Abstract
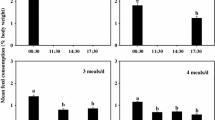
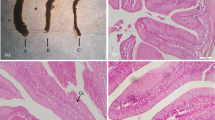
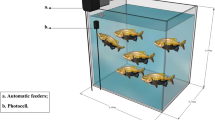
A 60-day feeding trial was conducted to investigate the effect of feeding frequency on growth, food consumption, body composition, and hematological responses of juvenile short barbeled velvetchin reared in floating sea cages. Fish (mean body weight of 28.8 g) were hand-fed to apparent satiety using a commercial diet (49.0% protein) at four different feeding frequencies (from one to four meals daily). Weight gain, specific growth rate, and feeding rates in fish fed three and four meals daily were significantly higher than those of fish fed one or two meals daily. The feed efficiency and inter-individual size variation were not significantly affected by feeding frequency. The highest feed intake of fish occurred at the first meal each day. The crude lipid content of fish fed three and four meals daily was significantly higher than that of fish fed one or two meals daily. The blood plasma glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase and glutamic pyruvic transaminase contents in fish fed one meal per day were significantly higher than those in fish fed at other frequencies. Our results suggest that the optimum feeding frequency for juvenile short barbeled velvetchin weighing 30–150 g and reared in sea cages is three meals daily.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
An HS, Kang HW, Han HS, Park JY, Hong CG, Park J, Myeong JI, An CM (2014) Genetic differences between the wild and hatchery-produced populations of Korean short barbeled grunter (Hapalogenys nitens) determined with microsatellite markers. Genet Mol Res 13(4):8901–8912
Andrews JW, Page JW (1975) The effects of frequency of feeding on culture of catfish. Trans Am Fish Soc 104(2):317–321
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis, vol 15. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington. https://doi.org/10.12691/jfnr-2-4-9
Baloi M, de Carvalho CVA, Sterzelecki FC, Passini G, Cerqueira V (2016) Effects of feeding frequency on growth, feed efficiency and body composition of juvenile Brazilian sardine, Sardinella brasiliensis (Steindacher 1879). Aquac Res 47(2):554–560
Biswas G, Jena JK, Singh SK, Patmajhi P, Muduli HK (2006) Effect of feeding frequency on growth, survival and feed utilization in mrigal, Cirrhinus mrigala, and rohu, Labeo rohita, during nursery rearing. Aquaculture 254(1–4):211–218
Biswas G, Thirunavukkarasu AR, Sundaray JK, Kailasam M (2010) Optimization of feeding frequency of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) fry reared in net cages under brackish water environment. Aquaculture 305(1–4):26–31
Booth MA, Tucker BJ, Allan GL, Allan GL, Fielder DS (2008) Effect of feeding regime and fish size on weight gain, feed intake and gastric evacuation in juvenile Australian snapper Pagrus auratus. Aquaculture 282(1–4):104–110
Buurma BJ, Diana JS (1994) Effects of feeding frequency and handling on growth and mortality of cultured walking catfish Clarias fuscus. J World Aquac Soc 25(2):175–182
Cho SH, Lim YS, Lee JH, Lee JK, Park S, Lee S-M (2003) Effects of feeding rate and feeding frequency on survival, growth, and body composition of Ayu post-larvae Plecoglossus altivelis. J World Aquac Soc 34(1):85–91
Dada AA, Fagbenro OA, Fasakin EA (2002) Determination of optimum feeding frequency for Heterobranchus bidorsalis fry in outdoor concrete tanks. J Aquac Trop 17(3):167–174
Dwyer KS, Brown JA, Parrish C, Lall SP (2002) Feeding frequency affects food consumption, feeding pattern and growth of juvenile yellowtail flounder (Limanda ferruginea). Aquaculture 213(1–4):279–292
Guo Z, Cui J, Li M, Liu H, Zhang M, Meng F, Shi G, Wang R, He X, Zhao Y (2018) Effect of feeding frequency on growth performance, antioxidant status, immune response and resistance to hypoxia stress challenge on juvenile dolly varden char Salvelinus malma. Aquaculture 486:197–201
Jarboe HH, Grant WJ (1996) Effects of feeding time and frequency on growth of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus in closed recirculatory raceway systems. J World Aquac Soc 27(2):235–239
Jobling M (1982) Some observations on the effects of feeding frequency on the food intake and growth of plaice, Pleuronectes platessa L. J Fish Biol 20(4):431–444
Kang HW, Jun JC, Kang DY, Jo KC (2009) Influence of low salinity and cold water temperature on the hatching, survival and growth of the offspring of grunt, Hapalogenys nitens. Kor J Ichthyol 21(3):158–166
Kang HW, Cho JK, Son MH, Park JY, Hong CG, Chung JS, Chung EY (2015) Gonadal development, spawning and plasma sex steroid levels of the indoor cultured grunt, Hapalogenys nitens. Dev Reprod 19(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.12717/devrep.2015.19.1.033
Kayano Y, Yao S, Yamamoto S, Nakagawa H (1993) Effects of feeding frequency on the growth and body constituents of young red-spotted grouper, Epinephelus akaara. Aquaculture 110(3–4):271–278
Küçük E, Aydin İ, Polat H, Eroldoğan OT, Şahin T (2014) Effect of feeding frequency on growth, feed efficiency and nutrient utilization of juvenile flounder (Platichthys flesus Iuscus). Aquac Int 22(2):723–732
Lee SM, Pham MA (2010) Effects of feeding frequency and feed type on the growth, feed utilization and body composition of juvenile olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquac Res 41(9):166–171
Lee SM, Hwang UG, Cho SH (2000) Effects of feeding frequency and dietary moisture content on growth, body composition and gastric evacuation of juvenile Korean rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Aquaculture 187(3–4):399–409
Li J, Zhang JQ, Ou YJ, Zhang JS, Liu Z, Liao R et al (2007) Study on the growth performance of skewband grunt Hapalogenys nitens in sea gulf net cage. South China Fish Sci 3(4):1–6
Li XF, Tian HY, Zhang DD, Jiang GZ, Liu WB (2014) Feeding frequency affects stress, innate immunity and disease resistance of juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Shellfish Immunol 38(1):80–87
Liu FG, Liao IC (1999) Effect of feeding regimen on the food consumption, growth, and body composition in hybrid striped bass Morone saxatilis × M chrysops. Fish Sci 65(4):513–519
Lupatsch I, Kissil GW, Sklan D (2003) Comparison of energy and protein efficiency among three fish species gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata), European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and white grouper (Epinephelus aeneus): energy expenditure for protein and lipid deposition. Aquaculture 225(1–4):175–189
Mizanur RM, Bai SC (2014) The optimum feeding frequency in growing Korean rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli) rearing at the temperature of 15 °C and 19 °C. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 27(9):1319–1327
Mizanur RM, Park G, Yun HH, Lee S, Choi S, Bai SC (2014) The effects of feeding rates in juvenile Korean rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli) reared at 17 °C and 20 °C water temperatures. Aqauc Int 22(3):1121–1130
National Fisheries and Development Institute (NFRDI) (2004) Commercial fishes of the coastal and offshore waters in Korea. NFRDI, Busan. http://www.riss.kr/link?id=M9553498
Oh SY, Venmathi Maran BA (2015) Feeding frequency influences growth, feed consumption and body composition of juvenile rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus). Aquac Int 23(1):175–184
Ruohonen K, Grove DJ (1996) Gastrointestinal responses of rainbow trout to dry pellet and low-fat herring diets. J Fish Biol 49(3):501–513
Schnaittacher G, King W, Berlinsky DL (2005) The effects of feeding frequency on growth of juvenile Atlantic halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus L. Aquac Res 36(4):370–377
Silva CR, Gomes LC, Brandão FR (2007) Effect of feeding rate and frequency on tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) growth, production and feeding costs during the first growth phase in cages. Aquaculture 264(1–4):135–139
Sunde LM, Imsland AK, Folkvord A, Stefansson SO (1998) Effects of size grading on growth and survival of juvenile turbot at two temperatures. Aquac Int 6:19–32
Tucker BJ, Booth MA, Allan GL, Booth D, Fielder D (2006) Effects of photoperiod and feeding frequency on performance of newly weaned Australian snapper Pagrus auratus. Aquaculture 258(1–4):514–520
Wang N, Hayward RS, Noltie DB (1998) Effect of feeding frequency on food consumption, growth, size variation, and feeding pattern of age-0 hybrid sunfish. Aquaculture 165(3–4):261–267
Wang Y, Kong LJ, Li K, Bureau DP (2007) Effects of feeding frequency and ration level on growth, feed utilization and nitrogen waste output of cuneate drum (Nibea miichthioides) reared in net pens. Aquaculture 271(1–4):350–356
Wang N, Xu X, Kestemont P (2009) Effect of temperature and feeding frequency on growth performances, feed efficiency and body composition of pikeperch juveniles (Sander lucioperca). Aquaculture 289(1–2):70–73
Webster CD, Tidwell JH, Yancey DH (1992) Effect of protein level and feeding frequency on growth and body composition of cage-reared channel catfish. Prog Fish Cult 54(2):92–96
Xie F, Ai Q, Mai K, Xu W, Ma H (2011) The optimal feeding frequency of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea, Richardson) larvae. Aquaculture 311(1–4):162–167
Zhang Y, Hu J, Xie Y, Zhong Y, Huang C (2003) Effects of diets on growth and survival rates of artificially-produced juveniles of Hapalogenys nitens. Mar Sci 27(1):30–33
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Development of Technology for Mass Production of Useful Marine Bioproducts project (KIOST project no. PE99722), funded by the Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology, and the Technology Development of Long-term Environmental Monitoring System and the Safety Standards of Maritime Activities to Solve Environmental and Safety Issues due to the Offshore Wind Farm program of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP), funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea (nos. 20163010024660, PN67590).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, SY., Maran, B.A.V. & Park, J.W. Optimum feeding frequency for juvenile short barbeled velvetchin Hapalogenys nigripinnis reared in floating sea cages. Fish Sci 85, 379–385 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-019-01288-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-019-01288-1