Abstract
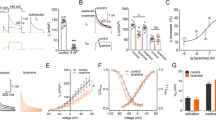
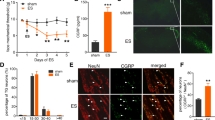
Amitriptyline (AMI), a tricyclic antidepressant, has been widely used to prevent migraine attacks and alleviate other various chronic pain, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Accumulated evidence suggests that the efficacy of AMI is related to the blockade of voltage-gated sodium channels. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of AMI on Nav1.8 currents in nociceptive trigeminal neurons and trigeminovascular nociception induced by electrical stimulation of the dura mater surrounding the superior sagittal sinus (SSS) in rats, as in the animal model of vascular headaches such as migraines. Using a whole-cell voltage recording technique, we showed that Nav1.8 currents were blocked by AMI in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 value of 6.82 μM in acute isolated trigeminal ganglion neurons of the rats. AMI caused a hyperpolarizing shift in the voltage-dependent activation and steady-state inactivation and significantly blocked in a use-dependent manner and slowed the recovery from the inactivation of Nav1.8 currents. In addition, the systemic administration of AMI and A-803467 (a selective Nav1.8 channel blocker) potently alleviated the nociceptive behaviors (head flicks and grooming) induced by the electrical stimulation of the dura mater surrounding the SSS. Taken together, our data suggest that Nav1.8 currents in nociceptive trigeminal neurons are blocked by AMI through modulating the activation and inactivation kinetics, which may contribute to anti-nociceptive effect of AMI in animal models of migraines.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguggia, M. (2012). Allodynia and migraine. Neurological Science, 33(Suppl 1), S9–S11.
Akopian, A. N., Souslova, V., England, S., Okuse, K., Ogata, N., Ure, J., et al. (1999). The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nature Neuroscience, 2(6), 541–548.
Amaya, F., Decosterd, I., Samad, T. A., Plumpton, C., Tate, S., Mannion, R. J., et al. (2000). Diversity of expression of the sensory neuron-specific TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium ion channels SNS and SNS2. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 15(4), 331–342.
Andlin-Sobocki, P., Jonsson, B., Wittchen, H. U., & Olesen, J. (2005). Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe. European Journal of Neurology, 12(Suppl 1), 1–27.
Antonova, M., Wienecke, T., Olesen, J., & Ashina, M. (2012). Prostaglandin E(2) induces immediate migraine-like attack in migraine patients without aura. Cephalalgia, 32(11), 822–833.
Arsenault, A., & Sawynok, J. (2009). Perisurgical amitriptyline produces a preventive effect on afferent hypersensitivity following spared nerve injury. Pain, 146(3), 308–314.
Atasoy, H. T., Unal, A. E., Atasoy, N., Emre, U., & Sumer, M. (2005). Low income and education levels may cause medication overuse and chronicity in migraine patients. Headache, 45(1), 25–31.
Ates, O., Kurt, S., Altinisik, J., Karaer, H., & Sezer, S. (2011). Genetic variations in tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-10 genes, and migraine susceptibility. Pain Medicine, 12(10), 1464–1469.
Barber, M. J., Starmer, C. F., & Grant, A. O. (1991). Blockade of cardiac sodium channels by amitriptyline and diphenylhydantoin. Evidence for two use-dependent binding sites. Circulation Research, 69(3), 677–696.
Bielefeldt, K., Ozaki, N., Whiteis, C., & Gebhart, G. F. (2002). Amitriptyline inhibits voltage-sensitive sodium currents in rat gastric sensory neurons. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 47(5), 959–966.
Blair, N. T., & Bean, B. P. (2002). Roles of tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Na+ current, TTX-resistant Na+ current, and Ca2+ current in the action potentials of nociceptive sensory neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 22(23), 10277–10290.
Bongenhielm, U., Nosrat, C. A., Nosrat, I., Eriksson, J., Fjell, J., & Fried, K. (2000). Expression of sodium channel SNS/PN3 and ankyrin(G) mRNAs in the trigeminal ganglion after inferior alveolar nerve injury in the rat. Experimental Neurology, 164(2), 384–395.
Cang, C. L., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y. Q., & Zhao, Z. Q. (2009). PKCepsilon-dependent potentiation of TTX-resistant Nav1.8 current by neurokinin-1 receptor activation in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Molecular Pain, 5, 33.
Chen, X., Pang, R. P., Shen, K. F., Zimmermann, M., Xin, W. J., Li, Y. Y., et al. (2011). TNF-alpha enhances the currents of voltage gated sodium channels in uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons following motor nerve injury. Experimental Neurology, 227(2), 279–286.
Cheng, K. I., Wang, H. C., Chang, L. L., Wang, F. Y., Lai, C. S., Chou, C. W., et al. (2012). Pretreatment with intrathecal amitriptyline potentiates anti-hyperalgesic effects of post-injury intra-peritoneal amitriptyline following spinal nerve ligation. BMC Neurology, 12(1), 44.
Cregg, R., Momin, A., Rugiero, F., Wood, J. N., & Zhao, J. (2010). Pain channelopathies. The Journal of Physiology, 588(Pt 11), 1897–1904.
D’Amico, D. (2010). Pharmacological prophylaxis of chronic migraine: A review of double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Neurological Science, 31(Suppl 1), S23–S28.
De Fusco, M., Marconi, R., Silvestri, L., Atorino, L., Rampoldi, L., Morgante, L., et al. (2003). Haploinsufficiency of ATP1A2 encoding the Na+/K+ pump alpha2 subunit associated with familial hemiplegic migraine type 2. Nature Genetics, 33(2), 192–196.
Dichgans, M., Freilinger, T., Eckstein, G., Babini, E., Lorenz-Depiereux, B., Biskup, S., et al. (2005). Mutation in the neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel SCN1A in familial hemiplegic migraine. Lancet, 366(9483), 371–377.
Dick, I. E., Brochu, R. M., Purohit, Y., Kaczorowski, G. J., Martin, W. J., & Priest, B. T. (2007). Sodium channel blockade may contribute to the analgesic efficacy of antidepressants. Journal of Pain, 8(4), 315–324.
Djouhri, L., Newton, R., Levinson, S. R., Berry, C. M., Carruthers, B., & Lawson, S. N. (2003). Sensory and electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig sensory neurones expressing Nav 1.7 (PN1) Na+ channel alpha subunit protein. Journal of Physiology, 546(Pt 2), 565–576.
Ducros, A. (2006). [Mechanisms and genetics of migraine]. CNS Drugs, 20 Spec no. 1, 1–11.
Ebersberger, A., Natura, G., Eitner, A., Halbhuber, K. J., Rost, R., & Schaible, H. G. (2011). Effects of prostaglandin D2 on tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ currents in DRG neurons of adult rat. Pain, 152(5), 1114–1126.
Elliott, A. A., & Elliott, J. R. (1993). Characterization of TTX-sensitive and TTX-resistant sodium currents in small cells from adult rat dorsal root ganglia. The Journal of Physiology, 463, 39–56.
Eriksson, J., Jablonski, A., Persson, A. K., Hao, J. X., Kouya, P. F., Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z., et al. (2005). Behavioral changes and trigeminal ganglion sodium channel regulation in an orofacial neuropathic pain model. Pain, 119(1–3), 82–94.
Estebe, J. P., Gentili, M. E., Le Corre, P., Le Verge, R., Moulinoux, J. P., & Ecoffey, C. (2002). Sciatic nerve block with bupivacaine-loaded microspheres prevents hyperalgesia in an inflammatory animal model. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia, 49(7), 690–693.
Fang, Z., Park, C. K., Li, H. Y., Kim, H. Y., Park, S. H., Jung, S. J., et al. (2007). Molecular basis of Ca(v)2.3 calcium channels in rat nociceptive neurons. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(7), 4757–4764.
Finnerup, N. B., Otto, M., McQuay, H. J., Jensen, T. S., & Sindrup, S. H. (2005). Algorithm for neuropathic pain treatment: An evidence based proposal. Pain, 118(3), 289–305.
Fusayasu, E., Kowa, H., Takeshima, T., Nakaso, K., & Nakashima, K. (2007). Increased plasma substance P and CGRP levels, and high ACE activity in migraineurs during headache-free periods. Pain, 128(3), 209–214.
Gerner, P., Mujtaba, M., Sinnott, C. J., & Wang, G. K. (2001). Amitriptyline versus bupivacaine in rat sciatic nerve blockade. Anesthesiology, 94(4), 661–667.
Gold, M. S., Levine, J. D., & Correa, A. M. (1998). Modulation of TTX-R INa by PKC and PKA and their role in PGE2-induced sensitization of rat sensory neurons in vitro. The Journal of Neuroscience, 18(24), 10345–10355.
Hille, B. (1977). Local anesthetics: Hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. The Journal of General Physiology, 69(4), 497–515.
Hur, Y. K., Choi, I. S., Cho, J. H., Park, E. J., Choi, J. K., Choi, B. J., et al. (2008). Effects of carbamazepine and amitriptyline on tetrodotoxinresistant Na+ channels in immature rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 31(2), 178–182.
Ishii, Y., & Sumi, T. (1992). Amitriptyline inhibits striatal efflux of neurotransmitters via blockade of voltage-dependent Na+ channels. European Journal of Pharmacology, 221(2–3), 377–380.
Jang, M. U., Park, J. W., Kho, H. S., Chung, S. C., & Chung, J. W. (2011). Plasma and saliva levels of nerve growth factor and neuropeptides in chronic migraine patients. Oral Diseases, 17(2), 187–193.
Jarvis, M. F., Honore, P., Shieh, C. C., Chapman, M., Joshi, S., Zhang, X. F., et al. (2007). A-803467, a potent and selective Nav1.8 sodium channel blocker, attenuates neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(20), 8520–8525.
Joshi, S. K., Honore, P., Hernandez, G., Schmidt, R., Gomtsyan, A., Scanio, M., et al. (2009). Additive antinociceptive effects of the selective Nav1.8 blocker A-803467 and selective TRPV1 antagonists in rat inflammatory and neuropathic pain models. Journal of Pain, 10(3), 306–315.
Joshi, S. K., Mikusa, J. P., Hernandez, G., Baker, S., Shieh, C. C., Neelands, T., et al. (2006). Involvement of the TTX-resistant sodium channel Nav 1.8 in inflammatory and neuropathic, but not post-operative, pain states. Pain, 123(1–2), 75–82.
Kerr, B. J., Souslova, V., McMahon, S. B., & Wood, J. N. (2001). A role for the TTX-resistant sodium channel Nav 1.8 in NGF-induced hyperalgesia, but not neuropathic pain. NeuroReport, 12(14), 3077–3080.
Kwiecinski, H. (2005). Is migraine a neuronal channelopothy? Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska, 39(4 Suppl 1), S61–S64.
Lai, J., Gold, M. S., Kim, C. S., Bian, D., Ossipov, M. H., Hunter, J. C., et al. (2002). Inhibition of neuropathic pain by decreased expression of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel, NaV1.8. Pain, 95(1–2), 143–152.
Laird, J. M., Souslova, V., Wood, J. N., & Cervero, F. (2002). Deficits in visceral pain and referred hyperalgesia in Nav1.8 (SNS/PN3)-null mice. The Journal of Neuroscience, 22(19), 8352–8356.
Leffler, A., Reiprich, A., Mohapatra, D. P., & Nau, C. (2007). Use-dependent block by lidocaine but not amitriptyline is more pronounced in tetrodotoxin (TTX)-Resistant Nav1.8 than in TTX-sensitive Na+ channels. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 320(1), 354–364.
Liang, J., Liu, X., Zheng, J., & Yu, S. (2013). Effect of amitriptyline on tetrodotoxin-resistant Nav1.9 currents in nociceptive trigeminal neurons. Molecular Pain, 9(1), 31.
Liang, J., Yu, S., Dong, Z., Wang, X., Liu, R., Chen, X., et al. (2011). The effects of OB-induced depression on nociceptive behaviors induced by electrical stimulation of the dura mater surrounding the superior sagittal sinus. Brain Research, 1424, 9–19.
Matthews, E. A., Wood, J. N., & Dickenson, A. H. (2006). Na(v) 1.8-null mice show stimulus-dependent deficits in spinal neuronal activity. Molecular Pain, 2, 5.
McGaraughty, S., Chu, K. L., Scanio, M. J., Kort, M. E., Faltynek, C. R., & Jarvis, M. F. (2008). A selective Nav1.8 sodium channel blocker, A-803467 [5-(4-chlorophenyl-N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)furan-2-carboxamide], attenuates spinal neuronal activity in neuropathic rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 324(3), 1204–1211.
McGowan, E., Hoyt, S. B., Li, X., Lyons, K. A., & Abbadie, C. (2009). A peripherally acting Na(v)1.7 sodium channel blocker reverses hyperalgesia and allodynia on rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 109(3), 951–958.
Mert, T., & Gunes, Y. (2012). Antinociceptive activities of lidocaine and the nav1.8 blocker a803467 in diabetic rats. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science, 51(5), 579–585.
Moon, J. Y., Song, S., Yoon, S. Y., Roh, D. H., Kang, S. Y., Park, J. H., et al. (2012). The differential effect of intrathecal Nav1.8 blockers on the induction and maintenance of capsaicin- and peripheral ischemia-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 114(1), 215–223.
Moskowitz, M. A. (1984). The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Annals of Neurology, 16(2), 157–168.
Moskowitz, M. A. (1991). The visceral organ brain: Implications for the pathophysiology of vascular head pain. Neurology, 41(2 (Pt 1)), 182–186.
Natura, G., von Banchet, G. S., & Schaible, H. G. (2005). Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances TTX-resistant sodium currents in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons from adult rats. Pain, 116(3), 194–204.
Nau, C., Seaver, M., Wang, S. Y., & Wang, G. K. (2000). Block of human heart hH1 sodium channels by amitriptyline. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 292(3), 1015–1023.
Olesen, J., Burstein, R., Ashina, M., & Tfelt-Hansen, P. (2009). Origin of pain in migraine: Evidence for peripheral sensitisation. The Lancet Neurology, 8(7), 679–690.
Ophoff, R. A., Terwindt, G. M., Vergouwe, M. N., van Eijk, R., Oefner, P. J., Hoffman, S. M., et al. (1996). Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell, 87(3), 543–552.
Pancrazio, J. J., Kamatchi, G. L., Roscoe, A. K., & Lynch, C, 3rd. (1998). Inhibition of neuronal Na+ channels by antidepressant drugs. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 284(1), 208–214.
Parada, C. A., Vivancos, G. G., Tambeli, C. H., Cunha, F. Q., & Ferreira, S. H. (2003). Activation of presynaptic NMDA receptors coupled to NaV1.8-resistant sodium channel C-fibers causes retrograde mechanical nociceptor sensitization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(5), 2923–2928.
Park, C. K., Bae, J. H., Kim, H. Y., Jo, H. J., Kim, Y. H., Jung, S. J., et al. (2010). Substance P sensitizes P2X3 in nociceptive trigeminal neurons. Journal of Dental Research, 89(10), 1154–1159.
Porreca, F., Lai, J., Bian, D., Wegert, S., Ossipov, M. H., Eglen, R. M., et al. (1999). A comparison of the potential role of the tetrodotoxin-insensitive sodium channels, PN3/SNS and NaN/SNS2, in rat models of chronic pain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(14), 7640–7644.
Renganathan, M., Cummins, T. R., & Waxman, S. G. (2001). Contribution of Na(v)1.8 sodium channels to action potential electrogenesis in DRG neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 86(2), 629–640.
Rogawski, M. A., & Loscher, W. (2004). The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs for the treatment of nonepileptic conditions. Nature Medicine, 10(7), 685–692.
Rush, A. M., Craner, M. J., Kageyama, T., Dib-Hajj, S. D., Waxman, S. G., & Ranscht, B. (2005). Contactin regulates the current density and axonal expression of tetrodotoxin-resistant but not tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in DRG neurons. European Journal of Neuroscience, 22(1), 39–49.
Schwedt, T. J., Krauss, M. J., Frey, K., & Gereau, R. W. (2011). Episodic and chronic migraineurs are hypersensitive to thermal stimuli between migraine attacks. Cephalalgia, 31(1), 6–12.
Sleeper, A. A., Cummins, T. R., Dib-Hajj, S. D., Hormuzdiar, W., Tyrrell, L., Waxman, S. G., et al. (2000). Changes in expression of two tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels and their currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons after sciatic nerve injury but not rhizotomy. Journal of Neuroscience, 20(19), 7279–7289.
Smitherman, T. A., Walters, A. B., Maizels, M., & Penzien, D. B. (2010). The use of antidepressants for headache prophylaxis. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 17(5), 462–469.
Song, J. H., Ham, S. S., Shin, Y. K., & Lee, C. S. (2000). Amitriptyline modulation of Na(+) channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. European Journal of Pharmacology, 401(3), 297–305.
Steiner, T. J., Stovner, L. J., & Birbeck, G. L. (2013). Migraine: The seventh disabler. Journal of Headache Pain, 14(1), 1.
Sudoh, Y., Cahoon, E. E., Gerner, P., & Wang, G. K. (2003). Tricyclic antidepressants as long-acting local anesthetics. Pain, 103(1–2), 49–55.
Sung, B., & Wang, G. K. (2004). Peripherally administered amitriptyline derivatives have differential anti-allodynic effects in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience Letters, 357(2), 115–118.
Suter, M. R., Kirschmann, G., Laedermann, C. J., Abriel, H., & Decosterd, I. (2013). Rufinamide attenuates mechanical allodynia in a model of neuropathic pain in the mouse and stabilizes voltage-gated sodium channel inactivated state. Anesthesiology, 118(1), 160–172.
Tarnawa, I., Bolcskei, H., & Kocsis, P. (2007). Blockers of voltage-gated sodium channels for the treatment of central nervous system diseases. Recent Patents on CNS Drug Discovery, 2(1), 57–78.
Tepper, S. J., Rapoport, A., & Sheftell, F. (2001). The pathophysiology of migraine. Neurologist, 7(5), 279–286.
Thorstrand, C., Bergstrom, J., & Castenfors, J. (1976). Cardiac effects of amitriptyline in rats. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation, 36(1), 7–15.
Veneroni, O., Maj, R., Calabresi, M., Faravelli, L., Fariello, R. G., & Salvati, P. (2003). Anti-allodynic effect of NW-1029, a novel Na(+) channel blocker, in experimental animal models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain, 102(1–2), 17–25.
Villarreal, C. F., Sachs, D., Cunha, F. Q., Parada, C. A., & Ferreira, S. H. (2005). The role of Na(V)1.8 sodium channel in the maintenance of chronic inflammatory hypernociception. Neuroscience Letters, 386(2), 72–77.
Wang, G. K., Russell, C., & Wang, S. Y. (2004). State-dependent block of voltage-gated Na+ channels by amitriptyline via the local anesthetic receptor and its implication for neuropathic pain. Pain, 110(1–2), 166–174.
Weir, G. A., & Cader, M. Z. (2011). New directions in migraine. BMC Medicine, 9, 116.
Wu, W., Ye, Q., Wang, W., Yan, L., Wang, Q., Xiao, H., et al. (2012). Amitriptyline modulates calcium currents and intracellular calcium concentration in mouse trigeminal ganglion neurons. Neuroscience Letters, 506(2), 307–311.
Yan, L., Wang, Q., Fu, Q., Ye, Q., Xiao, H., & Wan, Q. (2010). Amitriptyline inhibits currents and decreases the mRNA expression of voltage-gated sodium channels in cultured rat cortical neurons. Brain Research, 1336, 1–9.
Yu, S., He, M., Liu, R., Feng, J., Qiao, X., Yang, X., et al. (2013). Headache yesterday in China: A new approach to estimating the burden of headache, applied in a general-population survey in China. Cephalalgia, 33(15), 1211–1217.
Yu, S., Liu, R., Zhao, G., Yang, X., Qiao, X., Feng, J., et al. (2012). The prevalence and burden of primary headaches in China: A population-based door-to-door survey. Headache, 52(4), 582–591.
Yu, Y., Zhao, F., Guan, S., & Chen, J. (2011). Antisense-mediated knockdown of Na(V)1.8, but not Na(V)1.9, generates inhibitory effects on complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain in rat. PLoS One, 6(5), e19865.
Zahradnik, I., Minarovic, I., & Zahradnikova, A. (2008). Inhibition of the cardiac L-type calcium channel current by antidepressant drugs. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 324(3), 977–984.
Zimmermann, K., Leffler, A., Babes, A., Cendan, C. M., Carr, R. W., Kobayashi, J., et al. (2007). Sensory neuron sodium channel Nav1.8 is essential for pain at low temperatures. Nature, 447(7146), 855–858.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30970417 and 81171058) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20100481477).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jingyao Liang and Xiaoyan Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Liu, X., Pan, M. et al. Blockade of Nav1.8 Currents in Nociceptive Trigeminal Neurons Contributes to Anti-trigeminovascular Nociceptive Effect of Amitriptyline. Neuromol Med 16, 308–321 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8282-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8282-6