
Singh J (2016) Friction 4(3):191
Rodriguez J, Poza P, Garrido MA, Rico A (2007) Wear 262(3–4):292
Guo X, Song K, Liang S, Wang X, Xang Y (2016) Tribo Trans 59(1):170
Al-Qutub AM, Allam IM, Samad MAA (2008) J Mat Sci 43(17):5797
Ghahremanian M, Niroumand B, Panjepour M (2012) Met Mater Int 18(1):149
Sannino AP, Rack HJ (1995) Wear 189(1–2):1
Prakash KP, Moorthy RS, Gopal PM, Kavimani V (2016) Int J Refra Met Hard Mater 54:223
Prakash KS, Kanagaraj A, Gopal PM (2015) Trans Non Met Soc China 25(12):3893
Sahin Y, Ozdin KA (2008) Mat Des 29(3):728
Deuis RL, Subramanian C, Yellup JM (1997) Comp Sci Tech 57(4):415
Basavarajappa S, Chandramohan G (2006) J Mater Eng Per 15(6):656
Urena A, Rams J, Campo M, Sanchez M (2009) Wear 266(11–12):1128
Carvalho O, Buciumeanu M, Madeira S, Soares D, Silva FS, Miranda G (2015) Tribo Int 90:148
Puga H, Barbosa J, Soares D, Silva F, Ribeiro S (2009) J Mater Proces Tech 209(11):5195
Chiba R, Yoshimura M (2015) J Manuf Proces 17:1
Agarwal M, Srivastava R (2016) Mat Manu Pro 31(15):1958
Wei-min M, Qiu Z, Da-ping Z (2010) Trans Non Met Soc China 20:1769
Kumar D, Roy H, Show BK (2015) Tribo Trans 58(3):518
Prasad BK (2006) Wear 260(11–12):1333
Apps PJ, Bowen JR, Prangnell PB (2003) Acta Mater 51:2811
Wang QG (2003) Met Mat Trans A 34(12):2887
Akbari MK, Baharvandi HR, Mirzaee O (2014) J Comp Mat 48(27):3315
Asavarajappa SB, Chandramohan G, Subramanian R, Chandrasekar A (2006) Mat Sci Poland 24 (2/1):357
Gopal PM, Prakash KS, Nagaraja S, Aravinth NK (2017) Tribo Inter 116:338
Chen CM, Yang CC, Chao CG (2005) Mat Sci Eng A 397:178
Kundu S, Das SK, Sahoo P (2016) Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9450-8
Prakash KP, Gopal PM, Kavimani V (2017) Ind J Eng Mat Science 24:270
Onat A (2010) J Alloys Comp 489:119
Singh M, Mondal DP, Jha AK, Yegneswaran AH (2003) J Mat Eng Per 12(3):331
Hanif M, Wani MF (2016) Mat Lett 176:91
Singh S, Singh G, Kumar L, Singh S (2015) J Eng Tribo 229(5):597
Sharma V, Kumar S, Panwar RS, Pandey OP (2012) J Mat Sci 47(18):6633
Acknowledgements
The Authors would like to thank Dr. Prabhat Kumar Dwivedi, Senior Scientific Officer, center of nanosciences, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, for his assistance extended during this work. Authors are highly appreciating the contribution of Workshop and Machine element lab members of Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, Allahabad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Worn out specimens were taken for measurement of weight loss with an accuracy of ± 0.0001 mg after end of each operation. Specific wear rate ‘k’ (mm3/Nm), was calculated by equation (1) and coefficient of friction ‘μ’ by equation (1) as:
Here,
m = Specimen mass loss (g), ρ = Density of the pin material (g/cm3) , t = Time duration for the test (s), Vs = Sliding velocity (m/s) , FN = Applied Load, and FT = Tangential applied forces
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, M., Srivastava, R. Friction, Wear and Mechanical Properties of Al-Si LM6 Cast Alloy Processed in Semi-solid Stage. Silicon 11, 355–366 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9849-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9849-5