Abstract
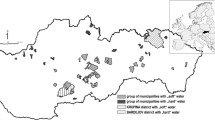
In order to determine the spatial variation of longevity population and elements contained in the drinking water of longevity region in Jiangjin and investigate the relationship between the elements in drinking water and longevity, population censuses on township level and 98 drinking water samples from Jiangjin District, Chongqing City in West China were collected and analyzed. Population statistics on township level showed that the number of centenarians per 100,000 inhabitants (OC), centenarity index (CI), and number of centenarians per 10,000 over 65-year-old subjects (UC) present obvious geographic distribution properties, generally Central region > Northern region > Southern region (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.05). Moderate hard water (150 mg/L < total hardness (TH) = 156.17 mg/L < 300 mg/L) was mainly found in drinking water from longevity township (OC > 7.5) in Jiangjin District, whereas soft water (75 mg/L < TH = 111.23 mg/L < 150 mg/L) was mostly in non-longevity township (OC < 7.5). The mean concentration of strontium (Sr) (0.73 mg/L) in drinking water from the longevity township was apparently higher than that of non-longevity township (0.44 mg/L) (Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.019 < 0.05). The concentrations of Ba, Li, Mn, Ni, and Se in drinking water from longevity township were also higher than those of non-longevity township (Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.05). The research indicates that exercising strict control over the concentrations of TH, Sr, Ba, Li, Mn, Ni, and Se in drinking water might be good for the health and prolong people’s life.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ljungquist B, Berg S, Lanke J, McClearn GE, Pedersen NL (1998) The effect of genetic factors for longevity: a comparison of identical and fraternal twins in the Swedish Twin Registry. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Med Sci 53(6):M441–M446
Kirkwood TB (2005) Understanding the odd science of aging. Cell 120(4):437–447
Pope CA III, Ezzati M, Dockery DW (2013) Fine particulate air pollution and life expectancies in the United States: the role of influential observations. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 63(2):129–132
Liu Y-L, Luo K-L, Lin X-X, Gao X, Ni R-X, Wang S-B, Tian X-L (2014) Regional distribution of longevity population and chemical characteristics of natural water in Xinjiang, China. Sci Total Environ 473:54–62
Wang S, Luo K, Liu Y (2015) Spatio-temporal distribution of human lifespan in China. Sci Rep 5:832–846
Huang B, Zhao Y, Sun W, Yang R, Gong Z, Zou Z, Ding F, Su J (2009) Relationships between distributions of longevous population and trace elements in the agricultural ecosystem of Rugao County, Jiangsu, China. Environ Geochem Health 31(3):379–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9177-6
Pes GM, Tolu F, Poulain M, Errigo A, Masala S, Pietrobelli A, Battistini N, Maioli M (2013) Lifestyle and nutrition related to male longevity in Sardinia: an ecological study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 23(3):212–219
Hamilton EI, Minski MJ, Cleary JJ (1973) The concentration and distribution of some stable elements in healthy human tissues from the United Kingdom: an environment study. Sci Total Environ 1:341–374
Luo K, Liu Y, Li H (2012) Fluoride content and distribution pattern in groundwater of eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou, China. Environ Geochem Health 34(1):89–101
Lin N, Tang J, Bian J (2004) Geochemical environment and health problems in China. Environ Geochem Health 26(1):81–88
Lv J, Wang W, Krafft T, Li Y, Zhang F, Yuan F (2011) Effects of several environmental factors on longevity and health of the human population of Zhongxiang, Hubei, China. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(2):702–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8914-8
Li X, Liu Z, Yao Y, Y-m L, Guo D-m JW, Wu G-r, Li Z, Gao X-b (2016) Comparison of the mineral elements in drinking water between Mengshan longevity district and Jinan city. Trace Elements and Electrolytes 33(07):116–119. https://doi.org/10.5414/tex01425
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Keller WD (1978) Drinking water: a geochemical factor in human health. Geol Soc Am Bull 89(3):334. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1978)89<334:dwagfi>2.0.co;2
Webster J, Brown K, Vincent W (1994) Geochemical processes affecting meltwater chemistry and the formation of saline ponds in the Victoria Valley and Bull Pass region, Antarctica. Hydrobiologia 281(3):171–186
Ritter L, Solomon K, Sibley P, Hall K, Keen P, Mattu G, Linton B (2002) Sources, pathways, and relative risks of contaminants in surface water and groundwater: a perspective prepared for the Walkerton inquiry. J Toxic Environ Health A 65(1):1–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/152873902753338572
Fraga CG (2005) Relevance, essentiality and toxicity of trace elements in human health. Mol Asp Med 26(4):235–244
Villaescusa I, Bollinger J-C (2008) Arsenic in drinking water: sources, occurrence and health effects (a review). Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7(4):307–323
Mandinic Z, Curcic M, Antonijevic B, Carevic M, Mandic J, Djukic-Cosic D, Lekic CP (2010) Fluoride in drinking water and dental fluorosis. Sci Total Environ 408(17):3507–3512
Wen D, Zhang F, Zhang E, Wang C, Han S, Zheng Y (2013) Arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater of China. J Geochem Explor 135:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.10.012
Ahmed KM, Bhattacharya P, Hasan MA, Akhter SH, Alam SM, Bhuyian MH, Imam MB, Khan AA, Sracek O (2004) Arsenic enrichment in groundwater of the alluvial aquifers in Bangladesh: an overview. Appl Geochem 19(2):181–200
Yildiz A, Karaca M, Biceroglu S, Nalbantcilar M, Coskun U, Arik F, Aliyev F, Yiginer O, Turkoglu C (2008) Effect of chronic arsenic exposure from drinking waters on the QT interval and transmural dispersion of repolarization. J Int Med Res 36(3):471–478. https://doi.org/10.1177/147323000803600311
Leoni V, Fabiani L, Ticchiarelli L (1985) Water hardness and cardiovascular mortality rate in Abruzzo, Italy. Archives of Environmental Health: An International Journal 40(5):274–278. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1985.10545931
Yang CY, Chang CC, Tsai SS, Chiu HF (2006) Calcium and magnesium in drinking water and risk of death from acute myocardial infarction in Taiwan. Environ Res 101(3):407–411
Larsson SC, Virtanen MJ, Mars M, Männistö S, Pietinen P, Albanes D, Virtamo J (2008) Magnesium, calcium, potassium, and sodium intakes and risk of stroke in male smokers. Arch Intern Med 168(5):459–465
Zhang W, Iso H, Ohira T, Date C, Tamakoshi A, Group JS (2012) Associations of dietary magnesium intake with mortality from cardiovascular disease: the JACC study. Atherosclerosis 221(2):587–595
Liu Y (2014) The relationship between longevity and chemical elements in the environment of Chengmai County, Hainan Province. The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing
Lv JM (2011) The research to the chemical geographic characteristics of the typical longevity regions in China. The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing
Bureau of Census of Sichuan Province (SCP) (1992) 1990 population data of Sichuan Province. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Bureau of Census of Chongqing City (CQC) (2000) Population data of Chongqing City. China Statistics Press, Beijing
State Statistics Bureau (SSB) (2012) 2010 population data of Chongqing City. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Fan XM (2006) Study on the distribution of longevous people in China. Population Journal 3:19–23
Magnolfi S, Petruzzi E, Pinzani P, Malentacchi F, Pazzagli M, Antonini F (2007) Longevity index (LI%) and centenarity index (CI%): new indicators to evaluate the characteristics of aging process in the Italian population. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 44(3):271–276
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEPPRC) (2002) Methods for chemical analysis of water and waste water, 4th edn. Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China (MHPRC) (2006) Standards for drinking water quality (GB 5749–2006). China Standards Press, Beijing
PRC General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (PRC) (2008) Drinking natural mineral water (GB8537–2008). China Standards Press, Beijing
Christensen K, Vaupel JW (1996) Determinants of longevity: genetic, environmental and medical factors. J Intern Med 240(6):333–341
Lee JH, Flaquer A, Costa R, Andrews H, Cross P, Lantigua R, Schupf N, Tang MX, Mayeux R (2004) Genetic influences on life span and survival among elderly African-Americans, Caribbean Hispanics, and Caucasians. Am J Med Genet A 128(2):159–164
Kikuchi H, Iwane S, Munakata A, Tamura K, Nakaji S, Sugawara K (1999) Trace element levels in drinking water and the incidence of colorectal cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med 188(3):217–225
Zhang W, Shen Y, Pan H, Lin K, Liu X, Darvell BW, Lu WW, Chang J, Deng L, Wang D (2011) Effects of strontium in modified biomaterials. Acta Biomater 7(2):800–808
Cipriani A, Pretty H, Hawton K, Geddes JR (2005) Lithium in the prevention of suicidal behavior and all-cause mortality in patients with mood disorders: a systematic review of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatr 162(10):1805–1819
Liaugaudaite V, Mickuviene N, Raskauskiene N, Naginiene R, Sher L (2017) Lithium levels in the public drinking water supply and risk of suicide: a pilot study. J Trace Elem Med Biol 43:197–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.03.009
Zarse K, Terao T, Tian J, Iwata N, Ishii N, Ristow M (2011) Low-dose lithium uptake promotes longevity in humans and metazoans. Eur J Nutr 50(5):387–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-011-0171-x
Voors A, Reddick R, Koch GG (1971) Trace metals may decrease hypercholesterolemia in crowded cholesterol-fed roosters. Environ Res 4(6):520–529
Acknowledgments
Support for this research was provided by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Nos. 41502329, 41472322, 41602124) and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2014CB238906). Special thanks are given to Dr. Yanpeng Sun at Harvard University and Lili Zhang from the Sichuan College of Architectural Technology. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yuan, Y. & Luo, K. Regional Distribution of Longevity Population and Elements in Drinking Water in Jiangjin District, Chongqing City, China. Biol Trace Elem Res 184, 287–299 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1159-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1159-z