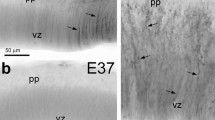
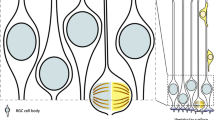
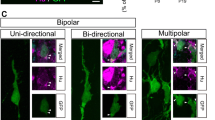
Abstract
The morphogenesis of the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus primarily occurs postnatally, and the DG is one of the few regions of continuous neurogenesis in the adult brain. Radial glial cells (RGCs), which contribute to DG development by participating in key steps of morphogenesis, are maintained in the subgranular zone (SGZ), where they play pivotal roles in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. It is clear that a series of molecules control the development of RGCs, thereby regulating the morphogenesis of the DG and neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. In this review, we provide an updated framework regarding the molecular mechanisms involved in the development of RGCs during DG morphogenesis and discuss the key steps that regulate DG formation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lagali PS, Corcoran CP, Picketts DJ (2010) Hippocampus development and function: role of epigenetic factors and implications for cognitive disease. Clin Genet 78:321–333
Fitzsimons C, van Hooijdonk L, Schouten M, Zalachoras I, Brinks V, Zheng T, Schouten T, Saaltink D, Dijkmans T, Steindler D (2013) Knockdown of the glucocorticoid receptor alters functional integration of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus and impairs fear-motivated behavior. Mol Psychiatry 18:993–1005
Zainuddin MS, Thuret S (2012) Nutrition, adult hippocampal neurogenesis and mental health. Br Med Bull 103:89–114
Acsady L, Kali S (2007) Models, structure, function: the transformation of cortical signals in the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:577–599
Hsu D (2007) The dentate gyrus as a filter or gate: a look back and a look ahead. Prog Brain Res 163:601–613
Zhao C, Teng EM, Summers RG, G-l M, Gage FH (2006) Distinct morphological stages of dentate granule neuron maturation in the adult mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 26:3–11
Witter MP (2007) The perforant path: projections from the entorhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:43–61
Rohde J, Kirschstein T, Wilkars W, Muller L, Tokay T, Porath K, Bender RA, Kohling R (2012) Upregulation of presynaptic mGluR2, but not mGluR3 in the epileptic medial perforant path. Neuropharmacol 62:1867–1873
Barry G, Piper M, Lindwall C, Moldrich R, Mason S, Little E, Sarkar A, Tole S, Gronostajski RM, Richards LJ (2008) Specific glial populations regulate hippocampal morphogenesis. J Neurosci 28:12328–12340
Zheng CH, Feng L (2006) Neuregulin regulates the formation of radial glial scaffold in hippocampal dentate gyrus of postnatal rats. J Cell Physiol 207:530–539
Guidi S, Bianchi P, Alstrup AK, Henningsen K, Smith DF, Bartesaghi R (2011) Postnatal neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and subventricular zone of the Gottingen minipig. Brain Res Bull 85:169–179
Gould E, Tanapat P, McEwen BS, Flugge G, Fuchs E (1998) Proliferation of granule cell precursors in the dentate gyrus of adult monkeys is diminished by stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3168–3171
Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH (2010) New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 11:339–350
Bruel-Jungerman E, Rampon C, Laroche S (2007) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and memory: facts and hypotheses. Rev Neurosci 18:93–114
Gil JM, Mohapel P, Araujo IM, Popovic N, Li JY, Brundin P, Petersen A (2005) Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in R6/2 transgenic Huntington’s disease mice. Neurobiol Dis 20:744–751
Fedele V, Roybon L, Nordstrom U, Li JY, Brundin P (2011) Neurogenesis in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease is impaired at the level of NeuroD1. Neuroscience 173:76–81
Kohl Z, Kandasamy M, Winner B, Aigner R, Gross C, Couillard-Despres S, Bogdahn U, Aigner L, Winkler J (2007) Physical activity fails to rescue hippocampal neurogenesis deficits in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Brain Res 1155:24–33
DeCarolis NA, Mechanic M, Petrik D, Carlton A, Ables JL, Malhotra S, Bachoo R, Götz M, Lagace DC, Eisch AJ (2013) In vivo contribution of nestin‐and GLAST‐lineage cells to adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Hippocampus 23:708–719
Eckenhoff MF, Rakic P (1984) Radial organization of the hippocampal dentate gyrus: a Golgi, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical analysis in the developing rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 223:1–21
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 4:1313–1317
Rickmann M, Amaral DG, Cowan WM (1987) Organization of radial glial cells during the development of the rat dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 264:449–479
Stanfield BB, Cowan WM (1979) The development of the hippocampus and dentate gyrus in normal and reeler mice. J Comp Neurol 185:423–459
Shetty AK, Turner DA (1996) Development of fetal hippocampal grafts in intact and lesioned hippocampus. Prog Neurobiol 50:597–653
Li H, Jin G, Qin J, Yang W, Tian M, Tan X, Zhang X, Shi J, Zou L (2011) Identification of neonatal rat hippocampal radial glia cells in vitro. Neurosci Lett 490:209–214
Chanas-Sacre G, Rogister B, Moonen G, Leprince P (2000) Mini-review-radial glia phenotype: origin, regulation, and transdifferentiation. J Neurosci Res 61:357–363
Edwards MA, Yamamoto M, Caviness VS Jr (1990) Organization of radial glia and related cells in the developing murine CNS. An analysis based upon a new monoclonal antibody marker. Neuroscience 36:121–144
Brunne B, Zhao S, Derouiche A, Herz J, May P, Frotscher M, Bock HH (2010) Origin, maturation, and astroglial transformation of secondary radial glial cells in the developing dentate gyrus. Glia 58:1553–1569
Lledo PM, Alonso M, Grubb MS (2006) Adult neurogenesis and functional plasticity in neuronal circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:179–193
Sievers J, Hartmann D, Pehlemann FW, Berry M (1992) Development of astroglial cells in the proliferative matrices, the granule cell layer, and the hippocampal fissure of the hamster dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 320:1–32
Schmechel DE, Rakic P (1979) A Golgi study of radial glial cells in developing monkey telencephalon: morphogenesis and transformation into astrocytes. Anat Embryol (Berl) 156:115–152
Nadarajah B, Parnavelas JG (2002) Modes of neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:423–432
Solecki DJ (2012) Sticky situations: recent advances in control of cell adhesion during neuronal migration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 22:791–798
Lin Y, Chen L, Lin C, Luo Y, Tsai RY, Wang F (2009) Neuron-derived FGF9 is essential for scaffold formation of Bergmann radial fibers and migration of granule neurons in the cerebellum. Dev Biol 329:44–54
Hall AC, Mira H, Wagner J, Arenas E (2003) Region‐specific effects of glia on neuronal induction and differentiation with a focus on dopaminergic neurons. Glia 43:47–51
Virgintino D, Errede M, Rizzi M, Girolamo F, Strippoli M, Wälchli T, Robertson D, Frei K, Roncali L (2013) The CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 ligand-receptor system regulates neuro-glio-vascular interactions and vessel growth during human brain development. J Inherit Metab Dis 36:455–466
Kempermann G, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G (2004) Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 27:447–452
Kriegstein A, Alvarez-Buylla A (2009) The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:149–184
Suh H, Consiglio A, Ray J, Sawai T, D’Amour KA, Gage FH (2007) In vivo fate analysis reveals the multipotent and self-renewal capacities of Sox2 + neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell 1:515–528
Encinas JM, Michurina TV, Peunova N, Park J-H, Tordo J, Peterson DA, Fishell G, Koulakov A, Enikolopov G (2011) Division-coupled astrocytic differentiation and age-related depletion of neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell 8:566–579
Bonaguidi MA, Wheeler MA, Shapiro JS, Stadel RP, Sun GJ, Ming GL, Song H (2011) In vivo clonal analysis reveals self-renewing and multipotent adult neural stem cell characteristics. Cell 145:1142–1155
Kempermann G (2011) The pessimist’s and optimist’s views of adult neurogenesis. Cell 145:1009–1011
Ghashghaei HT, Lai C, Anton ES (2007) Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet? Nat Rev Neurosci 8:141–151
Pinto L, Götz M (2007) Radial glial cell heterogeneity—the source of diverse progeny in the CNS. Prog Neurobiol 83:2–23
McMahon SS, McDermott KW (2007) Developmental potential of radial glia investigated by transplantation into the developing rat ventricular system in utero. Exp Neurol 203:128–136
Gao Z, Godbout R (2013) Reelin-Disabled-1 signaling in neuronal migration: splicing takes the stage. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:2319–2329
Rice DS, Curran T (2001) Role of the reelin signaling pathway in central nervous system development. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1005–1039
Hiesberger T, Trommsdorff M, Howell BW, Goffinet A, Mumby MC, Cooper JA, Herz J (1999) Direct binding of Reelin to VLDL receptor and ApoE receptor 2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of disabled-1 and modulates tau phosphorylation. Neuron 24:481–489
Weiss KH, Johanssen C, Tielsch A, Herz J, Deller T, Frotscher M, Förster E (2003) Malformation of the radial glial scaffold in the dentate gyrus of reeler mice, scrambler mice, and ApoER2/VLDLR‐deficient mice. J Comp Neurol 460:56–65
Frotscher M, Haas CA, Förster E (2003) Reelin controls granule cell migration in the dentate gyrus by acting on the radial glial scaffold. Cereb Cortex 13:634–640
Sibbe M, Forster E, Basak O, Taylor V, Frotscher M (2009) Reelin and Notch1 cooperate in the development of the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 29:8578–8585
D’Arcangelo G (2005) The reeler mouse: anatomy of a mutant. Int Rev Neurobiol 71:383–417
Zhao S, Chai X, Förster E, Frotscher M (2004) Reelin is a positional signal for the lamination of dentate granule cells. Development 131:5117–5125
Brunne B, Franco S, Bouche E, Herz J, Howell BW, Pahle J, Muller U, May P, Frotscher M, Bock HH (2013) Role of the postnatal radial glial scaffold for the development of the dentate gyrus as revealed by Reelin signaling mutant mice. Glia 61:1347–1363
Zhao S, Chai X, Frotscher M (2007) Balance between neurogenesis and gliogenesis in the adult hippocampus: role for reelin. Dev Neurosci 29:84–90
Rice DS, Sheldon M, D’Arcangelo G, Nakajima K, Goldowitz D, Curran T (1998) Disabled-1 acts downstream of Reelin in a signaling pathway that controls laminar organization in the mammalian brain. Development 125:3719–3729
Park TJ, Curran T (2008) Crk and Crk-like play essential overlapping roles downstream of disabled-1 in the Reelin pathway. J Neurosci 28:13551–13562
Meseke M, Rosenberger G, Forster E (2013) Reelin and the Cdc42/Rac1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor alphaPIX/Arhgef6 promote dendritic Golgi translocation in hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 37:1404–1412
Leemhuis J, Bock HH (2011) Reelin modulates cytoskeletal organization by regulating Rho GTPases. Commun Integr Biol 4:254–257
Chédotal A (2010) Should I stay or should I go? Becoming a granule cell. Trends Neurosci 33:163–172
Dziembowska M, Tham TN, Lau P, Vitry S, Lazarini F, Dubois-Dalcq M (2005) A role for CXCR4 signaling in survival and migration of neural and oligodendrocyte precursors. Glia 50:258–269
Takabatake Y, Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Matsusaka T, Kurihara H, Koni PA, Nagasawa Y, Hamano T, Matsui I, Kawada N (2009) The CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis is essential for the development of renal vasculature. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:1714–1723
Bagri A, Gurney T, He X, Zou YR, Littman DR, Tessier-Lavigne M, Pleasure SJ (2002) The chemokine SDF1 regulates migration of dentate granule cells. Development 129:4249–4260
Berger O, Li G, Han SM, Paredes M, Pleasure SJ (2007) Expression of SDF-1 and CXCR4 during reorganization of the postnatal dentate gyrus. Dev Neurosci 29:48–58
Li G, Kataoka H, Coughlin SR, Pleasure SJ (2009) Identification of a transient subpial neurogenic zone in the developing dentate gyrus and its regulation by Cxcl12 and reelin signaling. Development 136:327–335
Schultheiss C, Abe P, Hoffmann F, Mueller W, Kreuder AE, Schutz D, Haege S, Redecker C, Keiner S, Kannan S, Claasen JH, Pfrieger FW, Stumm R (2013) CXCR4 prevents dispersion of granule neuron precursors in the adult dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 23:1345–1358
Mithal DS, Ren D, Miller RJ (2013) CXCR4 signaling regulates radial glial morphology and cell fate during embryonic spinal cord development. Glia 61:1288–1305
Diotel N, Vaillant C, Gueguen MM, Mironov S, Anglade I, Servili A, Pellegrini E, Kah O (2010) Cxcr4 and Cxcl12 expression in radial glial cells of the brain of adult zebrafish. J Comp Neurol 518:4855–4876
Rio C, Rieff HI, Qi P, Khurana TS, Corfas G (1997) Neuregulin and erbB receptors play a critical role in neuronal migration. Neuron 19:39–50
Anton ES, Marchionni MA, Lee KF, Rakic P (1997) Role of GGF/neuregulin signaling in interactions between migrating neurons and radial glia in the developing cerebral cortex. Development 124:3501–3510
Gierdalski M, Sardi SP, Corfas G, Juliano SL (2005) Endogenous neuregulin restores radial glia in a (ferret) model of cortical dysplasia. J Neurosci 25:8498–8504
Schmid RS, McGrath B, Berechid BE, Boyles B, Marchionni M, Sestan N, Anton ES (2003) Neuregulin 1-erbB2 signaling is required for the establishment of radial glia and their transformation into astrocytes in cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4251–4256
Mei L, Xiong WC (2008) Neuregulin 1 in neural development, synaptic plasticity and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:437–452
Yau HJ, Wang HF, Lai C, Liu FC (2003) Neural development of the neuregulin receptor ErbB4 in the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus: preferential expression by interneurons tangentially migrating from the ganglionic eminences. Cereb Cortex 13:252–264
Marone R, Hess D, Dankort D, Muller WJ, Hynes NE, Badache A (2004) Memo mediates ErbB2-driven cell motility. Nat Cell Biol 6:515–522
Mahar I, Tan S, Davoli MA, Dominguez-Lopez S, Qiang C, Rachalski A, Turecki G, Mechawar N (2011) Subchronic peripheral neuregulin-1 increases ventral hippocampal neurogenesis and induces antidepressant-like effects. PLoS One 6:e26610
Khalaf-Nazzal R, Francis F (2013) Hippocampal development—old and new findings. Neuroscience 248:225–242
Mi K, Johnson GV (2005) Role of the intracellular domains of LRP5 and LRP6 in activating the Wnt canonical pathway. J Cell Biochem 95:328–338
Choe Y, Pleasure SJ (2012) Wnt signaling regulates intermediate precursor production in the postnatal dentate gyrus by regulating CXCR4 expression. Dev Neurosci 34:502–514
Zhou CJ, Zhao C, Pleasure SJ (2004) Wnt signaling mutants have decreased dentate granule cell production and radial glial scaffolding abnormalities. J Neurosci 24:121–126
Choe Y, Kozlova A, Graf D, Pleasure SJ (2013) Bone morphogenic protein signaling is a major determinant of dentate development. J Neurosci 33:6766–6775
Fernandes M, Gutin G, Alcorn H, McConnell SK, Hébert JM (2007) Mutations in the BMP pathway in mice support the existence of two molecular classes of holoprosencephaly. Development 134:3789–3794
Galceran J, Miyashita-Lin EM, Devaney E, Rubenstein J, Grosschedl R (2000) Hippocampus development and generation of dentate gyrus granule cells is regulated by LEF1. Development 127:469–482
Li H, Chang YW, Mohan K, Su HW, Ricupero CL, Baridi A, Hart RP, Grumet M (2008) Activated Notch1 maintains the phenotype of radial glial cells and promotes their adhesion to laminin by upregulating nidogen. Glia 56:646–658
Gaiano N, Nye JS, Fishell G (2000) Radial glial identity is promoted by Notch1 signaling in the murine forebrain. Neuron 26:395–404
Anthony TE, Mason HA, Gridley T, Fishell G, Heintz N (2005) Brain lipid-binding protein is a direct target of Notch signaling in radial glial cells. Genes Dev 19:1028–1033
Lavado A, Lagutin OV, Chow LM, Baker SJ, Oliver G (2010) Prox1 is required for granule cell maturation and intermediate progenitor maintenance during brain neurogenesis. PLoS Biol 8:e1000460
Machon O, Backman M, Machonova O, Kozmik Z, Vacik T, Andersen L, Krauss S (2007) A dynamic gradient of Wnt signaling controls initiation of neurogenesis in the mammalian cortex and cellular specification in the hippocampus. Dev Biol 311:223–237
Yang Y, Tang Y, Xing Y, Zhao M, Bao X, Sun D, Tang X, Wu Y, Xu H, Fan X (2013) Activation of liver x receptor is protective against ethanol-induced developmental impairment of Bergmann glia and Purkinje neurons in the mouse cerebellum. Mol Neurobiol 49:176–186
Fan X, Xu H, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2010) ERbeta in CNS: new roles in development and function. Prog Brain Res 181:233–250
Fan X, Kim HJ, Bouton D, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2008) Expression of liver X receptor beta is essential for formation of superficial cortical layers and migration of later-born neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:13445–13450
Tian C, Gong Y, Yang Y, Shen W, Wang K, Liu J, Xu B, Zhao J, Zhao C (2012) Foxg1 has an essential role in postnatal development of the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 32:2931–2949
Le Guen T, Bahi-Buisson N, Nectoux J, Boddaert N, Fichou Y, Diebold B, Desguerre I, Raqbi F, Daire VC, Chelly J, Bienvenu T (2011) A FOXG1 mutation in a boy with congenital variant of Rett syndrome. Neurogenetics 12:1–8
Venere M, Han YG, Bell R, Song JS, Alvarez-Buylla A, Blelloch R (2012) Sox1 marks an activated neural stem/progenitor cell in the hippocampus. Development 139:3938–3949
Abranches E, Silva M, Pradier L, Schulz H, Hummel O, Henrique D, Bekman E (2009) Neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells in vitro: a road map to neurogenesis in the embryo. PLoS One 4:e6286
Favaro R, Valotta M, Ferri AL, Latorre E, Mariani J, Giachino C, Lancini C, Tosetti V, Ottolenghi S, Taylor V, Nicolis SK (2009) Hippocampal development and neural stem cell maintenance require Sox2-dependent regulation of Shh. Nat Neurosci 12:1248–1256
Ferri AL, Cavallaro M, Braida D, Di Cristofano A, Canta A, Vezzani A, Ottolenghi S, Pandolfi PP, Sala M, DeBiasi S (2004) Sox2 deficiency causes neurodegeneration and impaired neurogenesis in the adult mouse brain. Development 131:3805–3819
Gómez-López S, Wiskow O, Favaro R, Nicolis SK, Price DJ, Pollard SM, Smith A (2011) Sox2 and Pax6 maintain the proliferative and developmental potential of gliogenic neural stem cells in vitro. Glia 59:1588–1599
Pevny LH, Sockanathan S, Placzek M, Lovell-Badge R (1998) A role for SOX1 in neural determination. Development 125:1967–1978
Kan L, Israsena N, Zhang Z, Hu M, Zhao LR, Jalali A, Sahni V, Kessler JA (2004) Sox1 acts through multiple independent pathways to promote neurogenesis. Dev Biol 269:580–594
Thiel G (2013) How Sox2 maintains neural stem cell identity. Biochem J 450:e1–e2
Glaser T, Walton DS, Maas RL (1992) Genomic structure, evolutionary conservation and aniridia mutations in the human PAX6 gene. Nat Genet 2:232–239
Götz M, Stoykova A, Gruss P (1998) Pax6 controls radial glia differentiation in the cerebral cortex. Neuron 21:1031–1044
Heins N, Malatesta P, Cecconi F, Nakafuku M, Tucker KL, Hack MA, Chapouton P, Barde YA, Gotz M (2002) Glial cells generate neurons: the role of the transcription factor Pax6. Nat Neurosci 5:308–315
Suter DM, Tirefort D, Julien S, Krause KH (2009) A Sox1 to Pax6 switch drives neuroectoderm to radial glia progression during differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 27:49–58
Maekawa M, Takashima N, Arai Y, Nomura T, Inokuchi K, Yuasa S, Osumi N (2005) Pax6 is required for production and maintenance of progenitor cells in postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis. Genes Cells 10:1001–1014
Gan Q, Lee A, Suzuki R, Yamagami T, Stokes A, Nguyen BC, Pleasure D, Wang J, Chen HW, Zhou CJ (2014) Pax6 mediates beta-catenin signaling for self-renewal and neurogenesis by neocortical radial glial stem cells. Stem Cells 32:45–58
Zhao Y, Sheng HZ, Amini R, Grinberg A, Lee E, Huang S, Taira M, Westphal H (1999) Control of hippocampal morphogenesis and neuronal differentiation by the LIM homeobox gene Lhx5. Science 284:1155–1158
Zhao T, Kraemer N, Oldekamp J, Cankaya M, Szabo N, Conrad S, Skutella T, Alvarez Bolado G (2006) Emx2 in the developing hippocampal fissure region. Eur J Neurosci 23:2895–2907
Miquelajáuregui A, Varela-Echavarría A, Ceci ML, García-Moreno F, Ricaño I, Hoang K, Frade-Pérez D, Portera-Cailliau C, Tamariz E, De Carlos JA (2010) LIM-homeobox gene Lhx5 is required for normal development of Cajal–Retzius cells. J Neurosci 30:10551–10562
Pellegrini M, Mansouri A, Simeone A, Boncinelli E, Gruss P (1996) Dentate gyrus formation requires Emx2. Development 122:3893–3898
Campbell CE, Piper M, Plachez C, Yeh YT, Baizer JS, Osinski JM, Litwack ED, Richards LJ, Gronostajski RM (2008) The transcription factor Nfix is essential for normal brain development. BMC Dev Biol 8:52
Steele-Perkins G, Plachez C, Butz KG, Yang G, Bachurski CJ, Kinsman SL, Litwack ED, Richards LJ, Gronostajski RM (2005) The transcription factor gene Nfib is essential for both lung maturation and brain development. Mol Cell Biol 25:685–698
Deneen B, Ho R, Lukaszewicz A, Hochstim CJ, Gronostajski RM, Anderson DJ (2006) The transcription factor NFIA controls the onset of gliogenesis in the developing spinal cord. Neuron 52:953–968
Mason S, Piper M, Gronostajski RM, Richards LJ (2009) Nuclear factor one transcription factors in CNS development. Mol Neurobiol 39:10–23
Betancourt J, Katzman S, Chen B (2014) Nuclear factor one B regulates neural stem cell differentiation and axonal projection of corticofugal neurons. J Comp Neurol 522:6–35
Fan X, Kim HJ, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2007) Estrogen receptor beta is essential for sprouting of nociceptive primary afferents and for morphogenesis and maintenance of the dorsal horn interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13696–13701
Xu P, Guo L, Tang X, Xu H, Fan X (2011) ERbeta may contribute to the maintaining of radial glia cells polarity through cadherins during corticogenesis. Med Hypotheses 77:974–976
Gonzalez M, Cabrera Socorro A, Perez‐Garcia CG, Fraser JD, Lopez FJ, Alonso R, Meyer G (2007) Distribution patterns of estrogen receptor α and β in the human cortex and hippocampus during development and adulthood. J Comp Neurol 503:790–802
Namihira M, Kohyama J, Abematsu M, Nakashima K (2008) Epigenetic mechanisms regulating fate specification of neural stem cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:2099–2109
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF (2009) Regulation of non-coding RNA networks in the nervous system—what’s the REST of the story? Neurosci Lett 466:73–80
Vo NK, Cambronne XA, Goodman RH (2010) MicroRNA pathways in neural development and plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20:457–465
Nowakowski TJ, Mysiak KS, Pratt T, Price DJ (2011) Functional dicer is necessary for appropriate specification of radial glia during early development of mouse telencephalon. PLoS One 6:e23013
Li Q, Bian S, Hong J, Kawase-Koga Y, Zhu E, Zheng Y, Yang L, Sun T (2011) Timing specific requirement of microRNA function is essential for embryonic and postnatal hippocampal development. PLoS One 6:e26000
Nowakowski TJ, Fotaki V, Pollock A, Sun T, Pratt T, Price DJ (2013) MicroRNA-92b regulates the development of intermediate cortical progenitors in embryonic mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:7056–7061
Nigro A, Menon R, Bergamaschi A, Clovis YM, Baldi A, Ehrmann M, Comi G, De Pietri TD, Farina C, Martino G, Muzio L (2012) MiR-30e and miR-181d control radial glia cell proliferation via HtrA1 modulation. Cell Death Dis 3:e360
Bian S, Hong J, Li Q, Schebelle L, Pollock A, Knauss JL, Garg V, Sun T (2013) MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 regulates neural stem cell expansion and transition to intermediate progenitors in the developing mouse neocortex. Cell Rep 3:1398–1406
O’Banion MK (2011) Acute neuroinflammation and neurogenesis: a role for microglial COX-1. Cell Cycle 10:3819
Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD (2003) Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 302:1760–1765
Bethesda M (2011) Cyclooxygenase-1 is involved in the inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis after lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation. Cell Cycle 10:2568–2573
Ekdahl CT, Claasen JH, Bonde S, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2003) Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:13632–13637
Ekdahl C, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2009) Brain inflammation and adult neurogenesis: the dual role of microglia. Neuroscience 158:1021–1029
Lee SW, Haditsch U, Cord BJ, Guzman R, Kim SJ, Boettcher C, Priller J, Ormerod BK, Palmer TD (2013) Absence of CCL2 is sufficient to restore hippocampal neurogenesis following cranial irradiation. Brain Behav Immun 30:33–44
Green HF, Treacy E, Keohane AK, Sullivan AM, O’Keeffe GW, Nolan YM (2012) A role for interleukin-1β in determining the lineage fate of embryonic rat hippocampal neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 49:311–321
Raman L, Kong X, Kernie SG (2013) Pharmacological inhibition of the mTOR pathway impairs hippocampal development in mice. Neurosci Lett 541:9–14
Dalmau I, Finsen B, Toender N, Zimmer J, Gonzalez B, Castellano B (1997) Development of microglia in the prenatal rat hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 377:70–84
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81371197, 31271051), Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC 2013jjB10028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Tang, X., Wang, Y. et al. Radial Glia, the Keystone of the Development of the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus. Mol Neurobiol 51, 131–141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8692-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8692-y