Abstract
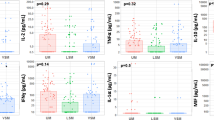
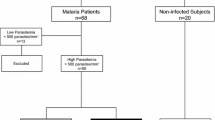
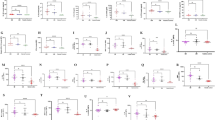
We investigated the prognostic role of TNF-alpha, IL-4 and IL-12 in a clinically well defined group of Plasmodium falciparum infected patients (n = 32) sequentially from Day 0 to Day 10 with a 2 day interval along with a control group of 16 healthy volunteers of same range of age and sex. Infection with malaria is often fatal because mitochondria are unable to generate enough ATP to maintain normal cellular function. ATP deficiency arises in malaria due to an inability of mitochondria through the effects of inflammatory cytokines on their function, to utilize available oxygen. In our study TNF-alpha and IL-12 levels were significantly elevated but IL-4 level showed persistent decline in Day 0, but subsequent measurement in Day 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 showed persistent decline in levels of TNF-alpha and IL-12, an elevation in IL-4 levels which were associated with disease prognosis of the infected patients. These results again provide evidence that cytokines are very much a dominant partner in malaria pathogenesis with a specific prognostic role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schofield L, Grau GE. Immunological processes in malaria pathogenesis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:722–35.
Berendt AR, Turner GDH, Newbold CI. Cerebral malaria: the sequestration hypothesis. Parasitol Today. 1994;10:412–4.
Clark IA, Rockett KA. The cytokine theory of human cerebral malaria. Parasitol Today. 1994;10:410–2.
Schofield and Hackett. Signal transduction in host cells by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol toxin of malaria parasites. J Exp Med. 1993;177:145–53.
Pichyangkul S, Saengkrai P, Webster HK. Plasmodium falciparum pigment induces monocytes to release high levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;51:430–5.
Ghigo D, Todde R, Ginsburg H, et al. Erythrocyte stages of Plasmodium falciparum exhibit a high nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity and release an NOS inducing soluble factor. J Exp Med. 1995;182:677–88.
Luty FJA, Perkins PJ, Lell B, Ott SR, Lehman GL, Luckner D, Greve B, Matousek P, Herbich K, Schmid D, Weinberg BJ, Kremsner GP. Low interleukin 12 activity in severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Infect Immun. 2000;68:3909–15.
Pasvol G. Cell–cell interaction in the pathogenesis of severe falciparum malaria. Clin Med. 2001;1:495–500.
Clark AI, Budd CA, Alleva ML, Cowden BW. Human malarial disease: a consequence of inflammatory cytokine release. Malar J. 2006;5:85–117.
Winkler S, Willheim M, Baier K, Schmid D, Aichelburg A, Graninger W, Kremsner PG. Reciprocal regulation of Th1 and Th2-cytokine-producing T cells during clearance of parasitemia in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Infect Immun. 1998;66:6040–4.
Day NP, Hien TT, Schollaardt T, Loc PP, Chuong LV, Chau TT, Mai NT, Phu NH, Sinh DX, Whithe NJ, Ho M. The prognostic and pathophysiology role of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in severe malaria. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:1288–97.
Plebanski M, Hill AVS. The immunology of malaria. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000;12:437–41.
Gogos CA, Drosou E, Bassaris HP, Skoutelis A. Pro-versus anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in patients with severe sepsis: a marker of prognosis and future therapeutic options. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:176–80.
McGuire W, Hill A, Allsopp CE, Greenwood BM, Kwiatkowski D. Variation in the TNF-alpha promoter region associated with susceptibility to cerebral malaria. Nature. 1994;371:508–10.
Kwiatkowski D, Cannon JG, Manogue KR, Cerami A, Dinarello CA, Greenwood BM. Tumour necrosis factor production in falciparum malaria and its association with schizont rupture. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989;77:361–6.
Kwiatkowski D, Molyneux ME, Stephens S, et al. Anti-TNF therapy inhibits fever in cerebral malaria. Q J Med. 1993;86:91–8.
Tripp CS, Wolf SF, Unanue ER. Interleukin 12 and tumor necrosis factor alpha are costimulators of interferon gamma production by natural killer cells in severe combined immunodeficiency mice with listeriosis, and interleukin 10 is a physiologic antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:3725–9.
Crutcher JM, Stevenson MM, Sedegah M, Hoffman SL. Interleukin 12 and malaria. Res Immunol. 1995;146:552–9.
Essner R, Rhoades K, McBride WH, Morton DL, Economou JS. IL-4 down-regulates interleukin-1 and TNF gene expression in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989;142:3857–61.
Paul WE. Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood. 1991;77:1859–70.
Nelms K, Keegan AD, Zamorano J, Ryan JJ, Paul WE. The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:701–38.
Vitetta ES, Ohara J, Myers C, Layton J, Krammer PH, Paul WE. Serological, biochemical, and functional identity of B-cell stimulatory factor-1 and B cell differentiation factor for IgGl. J Exp Med. 1985;162:1726–31.
Zubiaga AM, Muñoz E, Huber BT. IL-4 and IL-2 selectively rescue Th cell subsets from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. J Immunol. 1992;149:107–12.
Illera VA, Perandones CE, Stunz LL, Mower DA, Ashman RF. Apoptosis in splenic B lymphocytes. Regulation by protein kinase C and IL-4. J Immunol. 1993;151:2965–73.
Seder RA, Paul WE, Davis MM, De St Groth BF. The presence of interleukin-4 during in vitro priming determines the lymphokine producing potential of CD4+ T cells from T cell receptor transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 1992;179:1091–8.
Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. Th1 and Th2 cells: different pattern of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–73.
Zamorano J, Kelly AE, Austrian J, Wang HY, Keegan AD. Costimulation of resting B lymphocytes alters the IL-4-activated IRS2 signaling pathway in a STAT6 independent manner: implications for cell survival and proliferation. Cell Res. 2001;11:44–54.
Zamorano J, Wang HY, Wang LM, Pierce JH, Keegan AD. IL-4 protects cells from apoptosis via the insulin receptor substrate pathway and a second independent signaling pathway. J Immunol. 1996;157:4926–34.
Yanagida M, Fukamachi H, Ohgami K, Kuwaki T, Ishii H, Uzumaki H, et al. Effects of T-helper 2-type cytokines, interleukin-3 (IL-3), IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 on the survival of cultured human mast cells. Blood. 1995;86:3705–14.
Lutz MB, Schnare M, Menges M, Rossner S, Rollinghoff M, Schuler G, et al. Differential functions of IL-4 receptor types I and II for dendritic cell maturation and IL-12 production and their dependency on GM-CSF. J Immunol. 2002;169:3574–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, P.C., Sarangi, A., Sarangi, A.K. et al. Sequential Serum Cytokine Levels of TNF-Alpha, IL-4 and IL-12 are Associated with Prognosis in Plasmodium falciparum Malaria. Ind J Clin Biochem 29, 321–326 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0359-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0359-3