Abstract
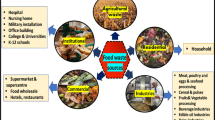
Food loss and food waste are recognized as two of the most challenging dilemmas facing the world today with serious repercussions on food security, the environment, and global as well as regional and national economies. This is not different in the Arab countries where the food loss and food waste generated per person sometimes exceeds 210 kg per year. Literature searches indicate there is a paucity of applied studies that investigate the drivers, sources, management, quantification, policies, interventions, and initiatives to reduce food loss and food waste in the Arab world, a region with more than 400 million inhabitants. Despite the importance of the topic, only twenty-five relevant articles were identified, providing limited data on food loss and food waste generation. The studies also use sampling procedures that do not allow for generalization of results over the Arab region or even for making comparisons among studies. The review concludes that further research on food loss and food waste along the food supply chain in the Arab world is necessary with a focus on trends, causes, and social, technological, behavioral, attitudinal, and cultural drivers. Investigating environmental and economic implications along with policy development and coping strategies, as well as consumer attitudes towards waste in general and food waste in particular are also important topics to be researched, especially given the variation in cultural and religious practices across the Arab world. The generation of such information and knowledge is indispensable for taking remedial action towards mitigating the problem of food loss and food waste.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, A. A. K., Al-Rekabi, W. S., & Yousif, Y. T. (2016). Integrated solid waste management for urban area in basrah district. Journal of Babylon University, 24(3), 666–675.
Abdelradi, F. (2018). Food waste behaviour at the household level: A conceptual framework. Waste Management, 71(Supplement C), 485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.10.001.
Abd Al-Kareem, F. A. (2014). Solid waste generation in the university of technology. Journal of Engineering and Development, 18(3), 162–172.
Abouabdillah, A., Capone, R., Youssfi, L. E. L., Debs, P., Harraq, A., El-Bilali, H., . . . Driouech, N. (2015). Household food waste in morocco: An exploratory survey. Lukavica. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20163076053.
Abu Qdais, H. A., Hamoda, M. F., & Newham, J. (1997). Analysis of residential solid waste at generation sites. Waste Management and Research, 15(4), 395–406. https://doi.org/10.1006/wmre.1996.0095.
Al-Domi, H., Al-Rawajfeh, H., Aboyousif, F., Yaghi, S., Mashal, R., & Fakhoury, J. (2011). Determining and addressing food plate waste in a group of students at the University of Jordan. Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, 10(9), 871–878.
Al-Fawaz, N. (2015). Need to reduce food waste. Arab News.
Algerian Food Bank (2013). http://www.algerianfoodbank.com/. Accessed May 15, 2017.
Aljamal, A., & Bagnied, M. (2012). Food consumption and waste in kuwait: The prospects for demandside approach to food security. International Review of Business Research Papers, 8(6), 15–26.
Al-Khatib, I. A., & Arafat, H. A. (2010). A review of residential solid waste management in the occupied Palestinian territory: A window for improvement? Waste Management and Research, 28(6), 481–488. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X09345274.
Al-Maliky, S. J. B., & ElKhayat, Z. Q. (2012). Kitchen food waste inventory for residential areas in Baghdad city. Modern Applied Science, 6(8), 45–51. https://doi.org/10.5539/mas.v6n8p45.
Al-Mas'udi, R. M., & Al-Haydari, M. A. S. (2015). Spatial analysis of residential waste solid in the city of Karbala
 . Journal of Kerbala University
. Journal of Kerbala University  , 13(2), 132–154.
, 13(2), 132–154.Almdal, T., Viggers, L., Beck, A. M., & Jensen, K. (2003). Food production and wastage in relation to nutritional intake in a general district hospital - wastage is not reduced by training the staff. Clinical Nutrition, 22(1), 47–51.
Al-Othman, A. A., & Hewedy, F. M. (1996). Dietary assessment of male students: A study of what they wasted while in residence. Nutrition and Health, 11(3), 197–206.
Al-Rawi, S. M., & Al-Tayyar, T. A. (2012). Solid waste composition and characteristics of Mosul City/IRAQ. Al-Mustansiriyah Journal of Science
 , 23(8): 19–34.
, 23(8): 19–34.Al-Shoshan, A. A. (1992). Study of the regular diet of selected hospitals of the Ministry of Health in Saudi Arabia: Edible plate waste and its monetary value. Journal of the Royal Society of Health, 112(1), 7–11.
Al-Zahrani, K., & Baig, M. (2014). Food waste in the kingdom of saudi arabia: Need for extension education programs to increase public awareness. Paper presented at the 10th International Academic Conference, Vienna.
Amara, A. A., Hamdan, S., & Melibary, N. (2013). Management of food in the hajj in line with the rationalization of consumption and preservation of the environment. Majallat Ᾱlam al-Tarbiyah, 14(43 Part 2), 195–216.
Arab News. (2016). Food wasted in makkah enough to feed millions going hungry globally. Arab News. http://www.arabnews.com/saudi-arabia/news/869206.
Arora, J., Marwaha, S., & Grover, R. (2002). Biotechnology in agriculture and environment. New Delhi: Asiatech Publishers Inc..
Baawain, M., Al-Mamun, A., Omidvarborna, H., & Al-Amri, W. (2017). Ultimate composition analysis of municipal solid waste in Muscat. Journal of Cleaner Production, 148, 355–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.013.
Baldwin, D. (2016). 33 per cent spike in food waste daily in UAE during Ramadan. Gulf News.
Barton, A. D., Beigg, C. L., MacDonald, I. A., & Allison, S. P. (2000). High food wastage and low nutritional intakes in hospital patients. Clinical Nutrition, 19(6), 445–449.
Bond, M., Meacham, T., Bhunnoo, R., & Benton, T. G. (2013). Food waste within global food systems. A Global Food Security report (www.foodsecurity.ac.uk).
Bouallagui, H., Ben Cheikh, R., Marouani, L., & Hamdi, M. (2003). Mesophilic biogas production from fruit and vegetable waste in a tubular digester. Bioresource Technology, 86(1), 85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00097-4.
Brinkman, H. J., de Pee, S., Sanogo, I., Subran, L., & Bloem, M. W. (2010). High food prices and the global financial crisis have reduced access to nutritious food and worsened nutritional status and health. Journal of Nutrition, 140(1), 153s–161s.
Buzby, J. C., & Hyman, J. (2012). Total and per capita value of food loss in the United States. Food Policy, 37(5), 561–570.
Canali, M., Amani, P., Aramyan, L., Gheoldus, M., Moates, G., Östergren, K., Silvennoinen, K., Waldron, K., & Vittuari, M. (2017). Food waste drivers in Europe, from identification to possible interventions. Sustainability (Switzerland), 9(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010037.
Capone, R., El Bilali, H., Debs, P., Bottalico, F., Cardone, G., Berjan, S., et al. (2016). Bread and bakery products waste in selected Mediterranean Arab countries. American Journal of Food and Nutrition, 4(2), 40–50. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajfn-4-2-2.
Chalak, A., Abou-Daher, C., Chaaban, J., & Abiad, M. G. (2016). The global economic and regulatory determinants of household food waste generation: A cross-country analysis. Waste Management, 48, 418–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.040.
Charbel, L., Capone, R., Grizi, L., Debs, P., Khalife, D., Bilali, H. E., et al. (2016). Preliminary insights on household food wastage in Lebanon. Journal of Food Security, 4(6), 131–137. https://doi.org/10.12691/jfs-4-6-2.
CIHEAM, & FAO (2016). Mediterra 2016. Zero Waste in the mediterranean. Natural resources, food and knowledge. International centre for advanced mediterranean Agronomic studies and food and agriculture organization of the United Nations-Paris: Presses de Sciences Po.
Darlington, R., Staikos, T., & Rahimifard, S. (2009). Analytical methods for waste minimisation in the convenience food industry. Waste Management, 29(4), 1274–1281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.08.027.
De Steur, H., Wesana, J., Dora, M. K., Pearce, D., & Gellynck, X. (2016). Applying value stream mapping to reduce food losses and wastes in supply chains: A systematic review. Waste Management, 58, 359–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.08.025.
Egyptian Food Bank (2006). http://www.egyptianfoodbank.com/en. Accessed May 15, 2017.
Elmenofi, G. A. G., Capone, R., Waked, S., Debs, P., Bottalico, F., & El-Bilali, H. (2015). An exploratory survey on household food waste in egypt. Lukavica. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20163076044.
El-Mobaidh, A. M., Razek Taha, M. A., & Lassheen, N. K. (2006). Classification of in-flight catering wastes in Egypt air flights and its potential as energy source (chemical approach). Waste Management, 26(6), 587–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2005.02.022.
Elsevier (2017). Scopus. https://www.scopus.com/.
Etaam-Saudi Food Bank (2012). http://saudifoodbank.com/. Accessed May 15, 2017.
FAO. (2009). How to feed the world in 2050. Rome: FAO.
FAO (2011). Global food losses and food waste. Rome.
FAO (2013a). Reducing the food wastage footprint. Rome.
FAO (2013b). Situation report-West Bank and Gaza strip.
FAO (2014). Food wastage footprint full cost accounting-final report. FAO, Rome.
FAO (2015). The state of food insecurity in the world 2015. Meeting the 2015 international hunger targets: Taking stock of uneven progress. Rome.
FAO (2017a). Situation report-Iraq.
FAO (2017b). Situation report-South Sudan.
FAO (2017c). Situation report-Syrian Arab Republic.
FAO (2017d). Situation report-Yemen.
FAO, WFP, & IFAD (2012). The state of food insecurity in the world 2012. Economic growth is necessary but not sufficient to accelerate reduction of hunger and malnutrition. FAO, Rome.
FoodBlessed (2012). https://foodblessed.org/about/. Accessed May 15, 2017.
Garcia-Garcia, G., Woolley, E., Rahimifard, S., Colwill, J., White, R., & Needham, L. (2016). A methodology for sustainable management of food waste. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 8, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9720-0.
Ghafar, A. A., & Masri, F. (Producer). (2016). The persistence of poverty in the arab world. Retrieved from http://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/opinion/2016/02/persistence-poverty-arabworld-160228072928685.html.
Gustavsson, J., Cederberg, C., Sonesson, U., Otterdijk, R., & Meybeck, A. (2011). Global food losses and food waste–extent, causes and prevention. Rome: FAO.
HLPE (2014). Food losses and waste in the context of sustainable food systems. A report by the High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security. Rome 2014.
Hsieh, H. F., & Shannon, S. E. (2005). Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qualitative Health Research, 15(9), 1277–1288.
IPCC (2007). Climate change 2007: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability, report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. In M. L. Parry, O. F. Canziani, J. P. Palutikof, P. J. v. d. Linden, & C. E. Hanson (Eds.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
James, J. B., & Ngarmsak, T. (2011). Processing of fresh cut tropical fruits and Vegetables: a technical guide. http://www.fao.org/docrep/014/i1909e/i1909e00.pdf.
Jamil, K. A., Usman, S., & Mohammed, F. (2016). Estimate the waste of grain consumption value: A case study of a sample of restaurants operating in the city of Arbil for 2016
 . AL-Anbar University journal of Economic and Administration Sciences
. AL-Anbar University journal of Economic and Administration Sciences  , 8(16): 393–417.
, 8(16): 393–417.Khaishgi, A. E. (2015). Food wastage a growing concern for UAE. The National.
Kim, J. H., Lee, J. C., & Pak, D. (2011). Feasibility of producing ethanol from food waste. Waste Management, 31(9–10), 2121–2125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.04.011.
Kummu, M., de Moel, H., Porkka, M., Siebert, S., Varis, O., & Ward, P. J. (2012). Lost food, wasted resources: Global food supply chain losses and their impacts on freshwater, cropland, and fertiliser use. Science of the Total Environment, 438, 477–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.092.
Langelaan, H., & Da Silva, F. (2013). Technology options for feeding 10 billion people. Food Engineering, 1, 1–16.
Lebanese Food Bank (2012). http://lebanesefoodbank.com/en/. Accessed May 15, 2017.
Levis, J. W., & Barlaz, M. A. (2011). What is the most environmentally beneficial way to treat commercial food waste? Environmental Science & Technology, 45(17), 7438–7444. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103556m.
Lin, C. S. K., Pfaltzgraff, L. A., Herrero-Davila, L., Mubofu, E. B., Abderrahim, S., Clark, J. H., Koutinas, A. A., Kopsahelis, N., Stamatelatou, K., Dickson, F., Thankappan, S., Mohamed, Z., Brocklesby, R., & Luque, R. (2013). Food waste as a valuable resource for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels. Current situation and global perspective. Energy and Environmental Science, 6(2), 426–464. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee23440h.
Lipinski, B., Hanson, C., Lomax, J., Kitinoja, L., Waite, R., & Searchinger, T. (2013). Reducing food loss and waste [working paper, installment 2 of creating a sustainable food future]. WRI, Washington, DC.
Matsakas, L., & Christakopoulos, P. (2015). Ethanol production from enzymatically treated dried food waste using enzymes produced on-site. Sustainability, 7(2), 1446–1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7021446.
Miller, D. D., & Welch, R. M. (2013). Food system strategies for preventing micronutrient malnutrition. Food Policy, 42, 115–128.
Munesue, Y., Masui, T., & Fushima, T. (2015). The effects of reducing food losses and food waste on global food insecurity, natural resources, and greenhouse gas emissions. Environmental Economics and Policy Studies, 17(1), 43–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10018-014-0083-0.
NEA (2016). Waste statistics and overall recycling 2016. Singapore’s National Environmental Agency http://www.nea.gov.sg/energy-waste/waste-management/waste-statistics-and-overall-recycling. Accessed 1 June 2017.
Oelofse, S. H. H., & Nahman, A. (2013). Estimating the magnitude of food waste generated in South Africa. Waste Management & Research, 31(1), 80–86. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242x12457117.
Ouda, O. K. M., Raza, S. A., Nizami, A. S., Rehan, M., Al-Waked, R., & Korres, N. E. (2016). Waste to energy potential: A case study of Saudi Arabia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 61, 328–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.04.005.
Parfitt, J., Barthel, M., & Macnaughton, S. (2010). Food waste within food supply chains: Quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365(1554), 3065–3081. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2010.0126.
Petticrew, M., & Roberts, H. (2008). Systematic reviews in the social sciences. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd..
Pfaltzgraff, L. A., De Bruyn, M., Cooper, E. C., Budarin, V., & Clark, J. H. (2013). Food waste biomass: A resource for high-value chemicals. Green Chemistry, 15(2), 307–314. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2gc36978h.
Pham, T. P. T., Kaushik, R., Parshetti, G. K., Mahmood, R., & Balasubramanian, R. (2015). Food waste-to-energy conversion technologies: Current status and future directions. Waste Management, 38(1), 399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.12.004.
Pirani, S. I., & Arafat, H. A. (2016). Reduction of food waste generation in the hospitality industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 132, 129–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.146.
Quested, T. E., Marsh, E., Stunell, D., & Parry, A. D. (2013). Spaghetti soup: The complex world of food waste behaviours. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 79, 43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.04.011.
Richter, B., & Bokelmann, W. (2016). Approaches of the German food industry for addressing the issue of food losses. Waste Management, 48, 423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.039.
Ruel, M. T., & Alderman, H. (2013). Nutrition-sensitive interventions and programmes: How can they help to accelerate progress in improving maternal and child nutrition? The Lancet, 382(9891), 536–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60843-0.
Rutten, M. M. (2013a). The economic impacts of (reducing) food waste and losses: A graphical exposition. Working paper No. 7. Wageningen: Wageningen School of Social Sciences (WASS).
Rutten, M. M. (2013b). What economic theory tells us about the impacts of reducing food losses and/or waste: Implications for research, policy and practice. Agriculture & Food Security, 2(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/2048-7010-2-13.
SAVE FOOD initiative (2011). https://www.save-food.org/. Accessed May 15, 2017.
Schneider, F. (2013a). The evolution of food donation with respect to waste prevention. Waste Management, 33(3), 755–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.10.025.
Schneider, F. (2013b). Review of food waste prevention on an international level. Waste and Resource Management, 166(4), 187–203.
Schott, A. B. S., Wenzel, H., & Jansen, J. L. (2016). Identification of decisive factors for greenhouse gas emissions in comparative life cycle assessments of food waste management - an analytical review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 119, 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.079.
Stenmarck, Å., Hanssen, O. J., Silvennoinen, K., Katajajuuri, J.-M., & Werge, M. (2011). Initiatives on prevention of food waste in the retail and wholesale trades. Retrieved from Copenhagen. http://norden.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A701989&dswid=-3225.
Stuart, T. (2009). Waste: Uncovering the global food scandal. Kirkus Reviews, 77(16), 864–865.
Sulaymon, A. H., Ibraheem, J. A., & Graimed, B. H. (2010). Household behavior on solid waste management a case of Al-Kut City
 Engineering and Technology Journal
Engineering and Technology Journal  , 28(24), 7037–7046.
, 28(24), 7037–7046.The World Bank (2017). World development indicators database archives. Accessed 12 Dec 2017.
Thyberg, K. L., & Tonjes, D. J. (2016). Drivers of food waste and their implications for sustainable policy development. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 106, 110–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.11.016.
Thyberg, K. L., Tonjes, D. J., & Gurevitch, J. (2015). Quantification of food waste disposal in the United States: A meta-analysis. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(24), 13946–13953. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03880.
United Arab Emirates Food Bank (2017). https://www.facebook.com/UAE-Food-Bank-296689817397832/?ref=page_internal. Accessed 15 May 2017.
Verghese, K., Lewis, H., Lockrey, S., & Williams, H. (2013). The role of packaging in minimising food waste in the supply chain of the future. Melbourne: RMIT University.
Verghese, K., Lewis, H., Lockrey, S., & Williams, H. (2015). Packaging's role in minimizing food loss and waste across the supply chain. Packaging Technology and Science, 28(7), 603–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/pts.2127.
Willersinn, C., Mouron, P., Mack, G., & Siegrist, M. (2017). Food loss reduction from an environmental, socio-economic and consumer perspective – The case of the Swiss potato market. Waste Management, 59, 451–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.10.007.
Yasir, R. A., & Abudi, Z. N. (2009). Characteristics and compositions of solid waste in Nassiriya City
 . Al-Qadisiya Journal for Engineering Sciences
. Al-Qadisiya Journal for Engineering Sciences  , 2(2), 136–148.
, 2(2), 136–148.Zayat, I. (2017). Arab countries face problem of food waste during Ramadan. The Arab Weekly.
Zhang, R. H., El-Mashad, H. M., Hartman, K., Wang, F. Y., Liu, G. Q., Choate, C., et al. (2007). Characterization of food waste as feedstock for anaerobic digestion. Bioresource Technology, 98(4), 929–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.02.039.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Imad P. Saoud of the Department of Biology of the American University of Beirut (AUB) and Ms. Mary Clare Leader, Corresponding Editor of the AUB Press, for their valuable feedback and editorial comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abiad, M.G., Meho, L.I. Food loss and food waste research in the Arab world: a systematic review. Food Sec. 10, 311–322 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-018-0782-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-018-0782-7



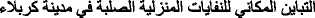 . Journal of Kerbala University
. Journal of Kerbala University  , 13(2), 132–154.
, 13(2), 132–154. , 23(8): 19–34.
, 23(8): 19–34. . AL-Anbar University journal of Economic and Administration Sciences
. AL-Anbar University journal of Economic and Administration Sciences  , 8(16): 393–417.
, 8(16): 393–417. Engineering and Technology Journal
Engineering and Technology Journal  , 28(24), 7037–7046.
, 28(24), 7037–7046.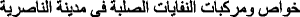 . Al-Qadisiya Journal for Engineering Sciences
. Al-Qadisiya Journal for Engineering Sciences  , 2(2), 136–148.
, 2(2), 136–148.