Abstract
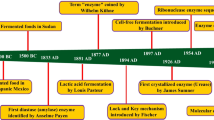
Enzymes are essential biological macromolecules, which catalyse chemical reactions and have impacted the human civilization tremendously. The importance of enzymes as biocatalyst was realized more than a century ago by eminent scientists like Kuhne, Buchner, Payen, Sumner, and the last three decades has seen exponential growth in enzyme industry, mainly due to the revolution in tools and techniques in molecular biology, biochemistry and production. This has resulted in high demand of enzymes in various applications like food, agriculture, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, environment and research sector. The cut-throat competition also pushes the enzyme industry to constantly discover newer and better enzymes regularly. The conventional methods to discover enzymes are generally costly, time consuming and have low success rate. Exploring the exponentially growing biological databases with the help of various computational tools can increase the discovering process, with less resource consumption and higher success rate. Present review discusses this approach, known as in-silico bioprospecting, which broadly involves computational searching of gene/protein databases to find novel enzymes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coker, J. A. (2016). Extremophiles and biotechnology: Current uses and prospects. F1000Research, 5, 396.
Anastas, P. T., & Warner, J. C. (1998). Green chemistry: Theory and practice. Oxford University Press: New York.
Savile, C. K., Janey, J. M., Mundorff, E. C., Moore, J. C., Tam, S., Jarvis, W. R., … Hughes, G. J. (2010). Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amines from ketones applied to sitagliptin manufacture. Science, 329(5989), 305–309.
Chamoli, M., & Pant, K. (2014). In-silico bioprospecting of the enzymes involved in the biosynthetic pathway of the alkaloid berberine and its distance study Through R. International Journal of Advanced Technology in Engineering and Science, 2(9), 165–178.
Musumeci, M. A., Lozada, M., Rial, D. V., Cormack, W. P. M., Jansson, J. K., Sjöling, S., … Dionisi, H. M. (2017). Prospecting biotechnologically-relevant monooxygenases from cold sediment metagenomes: An in silico approach. Marine Drugs, 15(4).
Tan, H., Wu, X., Xie, L., Huang, Z., Peng, W., & Gan, B. (2016). Identification and characterization of a mesophilic phytase highly resilient to high-temperatures from a fungus-garden associated metagenome. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100(5), 2225–2241.
Berón, C. M., Curatti, L., & Salerno, G. L. (2005). New strategy for identification of novel cry-type genes from bacillus thuringiensis strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(2), 761–765.
Tan, H., Wu, X., Xie, L., Huang, Z., Peng, W., & Gan, B. (2016). A novel phytase derived from an acidic peat-soil microbiome showing high stability under acidic plus pepsin conditions. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26(4), 291–301.
Shakeel, T., Gupta, M., Fatma, Z., Kumar, R., Kumar, R., Singh, R., … Yazdani, S. S. (2018). A consensus-guided approach yields a heat-stable alkane-producing enzyme and identifies residues promoting thermostability. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1–30.
Sharma, N., Thakur, N., Raj, T., Savitri, & Bhalla, T. C. (2017). Mining of microbial genomes for the novel sources of nitrilases. BioMed Research International, 2017.
Gupta, S., Singh, Y., Kumar, H., Raj, U., Rao, A. R., & Varadwaj, P. K. (2018). Identification of novel abiotic stress proteins in triticum aestivum through functional annotation of hypothetical proteins. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences, 10(1), 205–220.
Thornbury, M., Sicheri, J., Guinard, C., Mahoney, D., Routledge, F., Curry, M., … Getz, L. (2018). Discovery and Characterization of Novel Lignocellulose-Degrading Enzymes from the Porcupine Microbiome. bioRxiv, (February).
Toyama, D., de Morais, M. A. B., Ramos, F. C., Zanphorlin, L. M., Tonoli, C. C. C., Balula, A. F., et al. (2018). A novel β-glucosidase isolated from the microbial metagenome of Lake Poraquê (Amazon, Brazil). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1866(4), 569–579.
Qu, Y., Egelund, J., Gilson, P. R., Houghton, F., Gleeson, P. A., Schultz, C. J., & Bacic, A. (2008). Identification of a novel group of putative Arabidopsis thaliana β-(1,3)-galactosyltransferases. Plant Molecular Biology, 68(1–2), 43–59.
Foong, C. P., Lakshmanan, M., Abe, H., Taylor, T. D., Foong, S. Y., & Sudesh, K. (2018). A novel and wide substrate specific polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase from unculturable bacteria found in mangrove soil. Journal of Polymer Research, 25(1), 23.
Vaquero, M. E., De Eugenio, L. I., Martínez, M. J., & Barriuso, J. (2015). A novel CalB-type lipase discovered by fungal genomes mining. PLoS ONE, 10(4), 1–11.
Adam, N., & Perner, M. (2018). Novel hydrogenases from deep-sea hydrothermal vent metagenomes identified by a recently developed activity-based screen. ISME Journal, 12(5), 1225–1236.
Ferrer, M., Martínez-Martínez, M., Bargiela, R., Streit, W. R., Golyshina, O. V., & Golyshin, P. N. (2016). Estimating the success of enzyme bioprospecting through metagenomics: Current status and future trends. Microbial Biotechnology, 9(1), 22–34.
Uria, A. R., & Zilda, D. S. (2016). Metagenomics-guided mining of commercially useful biocatalysts from marine microorganisms. In Advances in Food and nutrition research.
Gasteiger, E., Hoogland, C., Gattiker, A., Duvaud, S., Wilkins, M. R., Appel, R. D., & Bairoch, A. (2005). Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. The Proteomics Protocols Handbook, 571–607.
Roumpeka, D. D., Wallace, R. J., Escalettes, F., Fotheringham, I., & Watson, M. (2017). A review of bioinformatics tools for bio-prospecting from metagenomic sequence data. Frontiers in Genetics.
Machielsen, R., Leferink, N. G. H., Hendriks, A., Brouns, S. J. J., Hennemann, H. G., Daußmann, T., & Van Der Oost, J. (2008). Laboratory evolution of Pyrococcus furiosus alcohol dehydrogenase to improve the production of (2S,5S)-hexanediol at moderate temperatures. Extremophiles, 12(4), 587–594.
Wang, N. Q., Sun, J., Huang, J., & Wang, P. (2014). Cloning, expression, and directed evolution of carbonyl reductase from Leifsonia xyli HS0904 with enhanced catalytic efficiency. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(20), 8591–8601.
Jakoblinnert, A., Wachtmeister, J., Schukur, L., Shivange, A. V., Bocola, M., Ansorge-Schumacher, M. B., & Schwaneberg, U. (2013). Reengineered carbonyl reductase for reducing methyl-substituted cyclohexanones. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 26(4), 291–298.
Hoelsch, K., Sührer, I., Heusel, M., & Weuster-Botz, D. (2013). Engineering of formate dehydrogenase: Synergistic effect of mutations affecting cofactor specificity and chemical stability. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97(6), 2473–2481.
Koudelakova, T., Chaloupkova, R., Brezovsky, J., Prokop, Z., Sebestova, E., Hesseler, M., … Damborsky, J. (2013). Engineering enzyme stability and resistance to an organic cosolvent by modification of residues in the access tunnel. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition, 52(7), 1959–1963.
Buller, A. R., Brinkmann-Chen, S., Romney, D. K., Herger, M., Murciano-Calles, J., & Arnold, F. H. (2015). Directed evolution of the tryptophan synthase β-subunit for stand-alone function recapitulates allosteric activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(47), 14599–14604.
Brinkmann-Chen, S., Flock, T., Cahn, J. K. B., Snow, C. D., Brustad, E. M., McIntosh, J. A., … Arnold, F. H. (2013). General approach to reversing ketol-acid reductoisomerase cofactor dependence from NADPH to NADH. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(27), 10946–10951.
Fox, R. J., & Huisman, G. W. (2008). Enzyme optimization: moving from blind evolution to statistical exploration of sequence-function space. Trends in Biotechnology, 26(3), 132–138.
Reetz, M. T., Rentzsch, M., Pletsch, A., Maywald, M., Maiwald, P., Peyralans, J. J. P., … Taglieber, A. (2007). Directed evolution of enantioselective hybrid catalysts: a novel concept in asymmetric catalysis. Tetrahedron, 63(28), 6404–6414.
Rubin-Pitel, S. B., Cho, C. M. H., Chen, W., & Zhao, H. (2007). Directed evolution tools in bioproduct and bioprocess development. Bioprocessing for Value-Added Products from Renewable Resources, 49–72.
Li, Y., & Cirino, P. C. (2014). Recent advances in engineering proteins for biocatalysis. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 111(7), 1273–1287.
Wang, M., Si, T., & Zhao, H. (2012). Biocatalyst development by directed evolution, Bioresource Technology, 40(6), 1301–1315.
Woodley, J. M. (2013). Protein engineering of enzymes for process applications. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 17(2), 310–316.
Zheng, G. W., & Xu, J. H. (2011). New opportunities for biocatalysis: Driving the synthesis of chiral chemicals. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 22(6), 784–792.
Lane, M. D., & Seelig, B. (2014). Advances in the directed evolution of proteins. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 22, 129–136.
Kaur, J., Kumar, A., & Kaur, J. (2018). Strategies for optimization of heterologous protein expression in E. coli: Roadblocks and reinforcements. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 106, 803–822.
Rosano, G. L., & Ceccarelli, E. A. (2014). Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Frontiers in Microbiology.
Funding
The manuscript is a review article and was not supported by any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamble, A., Srinivasan, S. & Singh, H. In-Silico Bioprospecting: Finding Better Enzymes. Mol Biotechnol 61, 53–59 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0132-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0132-1