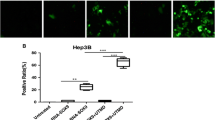
Abstract
Ultrasound-mediated microbubble destruction (sonoporation) is an efficient and safe nonviral technique for gene delivery. In the present work, we hypothesized that short hairpin RNA (shRNA) interference therapy targeting human Survivin gene could be transfected by the novel combination of ultrasound exposure (USE) and liposome microbubbles (LM). ShRNA vectors targeting Survivin were constructed and transfected under USE and LM conditions. The optimal transfection efficiency and cell injury were compared with those of polyethylenimine (PEI)-mediated transfection in different cancer cell lines (HeLa, HepG2, Ishikawa, MCF-7, and B16-F10). The effects of gene downregulation and cell apoptosis were further investigated. The results indicated that P + USE + LM group could significantly increase the gene expression as compared with plasmid group, plasmid + USE group, plasmid + LM group (P < 0.001). The transfection efficiency of the novel combination was nearly equal to PEI-mediated transfection in some cancer cell lines while the cell viability did not decrease markedly. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot analysis also confirmed that Survivin mRNA and protein expression could be knocked down significantly by shRNA transfection under USE and LM condition (P < 0.001). This is the first study to verify the role of shRNA therapy in vitro with novel combination of USE and LM. We concluded that this nonviral technique would be valuable in the gene transfection of shRNA and Survivin gene downregulation would lead to apparent cell apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoi A, Watanabe Y, Mori S, et al. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase-mediated suicide gene therapy using nano/microbubbles and ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008;34(3):425–34. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2007.09.004.
Yoon CS, Jung HS, Kim TK, et al. Comparison of the efficiency and toxicity of sonoporation with branched polyethylenimine-mediated gene transfection in various cultured cell lines. J Drug Target. 2008;16(10):773–9. doi:10.1080/10611860802470549.
Liang HD, Lu QL, Xue SA, et al. Optimisation of ultrasound-mediated gene transfer (sonoporation) in skeletal muscle cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2004;30(11):1523–9. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2004.08.021.
Newman CM, Bettinger T. Gene therapy progress and prospects: ultrasound for gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2007;14(6):465–75. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302925.
Yang F, Gu N, Chen D, et al. Experimental study on cell self-sealing during sonoporation. J Control Release. 2008;131(3):205–10. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.07.038.
Shen ZP, Brayman AA, Chen L, Miao CH. Ultrasound with microbubbles enhances gene expression of plasmid DNA in the liver via intraportal delivery. Gene Ther. 2008;15(16):1147–55. doi:10.1038/gt.2008.51.
Li YS, Reid CN, McHale AP. Enhancing ultrasound-mediated cell membrane permeabilisation (sonoporation) using a high frequency pulse regime and implications for ultrasound-aided cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2008;266(2):156–62. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.041.
Leong-Poi H, Kuliszewski MA, Lekas M, et al. Therapeutic arteriogenesis by ultrasound-mediated VEGF165 plasmid gene delivery to chronically ischemic skeletal muscle. Circ Res. 2007;101(3):295–303. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.148676.
Suzuki R, Takizawa T, Negishi Y, et al. Gene delivery by combination of novel liposomal bubbles with perfluoropropane and ultrasound. J Control Release. 2007;117(1):130–6. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.09.008.
Larina IV, Evers BM, Esenaliev RO. Optimal drug and gene delivery in cancer cells by ultrasound-induced cavitation. Anticancer Res. 2005;25(1A):149–56.
Rahim A, Taylor SL, Bush NL, et al. Physical parameters affecting ultrasound/microbubble-mediated gene delivery efficiency in vitro. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32(8):1269–79. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2006.04.014.
Meijering BD, Henning RH, Van Gilst WH, et al. Optimization of ultrasound and microbubbles targeted gene delivery to cultured primary endothelial cells. J Drug Target. 2007;15(10):664–71. doi:10.1080/10611860701605088.
Duvshani-Eshet M, Benny O, Morgenstern A, Machluf M. Therapeutic ultrasound facilitates antiangiogenic gene delivery and inhibits prostate tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6(8):2371–82. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0019.
Caplen NJ. Gene therapy progress and prospects. Downregulating gene expression: the impact of RNA interference. Gene Ther. 2004;11(16):1241–8. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302324.
McAnuff MA, Rettig GR, Rice KG. Potency of siRNA versus shRNA mediated knockdown in vivo. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96(11):2922–30. doi:10.1002/jps.20968.
Vandenbroucke RE, Lentacker I, Demeester J, De Smedt SC, Sanders NN. Ultrasound assisted siRNA delivery using PEG-siPlex loaded microbubbles. J Control Release. 2008;126(3):265–73. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.12.001.
Negishi Y, Endo Y, Fukuyama T, et al. Delivery of siRNA into the cytoplasm by liposomal bubbles and ultrasound. J Control Release. 2008;132(2):124–30. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.08.019.
Neu M, Fischer D, Kissel T. Recent advances in rational gene transfer vector design based on poly(ethylene imine) and its derivatives. J Gene Med. 2005;7(8):992–1009. doi:10.1002/jgm.773.
Ho J, Wang H, Forde GM. Process considerations related to the microencapsulation of plasmid DNA via ultrasonic atomization. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2008;101(1):172–81. doi:10.1002/bit.21876.
Weerasinghe P, Li Y, Guan Y, et al. T40214/PEI complex: a potent therapeutics for prostate cancer that targets STAT3 signaling. Prostate. 2008;68(13):1430–42. doi:10.1002/pros.20807.
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA, et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92(16):7297–301. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.16.7297.
Mehier-Humbert S, Bettinger T, Yan F, Guy RH. Ultrasound-mediated gene delivery: Kinetics of plasmid internalization and gene expression. J Control Release. 2005;104(1):203–11. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.01.011.
Chen ZY, Xie MX, Wang XF, Lü Q, Ding SW. Effects of lipid shell microbubble on ultrasound mediated EGFP gene delivery to transplanted tumors: initial experience. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol. 2008;7(7):424–8. doi:10.1007/s10330-008-0058-3.
Chen S, Ding JH, Bekeredjian R, et al. Efficient gene delivery to pancreatic islets with ultrasonic microbubble destruction technology. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(22):8469–74. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602921103.
Sangfelt SH. Apoptosis and cell growth inhibition as antitumor effector functions of interferons. Med Oncol. 2001;18(1):3–14. doi:10.1385/MO:18:1:3.
Harakeh S, Abu-El-Ardat K, Diab-Assaf M, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HTLV-1-positive and -negative leukemia cells. Med Oncol. 2008;25(1):30–9. doi:10.1007/s12032-007-0036-6.
Altieri DC. Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(1):46–54. doi:10.1038/nrc968.
Jiang G, Li J, Zeng Z, Xian L. Lentivirus-mediated gene therapy by suppressing survivin in BALB/c nude mice bearing oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006;5(4):435–40.
Caldas H, Holloway MP, Hall BM, Qualman SJ, Altura RA. Survivin-directed RNA interference cocktail is a potent suppressor of tumour growth in vivo. J Med Genet. 2006;43(2):119–28. doi:10.1136/jmg.2005.034686.
Bian AN, Gao YH, Tan KB, et al. Preparation of human hepatocellular carcinoma-targeted liposome microbubbles and their immunological properties. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(23):3424–7.
Liu P, Gao YH, Tan KB, Liu Z, Zuo S. Grey scale enhancement of rabbit liver and kidney by intravenous injection of a new lipid-coated ultrasound contrast agent. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(16):2369–72.
Siu T, Rohling RN, Chiao M. Power density requirement of a 4 MHz micro-ultrasonic transducer for sonodynamic therapy. Biomed Microdevices. 2008;10(1):89–97. doi:10.1007/s10544-007-9113-z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Liang, K., Liu, J. et al. Enhancement of survivin gene downregulation and cell apoptosis by a novel combination: liposome microbubbles and ultrasound exposure. Med Oncol 26, 491–500 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-008-9161-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-008-9161-0