Abstract
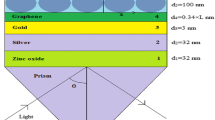
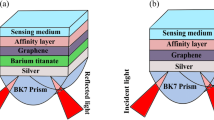
In this study, a molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor is proposed. The reflectance curves for the proposed SPR biosensor are analyzed and compared with the graphene based and the conventional SPR biosensors. It is observed that the performance parameters of the proposed biosensor- sensitivity, detection accuracy, and the quality factor are enhanced by the utilization of the adsorption property of MoS2 for monolayer and bi-layer MoS2. Also, the effect of increasing the number of layers of MoS2 on the reflectance curve is analyzed and compared.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otto A (1968) Excitation of surface plasma waves in silver by the method of frustrated total reflection. Springer Z Physik 216:398–410
Kretschmann E, Raether H (1968) Radiative decay of non-radiative surface plasmons excited by light. Springer Z Naturforsch 23(A):2135–2136
Liedberg B, Nylander C, Lundstrom I (1983) Surface plasmons resonance for gas detection and biosensing. Sens Actuators 4:299–304
Snopok B A, Kostyukevich K V, Lysenko S I, Lytvyn P M, Lytvyn O S, Mamykin S V, Zynyo S A, Shepelyavyj P E, Kostyukevich S A, Shirshov Y M, Venger E F (2001) Optical biosensors based on the surface plasmon resonance phenomenon: optimization of the metal layer parameters. Semicond Phys Quantum Electron Optoelectron 4(1):56–69
Zhu X M, Lin P H, Ao P, Sorensen L B (2002) Surface treatments for surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Elsevier Sens Actuators B: Chem 84(2–3):106–112
Ong B H, Yuan X, Tjin S C, Zhang J, Ng H M (2006) Optimised film thickness for maximum evanescent field enhancement of a bimetallic film surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Sens Actuators B: Chem 114 (2):1028–1034
Zhao J, Zhang X Y, Yonzon C R, Haes A J, Van Duyne R P (2006) Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Nanomedicine (Lond) 1(2):219–228
Lee K L, Lee C W, Wang W S, Wei P K (2007) Sensitive biosensor array using surface plasmon resonance on metallic nanoslits. J Biomed Opt 12(4):044023
Raether H (1988) Surface plasmons on smooth and rough surfaces and on grating. Springer, Berlin, p 111
Wu L, Chu H S, Koh W S, Li E P (2010) Highly sensitive graphene biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt Express 18(14):14395–1440
Homola J (2003) Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 377 (3):528–539
Lertvachirapaiboon C, Baba A, Ekgasit S, Thammacharoen C, Shinbo K, Kato K, Kaneko F (2011) Gold nanoparticles synthesis used for sensor applications. In: IEEE Conf Proc ISEIM
Choi S H, Kim Y L, Byun K M (2011) Graphene-on-silver substrates for sensitive surface plasmon resonance imaging biosensors. Opt Express 19(2):458–466
Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos S V, Grigorieva I V, Firsov A A (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306(5696):666– 669
Nair R R, Blake P, Grigorenko A N, Novoselov K S, Booth T J, Stauber T, Peres N M R, Geim A K (2008) Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science 320(5881):1308–1308
Kim J A, Hwang T, Dugasani S R, Amin R, Kulkarni R, Park S H, Kim T (2013) Graphene based fiber optic surface Plasmon resonance for bio-chemical sensor applications. Sens Actuators B: Chem 187:426–433
Elias D C, Gorbachev R V, Mayorov A S, Morozov S V, Zhukov A A, Blake P, Ponomarenko L A, Grigorieva I V, Novoselov K S, Guinea F, Geim A K (2011) Dirac conesreshaped by interaction effects in suspended graphene. Nat Phys 7:701–704
Zeng S, Hu S, Xia J, Anderson T, Dinh X Q, Meng X M, Coquet P, Yong K T (2015) Graphene–mos2 hybrid nanostructures enhanced surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Sens Actuators B Chem 207:801–810
Liu Y, Dong X, Chen P (2012) Biological and chemical sensors based on graphene materials. Chem Soc Rev 41:2283–2307
Szunerits S, Maalouli N, Wijaya E, Vilcot J P, Boukherroub R (2013) Recent advances in the development of graphene-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) interfaces. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:1435–1443
Verma A, Prakash A, Tripathi R (2014) Performance analysis of graphene based surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of pseudomonas-like bacteria. Opt Quantum Electron 47(5):1197–1205
Verma A, Prakash A, Tripathi R (2015) Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance biosensor using graphene and air gap. Opt Commun 357:106–112
Mak K F, Lee C, Hone J, Shan J, Heinz T F (2010) Atomically thin MoS2: a new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys Rev Lett 105:136805
Perkins F K, Friedman A L, Cobas E, Campbell P M, Jernigan G G, Jonker B T (2013) Chemical vapor sensing with monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett 13(2):668–673
Du J, Wang Q, Jiang G, Xu C, Zhao C, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Wen S, Zhang H (2014) Ytterbium-doped fiber laser passively mode locked by few-layer Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) saturable absorber functioned with evanescent field interaction. Sci Rep 4:6346. doi:10.1038/srep06346
Salihoglu O, Balci S, Kocabas C (2012) Plasmon-polaritons on graphene-metal surface and their use in biosensors. Appl Phys Lett 100(21):213110
Lopez-Sanchez O, Lembke D, Kayci M, Radenovic A, Kis A (2013) Ultrasensitive photodetectors based on monolayer MoS2. Nat Nanotechnol 8(7):497–501
Sharma B K (2014) Solid state physics and devices-the harbinger of third wave of civilization. I.C. chips of future generation part 3. Carriers-phonon interaction in graphene. OpenStax-CNX module: m44257
Zhu C, Zeng Z, Li H, Li F, Fan C, Zhang H (2013) Single-layer MoS2-based nanoprobes for homogeneous detection of biomolecules. J Am Chem Soc 135(16):5998–6001
Chen W, Santos E J G, Zhu W, Kaxiras E, Zhang Z (2013) Tuning the electronic and chemical properties of monolayer MoS2 adsorbed on transition metal substrates. Nano Lett 13(2):509– 514
Ou J Z, Chrimes A F, Wang Y, Tang S Y, Strano M S, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2014) Ion-driven photoluminescence modulation of quasi-twodimensional MoS2 nanoflakes for applications in biological systems. Nano Lett 14(2):857–863
Xu H, He D, Fu M, Wang W, Wu H, Wang Y (2014) Optical identification of MoS2/graphene heterostructure on SiO2/Si substrate. Opt Express 22(13):15969
Maurya J B, Prajapati Y K, Singh V, Saini J P, Tripathi R (2015) Performance of graphene–mos2 based surface plasmon resonance sensor using silicon layer. Opt Quant Electron 47(11):3599– 3611
Maurya J B, Prajapati Y K, Singh V, Saini J P (2015) Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensor based on graphene–MoS2 hybrid structure with TiO2–SiO2 composite layer. Appl Phys A 121 (2):525–533
Euzéby J P (1997) List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: a folder available on the Internet. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47(2):590–592
Jenkins A T A, Buckling A, Clarke D J, Jarvis K (2004) Study of the attachment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on Gold and modified Gold surfaces using surface plasmon resonance. Biotechnol Prog 20(4):1233–1236
Barnett A, Goldys E M (2010) Modeling of the SPR resolution enhancement for conventional and nanoparticle inclusive sensors by using statistical hypothesis testing. Opt Express 18(9):9384–9397
Bruna M, Borini S (2009) Optical constants of graphene layers in the visible range. Appl Phys Lett 94 (3):031901
Yamamoto M (2002) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) theory: tutorial. Rev Polarography 48:209
Pockrand I (1978) Surface plasma oscillations at silver surfaces with thin transparentand absorbing coatings. Surf Sci 72:577– 588
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurya, J.B., Prajapati, Y.K. & Tripathi, R. Effect of Molybdenum Disulfide Layer on Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for the Detection of Bacteria. Silicon 10, 245–256 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9431-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9431-y