Abstract
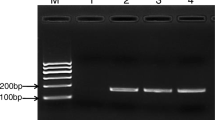
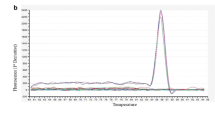
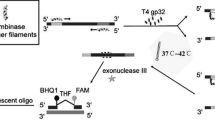
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (V. parahaemolyticus) is a zoonotic pathogen generally found in seafood. To detect the foodborne pathogen rapidly and accurately for food safety measures, we developed a real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) method. An evaluation of the specificity and sensitivity of the method is discussed here. A set of primers and probe was specially designed to target the tlh gene, which is usually regarded as a marker of total V. parahaemolyticus strains. During the reaction, target DNA was amplified and tagged with specific fluorophore within 10 min and at an incubation temperature of 40 °C. In addition to fast amplification and low temperature, the fluorescence signal was synchronized with the amplification of products for the generation of real-time data. The detection limit of this assay was 0.4 pg/μL of DNA, which is comparable to assays that use the bacterial culture as template, 4 × 103 cfu/mL. The real-time RPA method had a stable performance when testing the spiking shellfish samples at the same level of contamination by the pathogen in different kinds of shellfish. Thus, the real-time RPA method shows great potential for on-site detection of V. parahaemolyticus, especially in low-resource settings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bej AK, Patterson DP, Brasher CW, Vickery MCL, Jones DD, Kaysner CA (1999) Detection of total and hemolysin-producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish using multiplex PCR amplification of tl, tdh and trh. J Microbiol Methods 36:215–225
Blackstone GM, Nordstrom JL, Vickery MCL, Bowen MD, Meyer RF, Depaola A (2003) Detection of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oyster enrichments by real time PCR. J Microbiol Methods 53:149–155
Boyle DS, Lehman DA, Lillis L, Peterson D, Singhal M, Armes N, Parker M, Piepenburg O, Overbaugh J (2013) Rapid detection of HIV-1 proviral DNA for early infant diagnosis using recombinase polymerase amplification. MBio 4:e00135–e00113
Broberg CA, Calder TJ, Orth K (2011) Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell biology and pathogenicity determinants. Microbes Infect 13:992–1001
Clancy E, Higgins O, Forrest MS, Boo TW, Cormican M, Barry T, Piepenburg O, Smith TJ (2015) Development of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae in whole blood. BMC Infect Dis 15:481
Crannell ZA, Rohrman B, Richards-Kortum R (2014) Quantification of HIV-1 DNA using real-time recombinase polymerase amplification. Anal Chem 86:5615–5619
Craw P, Balachandran W (2012) Isothermal nucleic acid amplification technologies for point-of-care diagnostics: a critical review. Lab Chip 12:2469–2486
Daniels NA, Mackinnon L, Bishop R, Altekruse S, Ray B, Hammond RM, Thompson S, Wilson S, Bean NH, Griffin PM, Slutsker L (2000) Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections in the United States, 1973–1998. J Infect Dis 181:1661–1666
Euler M, Wang YJ, Otto P, Tomaso H, Escudero R, Anda P, Hufert FT, Weidmann M (2012) Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol 50:2234–2238
Faye O, Soropogui B, Patel P, ElWahed AA, Loucoubar C, Fall G, Kiory D, Magassouba N, Keita S, Kondé MK, Diallo AA, Koivogui L, Karlberg H, Mirazimi A, Nentwich O, Piepenburg O, Niedrig M, Weidmann M and Sall AA (2015) Development and deployment of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification Ebola virus detection assay in Guinea in 2015. Eurosurveillance: bulletin europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin 20
Fuenzalida L, Hernández C, Toro J, Rioseco ML, Romero J, Espejo RT (2006) Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish and clinical samples during two large epidemics of diarrhoea in southern Chile. Environ Microbiol 8:675–683
Gao W, Huang H, Zhang Y, Zhu P, Yan X, Fan J, Chen X (2017) Recombinase polymerase amplification-based assay for rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food samples. Food Anal Methods 10:1972–1981
Han HH, Li FQ, Yan WX, Guo YC, Li N, Liu XM, Zhu JH, Xu J, Chen Y, Li XG, Lv H, Zhang YQ, Cai T, Chen YZ (2015) Temporal and spatial variation in the abundance of total and pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish in China. PLoS One 10
He PY, Zhu GY, Luo JY, Wang HH, Yan Y, Chen LX, Gao WJ, Chen ZW (2016) Development and application of a one-tube multiplex real-time PCR with melting curve analysis for simultaneous detection of five foodborne pathogens in food samples. J Food Saf
Hsiao HI, Jan MS, Chi HJ (2016) Impacts of climatic variability on Vibrio parahaemolyticus outbreaks in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:504–507
Kanungo S, Sur D, Ali M, You YA, Pal D, Manna B, Niyogi SK, Sarkar B, Bhattacharya SK, Clemens JD, Nair GB (2012) Clinical, epidemiological, and spatial characteristics of Vibrio parahaemolyticus diarrhea and cholera in the urban slums of Kolkata, India. BMC Public Health 12:1–9
Kim J, Easley CJ (2011) Isothermal DNA amplification in bioanalysis strategies and applications. Bioanalysis 3:227–239
Kirs M, Depaola A, Fyfe R, Jones JL, Krantz JA, Laanen AV, Cotton D, Castle M (2011) A survey of oysters (Crassostrea gigas) in New Zealand for Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus. Int J Food Microbiol 147:149–153
Lillis L, Lehman DA, Siverson JB, Weis J, Cantera J, Parker M, Piepenburg O, Overbaugh J, Boyle DS (2016a) Cross-subtype detection of HIV-1 using reverse transcription and recombinase polymerase amplification. J Virol Methods 230:28–35
Lillis L, Siverson J, Lee A, Cantera J, Parker M, Piepenburg O, Lehman DA, Boyle DS (2016b) Factors influencing recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assay outcomes at point of care. Mol Cell Probes 30:74–78
Lutz S, Weber P, Focke M, Faltin B, Hoffmann J, Muller C, Mark D, Roth G, Munday P, Armes N, Piepenburg O, Zengerle R, Stetten vF (2010) Microfluidic lab-on-a-foil for nucleic acid analysis based on isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA). Lab Chip 10:887–893
Malcolm TTH, Cheah YK, Radzi CWJWM, Kasim FA, Kantilal HK, John TYH, Martinez-Urtaza J, Nakaguchi Y, Nishibuchi M, Son R (2015) Detection and quantification of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish by using multiplex PCR and loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Food Control 47:664–671
Mccarter LL (1999) The multiple identities of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 1:51–57
Mclaughlin JB, Depaola A, Bopp CA, Martinek KA, Napolilli NP, Allison CG, Murray SL, Thompson EC, Bird MM, Middaugh JP (2005) Outbreak of Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis associated with Alaskan oysters. N Engl J Med 353:1463–1470
Mudoh MF, Parveen S, Schwarz J, Rippen T, Chaudhuri A (2014) The effects of storage temperature on the growth of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and organoleptic properties in oysters. Front Public Health 2
Nishibuchi M, Kaper JB (1995) Thermostable direct hemolysin gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a virulence gene acquired by a marine bacterium. Infect Immun 63:2093–2099
Nordstrom JL, Vickery MCL, Blackstone GM, Murray SL, Depaola A (2007) Development of a multiplex real-time PCR assay with an internal amplification control for the detection of total and pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteria in oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5840–5847
Piepenburg O, Williams CH, Stemple DL, Armes NA (2006) DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLoS Biol 4:e204
Ren H, Yang MJ, Zhang GX, Liu SW, Wang XH, Ke YH, Du XY, Wang ZJ, Huang LY, Liu C, Chen ZL (2016) Development of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification assay for detection of Brucella in blood samples. Mol Cell Probes 30:122–124
Shen F, Davydova EK, Du WB, Kreutz JE, Piepenburg O, Ismagilov RF (2011) Digital isothermal quantification of nucleic acids via simultaneous chemical initiation of recombinase polymerase amplification reactions on SlipChip. Anal Chem 83:3533–3540
Shimohata T, Takahashi A (2010) Diarrhea induced by infection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Med Invest 57:179–182
Silvester R, Alexander D, Hatha M (2015) Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, virulence and plasmid profiles of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from a tropical estuary and adjoining traditional prawn farm along the southwest coast of India. Ann Microbiol 65:2141–2149
Su YC, Liu C (2007) Vibrio parahaemolyticus : a concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol 24:549–558
Valiadi M, Kalsi S, Jones IGF, Turner C, Sutton JM and Morgan H (2016) Simple and rapid sample preparation system for the molecular detection of antibiotic resistant pathogens in human urine. Biomed Microdevices In Press:1–10
Wang RZ, Zhong YF, Gu XS, Yuan J, Saeed AF, Wang SH (2015) The pathogenesis, detection, and prevention of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front Microbiol 6:144
Wang Y, Li DX, Wang Y, Li KW, Ye CY (2016) Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus by multiple endonuclease restriction real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique. Molecules 21:428–437
Ward LN, Bej AK (2006) Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish by use of multiplexed real-time PCR with TaqMan fluorescent probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2031–2042
West CKG, Klein SL, Lovell CR (2013) High frequency of virulence factor genes tdh, trh, and tlh in Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated from a pristine estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:2247–2252
Xia XM, Yu YX, Weidmann M, Pan YJ, Yan SL, Wang YJ (2014) Rapid detection of shrimp white spot syndrome virus by real time, isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay. PLoS One 9:e104667
Xu C, Li L, Jin WJ, Wan YS (2014) Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) of CaMV-35S promoter and nos terminator for rapid detection of genetically modified crops. Int J Mol Sci 15:18197–18205
Yang Y, Qin XD, Wang GX, Zhang YE, Shang YJ, Zhang ZD (2015) Development of a fluorescent probe-based recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Orf virus. Virol J 12:206
Yang MJ, Ke YH, Wang XS, Hang R, Wei L, Lu HJ, Zhang WY, Liu SW, Chang GH, Tian SG (2016) Development and evaluation of a rapid and sensitive EBOV-RPA test for rapid diagnosis of Ebola virus disease. Sci Rep 6
Yingkajorn M, Sermwittayawong N, Khamhaeng N, Nishibuchi M, Vuddhakul V (2015) Quantitative analysis of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shrimp derived from industrial processing. J Food Saf 36:254–259
Zaghloul H, El-shahat M (2014) Recombinase polymerase amplification as a promising tool in hepatitis C virus diagnosis. World J Hepatol 6:916–922
Zhang QH, Dong XH, Chen B, Zhang YH, Yao Z, Li WM (2015) Zebrafish as a useful model for zoonotic Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity in fish and human. Dev Comp Immunol 55:159–168
Zhong QP, Tian J, Wang B, Wang L (2016) PMA based real-time fluorescent LAMP for detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in viable but nonculturable state. Food Control 63:230–238
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Ningbo Academy of Inspection and Quarantine for providing the bacterial strain for this study and allowing us to finish the assay of culturing strains in the laboratory there. Authors also appreciated the assistance and guidance of the staff there and the professionals at the Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ningbo Science and Technology Innovation Team (2015C110018); Ningbo Marine Algae Biotechnology Team (2011B81007); Zhejiang Provincial Public Welfare Technology Program of China (2017C33133); K.C. Wang Magna Fund in Ningbo University (SS); LiDakSum Marine Biopharmaceutical Development Fund; National 111 Project of China; the Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System, China (CARS-49); Zhejiang Xinmiao Talents Program (2015R405013); and Scientific Research Foundation of Graduate School of Ningbo University (G16091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng Zhu and Weifang Gao contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Peng Zhu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Weifang Gao declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hailong Huang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jinpo Jiang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xianfeng Chen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jianzhong Fan declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xiaojun Yan declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, P., Gao, W., Huang, H. et al. Rapid Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Shellfish by Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. Food Anal. Methods 11, 2076–2084 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1188-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1188-z