Abstract
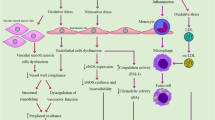
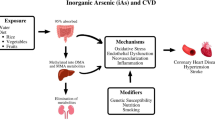
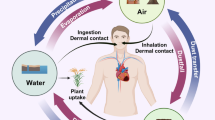
The incidence of arsenic toxicity has been observed in various countries including Taiwan, Bangladesh, India, Argentina, Australia, Chile, China, Hungary, Peru, Thailand, Mexico and United States of America. Arsenic is a ubiquitous element present in drinking water, and its exposure is associated with various cardiovascular disorders. Arsenic exposure plays a key role in the pathogenesis of vascular endothelial dysfunction as it inactivates endothelial nitric oxide synthase, leading to reduction in the generation and bioavailability of nitric oxide. In addition, the chronic arsenic exposure induces high oxidative stress, which may affect the structure and function of cardiovascular system. Further, the arsenic exposure has been noted to induce atherosclerosis by increasing the platelet aggregation and reducing fibrinolysis. Moreover, arsenic exposure may cause arrhythmia by increasing the QT interval and accelerating the cellular calcium overload. The chronic exposure to arsenic upregulates the expression of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule and vascular endothelial growth factor to induce cardiovascular pathogenesis. The present review critically discussed the detrimental role of arsenic in the cardiovascular system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nuntharatanapong, N., Chen, K., Sinhaseni, P., & Keaney, J. F. (2005). EGF receptor-dependent JNK activation is involved in arsenite-induced p21Cip1/Waf1 upregulation and endothelial apoptosis. American Journal of Physiology, Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 289(1), H99–H107.
Yousef, M. I., El-Demerdash, F. M., & Radwan, F. M. E. (2008). Sodium arsenite induced biochemical perturbations in rats: Ameliorating effect of curcumin. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 46(11), 3506–3511.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta, 58(1), 201–235.
Meharg, A. A., & Hartley-Whitaker, J. (2002). Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and nonresistant plant species. New Phytologist, 154(1), 29–43.
Tseng, C. H. (2008). Cardiovascular disease in arsenic-exposed subjects living in the arseniasis-hyperendemic areas in Taiwan. Atherosclerosis, 199(1), 12–18.
Ghosh, P., Roy, C., Das, N. K., & Sengupta, S. R. (2008). Epidemiology and prevention of chronic arsenicosis: An Indian perspective. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, 74(6), 582–593.
Chakraborti, D., Das, B., Rahman, M. M., Chowdhury, U. K., Biswas, B., Goswami, A. B., et al. (2009). Status of groundwater arsenic contamination in the state of West Bengal, India: A 20-year study report. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 53(5), 542–551.
Andrew, A. S., Jewell, D. A., Mason, R. A., Whitfield, M. L., Moore, J. H., & Karagas, M. R. (2008). Drinking-water arsenic exposure modulates gene expression in human lymphocytes from a U.S. population. Environmental Health Perspectives, 116(4), 524–531.
Lee, M. Y., Jung, B. I., Chung, S. M., Bae, O. N., Lee, J. Y., Park, J. D., et al. (2003). Arsenic-induced dysfunction in relaxation of blood vessels. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111(4), 513–517.
Kwok, R. K. (2007). A review and rationale for studying the cardiovascular effects of drinking water arsenic in women of reproductive age. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 222(3), 344–350.
Balakumar, P., Koladiya, R. U., Ramasamy, S., Rathinavel, A., & Singh, M. (2008). Pharmacological interventions to prevent vascular endothelial dysfunction: Future directions. Journal of Health Science, 54(1), 1–16.
Quyyumi, A. A. (1998). Endothelial function in health and disease: New insights into the genesis of cardiovascular disease. The American Journal of Medicine, 105(1), 32S–39S.
Schalkwijk, C. G., & Stehouwer, C. D. A. (2005). Vascular complications in diabetes mellitus: The role of endothelial dysfunction. Clinical Sciences, 109(2), 143–159.
Balakumar, P., Sharma, R., & Singh, M. (2008). Benfotiamine attenuates nicotine and uric acid-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction in rats. Pharmacological Research, 58(5–6), 356–363.
Balakumar, P., Chakkarwar, V. A., Krishan, P., & Singh, M. (2009). Vascular endothelial dysfunction: A tug of war in diabetic nephropathy? Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 63(3), 171–179.
Grabczewska, Z., Thews, M., Goralczyk, K., & Kubica, J. (2007). Endothelial function in patients with chest pain and normal coronary angiograms. Kardiologia Polska, 65(10), 1199–1206.
Desjardins, F., & Balligand, J. L. (2006). Nitric oxide-dependent endothelial function and cardiovascular disease. Acta Clinica Belgica, 61(6), 326–334.
Kawashima, S. (2004). The two faces of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. Endothelium, 11(2), 99–107.
Kawashima, S., & Yokoyama, M. (2004). Dysfunction of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 24(6), 998–1005.
Balakumar, P., Kaur, T., & Singh, M. (2008). Potential target sites to modulate vascular endothelial dysfunction: Current perspectives and future directions. Toxicology, 245(1–2), 49–64.
Cai, H., & Harrison, D. G. (2000). Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The role of oxidant stress. Circulation Research, 87(10), 840–844.
Balakumar, P., Jindal, S., Shah, D. I., & Singh, M. (2007). Experimental models for vascular endothelial dysfunction. Trends in Medical Research, 2(1), 12–20.
Balakumar, P., & Kaur, J. (2009). Is nicotine a key player or spectator in the induction and progression of cardiovascular disorders? Pharmacological Research, 60(5), 361–368.
Davignon, J., & Ganz, P. (2004). Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation, 109(23), III27–III32.
Savoia, C., & Schiffrin, E. L. (2007). Vascular inflammation in hypertension and diabetes: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Clinical Science, 112(7), 375–384.
Balakumar, P., Chakkarwar, V. A., & Singh, M. (2009). Ameliorative effect of combination of benfotiamine and fenofibrate in diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction and nephropathy in the rat. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 320(1–2), 149–162.
Tsou, T. C., Yeh, S. C., Tsai, E. M., Tsai, F. Y., Chao, H. R., & Chang, L. W. (2005). Arsenite enhances tumor necrosis factor-α-induced expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 209(1), 10–18.
Smith, K. R., Klei, L. R., & Barchowsky, A. (2001). Arsenite stimulates plasma membrane NADPH oxidase in vascular endothelial cells. American Journal Physiology Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 280(3), 442–449.
Bunderson, M., Coffin, J. D., & Beall, H. D. (2002). Arsenic induces peroxynitrite generation and cyclooxygenase-2 protein expression in aortic endothelial cells: Possible role in atherosclerosis. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 184(1), 11–18.
Chen, S. C., Tsai, M. H., Wang, H. J., Yu, H. S., & Chang, L. W. (2007). Involvement of substance P and neurogenic inflammation in arsenic-induced early vascular dysfunction. Toxicological Sciences, 95(1), 82–88.
Bae, O. N., Lim, K. M., Noh, J. Y., Chung, S. M., Kim, H., Lee, C. R., et al. (2007). Arsenite-enhanced procoagulant activity through phosphatidylserine exposure in platelets. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 20(12), 1760–1768.
Tsai, S. H., Hsieha, M. S., Chenb, L., Liang, Y. C., Linb, J. K., & Lin, S. Y. (2001). Suppression of fas ligand expression on endothelial cells by arsenite through reactive oxygen species. Toxicology, 123(1), 11–19.
Balakumar, P., Jindal, S., & Singh, M. (2007). Novel use of uric acid and sodium arsenite to induce vascular endothelial dysfunction in rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2(5), 437–446.
Jindal, S., Singh, M., & Balakumar, P. (2008). Effect of bis (maltolato) oxovanadium in uric acid and sodium arsenite-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction in rats. International Journal of Cardiology, 128(3), 383–391.
Tseng, C. H. (2002). An overview on peripheral vascular disease in blackfoot disease-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Angiology, 53(5), 529–537.
Yang, H. T., Chou, H. J., Han, B. C., & Huang, S. Y. (2007). Lifelong inorganic arsenic compounds consumption affected blood pressure in rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 45(12), 2479–2487.
Germolec, D. R., Spalding, J., Boorman, G. A., Wilmer, J. L., Yoshida, T., Simeonova, P. P., et al. (1997). Arsenic can mediate skin neoplasia by chronic stimulation of keratinocyte-derived growth factors. Mutation Research, 386(3), 209–218.
Kitchin, K. T. (2001). Recent advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: Modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 172(3), 249–261.
Sun, X., Pi, J., Liu, W., Hudson, L. G., Liu, K. J., & Feng, C. (2009). Induction of heme oxygenase 1 by arsenite inhibits cytokine-induced monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 236(2), 202–209.
Lee, P. C., Ho, I. C., & Lee, T. C. (2005). Oxidative stress mediates sodium arsenite-induced expression of heme oxygenase-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and interleukin-6 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Toxicological Sciences, 85(1), 541–550.
Yeh, J. Y., Cheng, L. C., Ou, B. R., Whanger, P. D., & Chang, L. W. (2002). Differential influences of various arsenic compounds on glutathione redox status and antioxidative enzymes in porcine endothelial cells. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 59(11), 1972–1982.
Barchowsky, A., Dudeka, E. J., Treadwellb, M. D., & Wetterhahn, K. E. (1996). Arsenic induces oxidant stress and NF-KB activation in cultured aortic endothelial cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 21(6), 783–790.
Simeonova, P. P., Wang, S., Toriuma, W., Kommineni, V., Matheson, J., & Unimye, N. (2000). Arsenic mediates cell proliferation and gene expression in the bladder epithelium: Association with activating protein-1 transactivation. Cancer Research, 60(13), 3445–3453.
Simeonova, P. P., Hulderman, T., Harki, D., & Luster, M. I. (2003). Arsenic exposure accelerates atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E−/− mice. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111(14), 1744–1748.
Jiang, S. J., Lin, T. M., Wu, H. L., Han, H. S., & Shi, G. Y. (2002). Decrease of fibrinolytic activity in human endothelial cells by arsenite. Thrombosis Research, 105(1), 55–62.
Fujiwara, Y., Nasake, Y., & Kaji, T. (2005). Sodium arsenite inhibits proteoglycan synthesis by vascular endothelial cells in culture. Journal of Health Sciences, 51(4), 461–468.
Lee, M. Y., Bae, O. N., Chung, S. M., Kang, K. T., Lee, J. Y., & Chung, J. H. (2002). Enhancement of platelet aggregation and thrombus formation by arsenic in drinking water: A contributing factor to cardiovascular disease. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 179(2), 83–88.
Wu, H. L., Yang, W. H., Wang, M. Y., & Shi, G. Y. (1993). Impaired fibrinolysis in patients with blackfoot disease. Thrombosis Research, 72(3), 211–218.
Kwok, R. K., Mendola, P., Liu, Z. Y., Savitz, D. A., Heiss, G., Ling, H. L., et al. (2007). Drinking water arsenic exposure and blood pressure in healthy women of reproductive age in Inner Mongolia, China. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 222(3), 337–343.
Lee, M. Y., Lee, Y. H., Lim, K. M., Chung, S. M., Bae, O. N., Kim, H., et al. (2005). Inorganic arsenite potentiates vasoconstriction through calcium sensitization in vascular smooth muscle. Environmental Health Perspectives, 113(10), 1330–1335.
Loyke, H. F. (2002). Effects of elements in human blood pressure control. Biological Trace Element Research, 85(3), 193–209.
Carmignani, M., Boscolo, P., & Iannacco, A. (1983). Effects of chronic exposure to arsenate on the cardiovascular function of rats. British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 40(3), 280–284.
Carmignani, M., Boscolo, P., & Castellino, N. (1985). Metabolic fate and cardiovascular effects of arsenic in rats and rabbits chronically exposed to trivalent and pentavalent arsenic. Archives of Toxicology Supplement, 8, 452–455.
Park, T.-G., Seong, Y. J., Suk, K. H., Ha, J.-H., & Kim, I. K. (2005). Enhanced contractility of vascular smooth muscle after brief exposure to arsenate. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 19(2), 305–311.
Soucy, N. V., Mayka, D., Klei, L. R., Nemec, A. A., Bauer, J. A., & Barchowsk, A. (2005). Neovascularization and angiogenic gene expression following chronic arsenic exposure in mice. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 5(1), 29–41.
Li, D., Lu, C., Wang, J., Hu, W., Cao, Z., Sun, D., et al. (2009). Developmental mechanisms of arsenite toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Aquatic Toxicology, 91(3), 229–237.
Ficker, E., Kuryshev, Y. A., Dennis, A. T., Obejero-Paz, C., Wang, L., Hawryluk, P., et al. (2004). Mechanisms of arsenic-induced prolongation of cardiac repolarization. Molecular Pharmacology, 66(1), 33–44.
Chen, C. J., Chiou, H. Y., Chiang, M. H., Lin, L. J., & Tai, T. Y. (1996). Dose–response relationship between ischemic heart disease mortality and long-term arsenic exposure. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 16(4), 504–510.
Tseng, C. H., Chong, C. K., Tseng, C. P., Hsueh, Y. M., Chiou, H. Y., Tseng, C. C., et al. (2003). Long-term arsenic exposure and ischemic heart disease in arseniasis-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Toxicology Letters, 137(1–2), 15–21.
Benowitz, N. L. (1992). Cardiotoxicity in the workplace. Occupational Medicine, 7(3), 465–478.
Goldsmith, S., & From, A. H. (1980). Arsenic-induced atypical ventricular tachycardia. The New England Journal of Medicine, 303(19), 1096–1098.
Manna, P., Sinha, M., & Sil, P. C. (2008). Arsenic-induced oxidative myocardial injury: Protective role of arjunolic acid. Archives of Toxicology, 82(3), 137–149.
Li, W. F., Sun, C. W., Cheng, T. J., Chang, K. H., Chen, C. J., & Wang, S. L. (2009). Risk of carotid atherosclerosis is associated with low serum paraoxonase (PON1) activity among arsenic exposed residents in southwestern Taiwan. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 236(2), 246–253.
Wang, J. P., Wang, S. L., Lin, Q., Zhang, L., Huang, D., & Ng, J. C. (2009). Association of arsenic and kidney dysfunction in people with diabetes and validation of its effects in rats. Environmental International, 35(3), 507–511.
Liu, J., Liu, Y., Habeebu, S. M., Waalkes, M. P., & Klaassen, C. D. (2000). Chronic combined exposure to cadmium and arsenic exacerbates nephrotoxicity, particularly in metallothionein-I/II null mice. Toxicology, 147(3), 157–166.
Navas-Acien, A., Silbergeld, E. K., Pastor-Barriuso, R., & Guallar, E. (2008). Arsenic exposure and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in US adults. The Journal of American Medical Association, 300(7), 814–822.
Rahman, M., Tondel, M., Ahmad, S. A., & Axelson, O. (1998). Diabetes mellitus associated with arsenic exposure in Bangladesh. American Journal of Epidemiology, 148(2), 198–203.
Tseng, C. H., Tai, T. Y., Chong, C. K., Tseng, C. P., Lai, M. S., Lin, B. J., et al. (2000). Long-term arsenic exposure and incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: A cohort study in arseniasis-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Environmental Health Perspectives, 108(9), 847–851.
Wang, S. L., Chiou, J. M., Chen, C. J., Tseng, C. H., Chou, W. L., Wang, C. C., et al. (2003). Prevalence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and related vascular diseases in southwestern arseniasis-endemic and nonendemic areas in Taiwan. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111(2), 155–159.
Izquierdo-Vega, J. A., Soto, C. A., Sanchez-Pena, L. C., De Vizcaya-Ruiz, A., & Del Razo, L. M. (2006). Diabetogenic effects and pancreatic oxidative damage in rats subchronically exposed to arsenite. Toxicology Letters, 160(2), 135–142.
Diaz-Villasenor, A., Burns, A. L., Salazar, A. M., Sordo, M., Hiriart, M., Cebrian, M. E., et al. (2008). Arsenite reduces insulin secretion in rat pancreatic β-cells by decreasing the calcium-dependent calpain-10 proteolysis of SNAP-25. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 231(3), 291–299.
Buchet, J. P., Heilier, J. F., Bernard, A., Lison, D., Jin, T., Wu, X., et al. (2003). Urinary protein excretion in humans exposed to arsenic and cadmium. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 76(2), 111–120.
Hong, F., Jin, T., & Zhang, A. (2004). Risk assessment on renal dysfunction caused by co-exposure to arsenic and cadmium using benchmark dose calculation in a Chinese population. BioMetals, 17(5), 573–580.
Nordberg, G. F., Jin, T., Hong, F., Zhang, A., Buchet, J. P., & Bernard, A. (2005). Biomarkers of cadmium and arsenic interactions. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 206(2), 191–197.
Banerjee, P., Bhattacharyya, S. S., Bhattacharjee, N., Pathak, S., Boujedaini, N., Belon, P., et al. (2009). Ascorbic acid combats arsenic-induced oxidative stress in mice liver. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72(2), 639–649.
Ramanathan, K., Balakumar, B. S., & Panneerselvam, C. (2002). Effects of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol on arsenic-induced oxidative stress. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 21(12), 675–680.
Mukherjee, S., Das, D., Mukherjee, M., Das, A. S., & Mitra, C. (2006). Synergistic effect of folic acid and vitamin B12 in ameliorating arsenic-induced oxidative damage in pancreatic tissue of rat. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 17(5), 319–327.
Wang, J. H., Redmond, H. P., Watson, R. W., Condron, C., & Bouchier-Hayes, D. (1996). The beneficial effect of taurine on the prevention of human endothelial cell death. Shock, 6(5), 331–338.
Sinha, M., Manna, P., & Sil, P. C. (2008). Arjunolic acid attenuates arsenic-induced nephrotoxicity. Pathophysiology, 15(3), 147–156.
Zhao, X. Y., Li, G. Y., Liu, Y., Chai, L. M., Chen, J. X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2008). Resveratrol protects against arsenic trioxide-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. British Journal of Pharmacology, 154(1), 105–113.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to Shri. Parveen Garg Ji, Honorable Chairman, ISF College of Pharmacy, Moga, Punjab, India for his inspiration and constant support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balakumar, P., Kaur, J. Arsenic Exposure and Cardiovascular Disorders: An Overview. Cardiovasc Toxicol 9, 169–176 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-009-9050-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-009-9050-6