Abstract
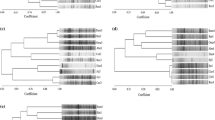
A feeding study was performed to monitor the effect of chitosan intake on the fecal microbiota of ten healthy human subjects. Diversity of microflora was monitored during 8 weeks including 4 weeks of chitosan supplementations. Using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis of 16S rRNA gene amplicons and quantitative PCR method we revealed possible changes originating in the overall bacterial composition and also in the subpopulation of Bifidobacterium group. DGGE profiles displayed high complexity and individuality for each subject. Considerable variations in the composition of band patterns were observed among different persons. A raised level of fecal Bacteroides in response to chitosan intake was found in all samples. Bifidobacterium levels following chitosan intake increased or remain unchanged. Non-significant increase was, surprisingly, found in the numbers of butyrate-producing bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guarner F., Malagelada J.R.: Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet361, 512–519 (2003).
Jackson C.R., Roden E.E., Churchill P.F.: Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis can fail to separate 16S rDNA fragments with multiple base differences. Mol.Biol.Today1, 49–51 (2000).
Jeon Y.J., Park P.J., Kim S.K.: Antimicrobial effect of chitooligosaccharides produce by bioreactor. Carbohydr.Polym.44, 71–76 (2001).
Kaats G.R., Michalek J.E., Preuss H.G.: Evaluating efficacy of a chitosan product using a double-blinded, placebo-controlled protocol. J.Am.Coll.Nutr.25, 389–394 (2006).
Kanauchi O., Deuchi K., Imasato Y., Shizukuishi M., Kobayashi E.: Mechanism of fat digestion by chitosan and for the synergistic effect of ascorbate. Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem.59, 786–790 (1995).
Kaufmann P., Pfefferkorn A., Teuber M., Meile L.: Identification and quantification of Bifidobacterium species isolated from food with genus-specific 16S rRNA-targeted probes by colony hybridization and PCR. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.62, 3668–3672 (1997).
Kleessen B., Kroesen A.J., Buhr H.J., Blaut M.: Mucosal and invading bacteria in patients with inflammatory bowel disease compared with controls. Scand.J.Gastroenterol.37, 1034–1041 (2002).
Krasaekoopt W., Bhandari B., Deeth H.: The influence of coating materials on some properties of alginate beads and survivability of microencapsulated probiotic. Internat.Dairy J.14, 737–743 (2004).
Lee W.H., Park Y.S., Jung J.S., Shin W.S.: Chitosan oligosaccharides, dp 2–8, have prebiotic effect on the Bifidobacterium bifidium and Lactobacillus sp. Anaerobe8, 319–324 (2002).
Matsuki T., Watanabe K., Fujimoto J., Miyamoto Y., Takada T., Matsumoto K., Oyaizu H., Tanaka R.: Development of 16S rRNA-gene-targeted group-specific primers for the detection and identification of predominant bacteria in human feces. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.68, 5445–5451 (2002).
Mrázek J., Štrosová L., Fliegerová K., Kott T., Kopečný J.: Diversity of insect intestinal microflora. Folia Microbiol. 53, 229–233 (2008).
Mrázek J., Tepšič K., Avguštin G., Kopečný J.: Diet-dependent shifts in ruminal butyrate-producing bacteria. Folia Microbiol. 51, 294–298 (2006).
No H.K., Park N.Y., Lee S.H., Meyers S.P.: Antibacterial activity of chitosans and chitosan oligomers with different molecular weights. Internat.J.Food Microbiol.74, 65–72 (2002).
Pang X., Ding D., Wei G., Zhang M., Wang L., Zhao L.: Molecular profiling of Bacteroides spp. in human feces by PCR-temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. J.Microbiol.Methods61, 413–417 (2005).
Suau A., Bonnet R., Sutren M., Goddon J.J., Gibson G.R., Collins M.D., Dore J.: Direct analysis of genes encoding 16S rRNA from complex communities reveals many novel molecular species within the human gut. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.65, 4799–4807 (1999).
Tsai G.J., Hwang S.P.: In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of shrimp chitosan against some intestinal bacteria. Fish Sci. 70, 675–681 (2004).
Wong J.M., De Souza R., Kendall C.W., Emam A., Jenkins D.J.: Colonic health: fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J.Clin. Gastroenterol.40, 235–243 (2006).
Yang T.C., Chou C.C., Li C.F.: Antibacterial activity of N-alkylated disaccharide chitosan derivatives. Internat.J.Food Microbiol.97, 237–245 (2005).
Zoetendal E.G., Akkermans A.D.L., De Vos D.M.: Temperature gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of 16S rRNA from human fecal samples reveals stable and host-specific communities of active bacteria. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.64, 3854–3859 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mrázek, J., Koppová, I., Kopečný, J. et al. PCR-DGGE-based study of fecal microbial stability during the long-term chitosan supplementation of humans. Folia Microbiol 55, 352–358 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0057-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0057-y