Abstract
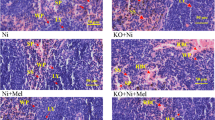
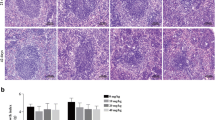
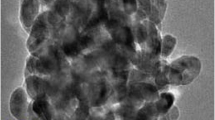
Some recent studies have been previously suggested that nanoparticulate titanium dioxide (TiO2) damaged liver function and decreased immunity of mice, but the spleen injury and its oxidative stress mechanism are still unclear. To understand the spleen injury induced by intragastric administration of nanoparticulate anatase TiO2 for consecutive 30 days, the spleen pathological changes, the oxidative stress, and p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways, along with nuclear factor-κB and nuclear factor-E2-related factor-2 (Nrf-2), were investigated as the upstream events of oxidative stress in the mouse spleen from exposure to nanoparticulate TiO2. The results suggested that nanoparticulate TiO2 caused congestion and lymph nodule proliferation of spleen tissue, which might exert its toxicity through oxidative stress, as it caused significant increases in the mouse spleen reactive oxygen species accumulations, subsequently leading to the strong lipid peroxidation and the significant expression of heme oxygenase-1 via the p38-Nrf-2 signaling pathway. The studies on the mechanism by which nanoparticulate TiO2 induced the p38-Nrf-2 signaling pathway are helpful to a better understanding of the nanoparticulate TiO2-induced oxidative stress and reduction of immune capacity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dagani R (2003) Nanomaterials: safe or unsafe? Chem Eng News 81:30–33
Service RF (2003) American Chemical Society meeting. Nanomaterials show signs of toxicity. Science 300:243
Warheit DB (2004) Nanoparticles: health impacts? Mater Today 7:32–35
Gurr J, Wang ASS, Chen C, Jan K (2005) Ultrafine titanium dioxide particle in the absence of photoactivation can induce oxidative damage to human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol 213:66–73
J Fisher, T Egerton (2001) Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Titanium Compounds, Inorganic
Choi H, Stathatos E, Dionysiou DD (2006) Solgel preparation of mesoporous photocatalytic TiO2 films and TiO2/Al2O3 composite membranes for environmental applications. Appl Catal B-Environ 63:60–67
Esterkin CR, Negro AC, Alfano OM, Cassano AE (2005) Air pollution remediation in a fixed bed photocatalytic reactor coated with TiO2. AIChE J 51:2298–2310
Jin CY, Zhu BS, Wang XF, Lu QH (2008) Cytotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mouse fibroblast cells. Chem Res Toxicol 21(9):1871–1877
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113(7):823–839
Afaq F, Abidi P, Matin R, Rahman Q (1998) Cytotoxicity, pro-oxidant effects and antioxidant depletion in rat lung alveolar macrophages exposed to ultrafine titanium dioxide. J Appl Toxicol 18:307–312
Federici G, Shaw BJ, Handy RD (2007) Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): gill injury, oxidative stress, and other physiological effects. Aquat Toxicol 84:415–430
Ma LL, Liu J, Li N, Wang J, Duan YM, Yan JY, Liu HT, Wang H, Hong FS (2010) Oxidative stress in the brain of mice caused by translocated nanoparticulate TiO2 delivered to the abdominal cavity. Biomaterials 31:99–105
Liu HT, Ma LL, Liu J, Zhao JF, Yan JY, Hong FS (2010) Toxicity of nano-anatase TiO2 to mice: liver injury, oxidative stress. Toxicol Environ Chem 92(1):175–186
Zhao JF, Wang J, Wang SS, Zhao XY, Yan JY, Ruan J, Li N, Duan YM, Wang H, Hong FS (2010) The mechanism of oxidative damage in nephrotoxicity of mice caused by nano-anatase TiO2. J Exp Nanoscience doi:10.1080/17458081003628931, 2010 in press
Duan YM, Liu J, Ma LL, Li N, Liu HT, Wang J, Zheng L, Liu C, Wang XF, Zhang XG, Yan JY, Wang H, Hong FS (2010) Toxicological characteristics of nanoparticulate anatase titanium dioxide in mice. Biomaterials 31:894–899
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869
Takeda K, Matsuzawa A, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H (2003) Roles of MAPKKK ASK1 in stress-induced cell death. Cell Struct Funct 28:23–29
Hagemann C, Blank JL (2001) The ups and downs of MEK kinase interactions. Cell Signall 13(12):863–875
Qadri I, Iwahashi M, Capasso JM, Hopken MW, Flores S, Schaack J, Simon FR (2004) Induced oxidative stress and activated expression of manganese superoxide dismutase during hepatitis C virus replication: role of JNK, p38 MAPK and AP-1. Biochem J 378:919–928
Camacho-Barquero L, Villegas I, Sánchez-Calvo JM, Talero E, Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Motilva V, Alarcón de la Lastra C (2007) Curcumin, a Curcuma longa constituent, acts on MAPK p38 pathway modulating COX-2 and iNOS expression in chronic experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol 7:333–342
Janssen YM, Barchowsky A, Treadwell M, Driscoll KE, Mossman BT (1995) Asbestos induces nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) DNA-binding activity and NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression in tracheal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8458–8462
Pinkus R, Weiner LM, Daniel V (1996) Role of oxidants and antioxidants in the induction of AP-1, NF-kappaB, and glutathione S-transferase gene expression. J Biol Chem 271:13422–13429
Sen CK, Packer L (1996) Antioxidant and redox regulation of gene transcription. FASEB J 10:709–720
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T, O’connor T, Yamamoto M (2003) Keap1 regulates both cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling and degradation of Nrf2 in response to electrophiles. Genes Cells 8:379–391
Maines MD (1988) Heme oxygenase: function, multiplicity, regulatory mechanism, and clinical applications. FASEB J 2:2557–2568
Choi AM, Alam J (1996) Heme oxygenase-1: function, regulation, and implication of a novel stress-inducible protein in oxidant-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 15(1):9–19
Maines MD (1997) The heme oxygenase system: a regulator of second messenger gases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:517–554
Okinaga S, Takahashi K, Takeda K, Yoshizawa M, Fujita H, Sasaki H, Shibahara S (1996) Regulation of human heme oxygenase-1 gene expression under thermal stress. Blood 87:5074–5084
Cantoni L, Rossi C, Rizzardini M, Gardina M, Ghezzi P (1991) Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor induce hepatic haeme oxygenase. Biochem J 279:891–894
Chen K, Gunter K, Maines MD (2002) Neurons overexpressing heme oxygenase-1 resist oxidative stress-mediated cell death. J Neurochem 75(1):304–313
Willis D, Moore AR, Frederick R, Willoughby DA (1996) Heme oxygenase: a novel target for the modulation of the inflammatory response. Nat Med 2:87–90
Yachie A, Niida Y, Wada T, Igarashi N, Kaneda H, Toma T, Ohta K, Kasahara Y, Koizumi S (1999) Oxidative stress causes enhanced endothelial cell injury in human heme oxygenase-1 deficiency. Clin Invest 103(1):129–135
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, Yamamoto M, Nabeshima Y (1997) An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 236:313–322
Chan K, Kan YW (1999) Nrf2 is essential for protection against acute pulmonary injury in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12731–12736
Hayes JD, Chanas SA, Henderson CJ, McMahon M, Sun C, Moffat GJ, Wolf CR, Yamamoto M (2000) The Nrf2 transcription factor contributes both to the basal expression of glutathione S-transferases in mouse liver and to their induction by the chemopreventive synthetic antioxidants, butylated hydroxyanisole and ethoxyquin. Biochem Soc Trans 28:33–41
Chan K, Han XD, Kan YW (2001) An important function of Nrf2 in combating oxidative stress: detoxification of acetaminophen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4611–4616
Kim YC, Masutani H, Yamaguchi Y, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Yodoi J (2110) Hemin induced activation of the thioredoxin gene by Nrf2. A differential regulation of the antioxidant responsive element by a switch of its binding factors. J Biol Chem 276:18399–18406
Kwak MK, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW (2002) Enhanced expression of the transcription factor Nrf2 by cancer chemopreventive agents: role of antioxidant response element-like sequences in the nrf2 promoter. Mol Cell Biol 22:2883–2892
Oliveira CP, Lopasso FP, Laurindo FR, Leitao RM, Laudanna A (2001) Protection against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by silymarin or verapamil. Transplant Proc 33:3010–3014
Nourooz-Zadeh J, Tajaddini-Sarmadi J, Wolff SP (1994) Measurement of plasma hydroperoxide concentrations by the ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange assay in conjunction with triphenylphosphine. Anal Biochem 220:403–409
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Meth Enzymol 52:302–310
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Ke LD, Chen Z (2000) A reliability test of standard-based quantitative PCR: exogenous vs endogenous standards. Mol Cell Probes 14(2):127–135
Liu WH, David Saint A (2002) Validation of a quantitative method for real time PCR kinetics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294:347–353
Wang JX, Zhou GQ, Chen CY, Yu HW, Wang TC, Ma YM, Jia G, Gao YX, Li B, Sun J, Li YF, Jia F, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2007) Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol Lett 168:176–185
Chen JY, Dong X, Zhao J, Tang GP (2009) In vivo acute toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to mice after intraperitioneal injection. J Appl Toxicol 29:330–337
Liu HT, Ma LL, Zhao JF, Liu J, Yan JY, Ruan J, Hong FS (2009) Biochemical toxicity of nano-anatase TiO2 particles in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 129(1):170–180
Long TC, Saleh N, Tilton RD, Lowry G, Veronesi B (2006) Titanium dioxide (P25) produces reactive oxygen species in immortalized brain microglia (BV2): implications for nanoparticle neurotoxicity. Environ Sci Technol 40:4346–4352
Long TC, Tajuba J, Sama P, Sale N, Swartz C, Parker J, Hester S, Lowry GV, Veronesi B (2007) Nano-TiO2 stimulates ROS in brain microglia and damages neurons in vitro. Environ Health Perspect 115:1631–1637
Gao HW, Xu Q, Chen L, Wang SL, Wang Y, Wu LL, Yuan Y (2008) Potential protein toxicity of synthetic pigments, binding of poncean S to human serum albumin. Biophys J 94:906–917
Xu Z, Liu XW, Ma YS, Gao HW (2010) Interactions of nano-TiO2 with lysozyme: insights into the enzyme toxicity of nanosized particles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:798–806
Maines MD (1988) Hemeoxygenase: function, multiplicity, regulatory mechanisms, and clinical applications. FASEB J 2:2557–2568
Morse D, Choi AM (2002) Heme oxygenase-1: the “emerging molecule” has arrived. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 27:8–16
Otterbein LE, Soares MP, Yamashita K, Bach FH (2003) Heme oxygenase-1: unleashing the protective properties of heme. Trends Immunol 24:449–455
Chen CY, Jang JH, Li MH, Surh YJ (2005) Resveratrol upregulates heme oxygenase-1 expression via activation of NF-E2-related factor 2 in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331:993–1000
Lee JS, Surh YJ (2005) Nrf2 as a novel molecular target for chemoprevention. Cancer Lett 224:171–184
Lim HJ, Lee KS, Lee S, Park JH, Choi HE, Go SH, Kwak HJ, Park HY (2007) 15d-PGJ2 stimulates HO-1 expression through p38 MAP kinase and Nrf-2 pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 223:20–27
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30901218), the Medical Development Foundation of Soochow University (grant no. EE120701, China), the National Bringing New Ideas Foundation of Student of China (grant nos. 57315427, 57315927), and the Bringing New Ideas Foundation of Postgraduate of Medical College of Soochow University (China) and the Soochow University Start-up Fund (grant no. Q4134918, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jue Wang, Na Li, Lei Zheng and Ying Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, N., Zheng, L. et al. P38-Nrf-2 Signaling Pathway of Oxidative Stress in Mice Caused by Nanoparticulate TiO2 . Biol Trace Elem Res 140, 186–197 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8687-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8687-0