Abstract
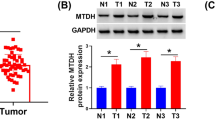
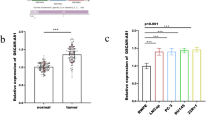
Accumulating evidence suggest that microRNAs play crucial roles in the development and progression of bladder cancer (BC). Here, we found that miR-212-3p was significantly down-regulated and negatively correlated with nuclear factor IA (NFIA) in human BC tissues. Bioinformatics analysis predicted that NFIA was a target gene of miR-212-3p. Then BC cell lines, T24 and J82 cells were transfected with miR-212-3p mimics or siNFIA to obtain miR-212-3p overexpression or NFIA knockdown cell lines, respectively. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to determine the expression of miR-212-3p and NFIA. Western blot analysis was utilized to detect NFIA expression. MTT assay showed either miR-212-3 overexpression or NFIA knockdown significantly inhibited the BC cell proliferation. Double staining with Annexin V-APC and 7-AAD showed the total number of apoptotic BC cells were remarkably increased after miR-212-3p overexpression or NFIA knockdown. Collectively, our results indicated that miR-212-3p targeting NFIA might serve as a promising target for BC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ahmadie HA, Iyer G, Lee BH, Scott SN, Mehra R, Bagrodia A, Jordan EJ, Gao SP, Ramirez R, Cha EK, Desai NB, Zabor EC, Ostrovnaya I, Gopalan A, Chen YB, Fine SW, Tickoo SK, Gandhi A, Hreiki J, Viale A, Arcila ME, Dalbagni G, Rosenberg JE, Bochner BH, Bajorin DF, Berger MF, Reuter VE, Taylor BS and Solit DB 2016 Frequent somatic CDH1 loss-of-function mutations in plasmacytoid variant bladder cancer. Nat. Genet. 48 356–358
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A and Bray F 2017 Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: A global overview and recent trends. Eur. Urol. 71 96–108
Bernard F, Gelsi-Boyer V, Murati A, Giraudier S, Trouplin V, Adelaide J, Rey J, Olschwang S, Vainchenker W, Chaffanet M, Vey N, Mozziconacci MJ and Birnbaum D 2009 Alterations of NFIA in chronic malignant myeloid diseases. Leukemia 23 583–585
Chen Y, Gao DY and Huang L 2015 In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: Challenges and strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 81 128–141
Chiyomaru T, Seki N, Inoguchi S, Ishihara T, Mataki H, Matsushita R, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Tatarano S, Itesako T, Nakagawa M and Enokida H 2015 Dual regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase genes EGFR and c-Met by the tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster in bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 46 487–496
Fu W, Tao T, Qi M, Wang L, Hu J, Li X, Xing N, Du R and Han B 2016 MicroRNA-132/212 upregulation inhibits TGF-beta-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting SOX4. Prostate 76 1560–1570
Hansen KF, Sakamoto K, Aten S, Snider KH, Loeser J, Hesse AM, Page CE, Pelz C, Arthur JS, Impey S and Obrietan K 2016 Targeted deletion of miR-132/-212 impairs memory and alters the hippocampal transcriptome. Learn. Mem. 23 61–71
Hiraike Y, Waki H, Yu J, Nakamura M, Miyake K, Nagano G, Nakaki R, Suzuki K, Kobayashi H and Yamamoto S 2017 NFIA co-localizes with PPARγ and transcriptionally controls the brown fat gene program. Nat. Cell Biol. 19 1081–1092
Hou P, Kang Y and Luo J 2018 Hypoxia-mediated miR-212-3p downregulation enhances progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through upregulation of Rab1a. Cancer Biol. Ther. 1–10
Jin H, Sun W, Zhang Y, Yan H, Liufu H, Wang S, Chen C, Gu J, Hua X, Zhou L, Jiang G, Rao D, Xie Q, Huang H and Huang C 2018 MicroRNA-411 downregulation enhances tumor growth by upregulating MLLT11 expression in human bladder cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids. 11 312–322
Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner SP, Malmström P-U, Choi W, Guo CC, Lotan Y and Kassouf W 2016 Bladder cancer. Lancet 388 2796–2810
Kang CM, Hu YW, Nie Y, Zhao JY, Li SF, Chu S, Li HX, Huang QS and Qiu YR 2016 Long non-coding RNA RP5-833A20.1 inhibits proliferation, metastasis and cell cycle progression by suppressing the expression of NFIA in U251 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 14 5288–5296
Lee JS, Xiao J, Patel P, Schade J, Wang J, Deneen B, Erdreich-Epstein A and Song HR 2014 A novel tumor-promoting role for nuclear factor IA in glioblastomas is mediated through negative regulation of p53, p21, and PAI1. Neuro Oncol 16 191–203
Lee J, Hoxha E and Song HR 2017 A novel NFIA-NFkappaB feed-forward loop contributes to glioblastoma cell survival. Neuro Oncol 19 524–534
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP 2005 Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120 15–20
Lin S and Gregory RI 2015 MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 15 321–333
Liu H, Li C, Shen C, Yin F, Wang K, Liu Y, Zheng B, Zhang W, Hou X, Chen X, Wu J, Wang X, Zhong C, Zhang J, Shi H, Ai J and Zhao S 2015 MiR-212-3p inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation by targeting SGK3. J. Neurooncol. 122 431–439
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD 2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 −ΔΔ C T method. Methods–A Companion Method Enzymol. 25 402–408
Matsushita R, Seki N, Chiyomaru T, Inoguchi S, Ishihara T, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Mataki H, Tatarano S, Itesako T, Nakagawa M and Enokida H 2015 Tumour-suppressive microRNA-144-5p directly targets CCNE1/2 as potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 113 282–289
Matsushita R, Yoshino H, Enokida H, Goto Y, Miyamoto K, Yonemori M, Inoguchi S, Nakagawa M and Seki N 2016 Regulation of UHRF1 by dual-strand tumor-suppressor microRNA-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p): Inhibition of bladder cancer cell aggressiveness. Oncotarget. 7 28460–28487
Messina G, Biressi S, Monteverde S, Magli A, Cassano M, Perani L, Roncaglia E, Tagliafico E, Starnes L, Campbell CE, Grossi M, Goldhamer DJ, Gronostajski RM and Cossu G 2010 Nfix regulates fetal-specific transcription in developing skeletal muscle. Cell 140 554–566
Ramalinga M, Roy A, Srivastava A, Bhattarai A, Harish V, Suy S, Collins S and Kumar D 2015 MicroRNA-212 negatively regulates starvation induced autophagy in prostate cancer cells by inhibiting SIRT1 and is a modulator of angiogenesis and cellular senescence. Oncotarget. 6 34446–34457
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ 2017 MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 16 203–222
Semenova EA, Kwon MC, Monkhorst K, Song JY, Bhaskaran R, Krijgsman O, Kuilman T, Peters D, Buikhuisen WA, Smit EF, Pritchard C, Cozijnsen M, van der Vliet J, Zevenhoven J, Lambooij JP, Proost N, van Montfort E, Velds A, Huijbers IJ and Berns A 2016 Transcription factor NFIB is a driver of small cell lung cancer progression in mice and marks metastatic disease in patients. Cell. Rep. 16 631–643
Tu H, Wei G, Cai Q, Chen X, Sun Z, Cheng C, Zhang L, Feng Y, Zhou H, Zhou B and Zeng T 2015 MicroRNA-212 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting FOXA1. Onco. Targets Ther. 8 2227–2235
Wada R, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, Fukamachi H and Yuasa Y 2010 miR-212 is downregulated and suppresses methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 in human gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 127 1106–1114
Wu R, Li F, Zhu J, Tang R, Qi Q, Zhou X, Li R, Wang W, Hua D and Chen W 2014 A functional variant at miR-132-3p, miR-212-3p, and miR-361-5p binding site in CD80 gene alters susceptibility to gastric cancer in a Chinese Han population. Med. Oncol. 31 60
Xie C, Chen B, Wu B, Guo J and Cao Y 2018 LncRNA TUG1 promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in osteosarcoma by regulating miR-212-3p/FOXA1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 97 1645–1653
Yang B, Zhou ZH, Chen L, Cui X, Hou JY, Fan KJ, Han SH, Li P, Yi SQ and Liu Y 2018 Prognostic significance of NFIA and NFIB in esophageal squamous carcinoma and esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma. Cancer. Med. 7 1756–1765
Zhao J, Qiao CR, Ding Z, Sheng YL, Li XN, Yang Y, Zhu DY, Zhang CY, Liu DL, Wu K and Zhao S 2017 A novel pathway in NSCLC cells: miR191, targeting NFIA, is induced by chronic hypoxia, and promotes cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Med. Rep. 15 1319–1325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Rita Mulherkar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Chen, H., Zhang, G. et al. MiR-212-3p inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting nuclear factor IA in bladder cancer. J Biosci 44, 80 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-019-9903-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-019-9903-5