Abstract
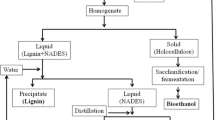
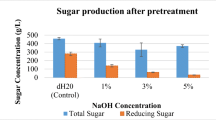
Sorghum was pretreated by sole ultrasound or supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2), as well as the method combining both to intensify enzymatic hydrolysis. The effect of the time (1–5 h) and temperature (30–70 °C) on ultrasonic pretreatment was investigated, and the best condition was determined as 5 h and 50 °C with the EH sugar yield of 33.69%. The influence of the time (6–48 h), temperature (40–80 °C), and pressure (15–25 MPa) on scCO2 pretreatment were also discussed in this study. The optimum condition of scCO2 pretreatment was identified as 60 °C, 20 MPa, and 36 h with the EH sugar yield of 43.57%. Compared with the sole ultrasonic or scCO2 pretreatment, scCO2 associated with the subsequent ultrasonic pretreatment did not show significant improvement in sugar yield. However, 30 MPa was an extremely effective pressure, which led to 45.50% EH sugar yield with 60 °C, 6-h pretreatment. Finally, the change of the microscopic structures of the sorghum stalk after the pretreatment was investigated using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, J. S., & Saka, S. (2010). Supplement issue: selected peer-reviewed papers of the conference on “Renewable Energy 2008-Recent Developments of Biomass Conversion Technologies” BEXCO, Busan, Republic of Korea, 13-17th October 2008. Bioresource Technology, 101, S1–S1.
Xiang, Q., Lee, Y. Y., Pettersson, P. O., et al. (2003). Heterogeneous aspects of acid hydrolysis of α-cellulose. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 107(1–3), 505–514.
Bjerre, A. B., Olesen, A. B., Fernqvist, T., et al. (1996). Pretreatment of wheat straw using combined wet oxidation and alkaline hydrolysis resulting in convertible cellulose and hemicellulose. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 49(5), 568–577.
Mandels, M., Hontz, L., & Nystrom, J. (2010). Enzymatic hydrolysis of waste cellulose. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 105(1), 1–25.
Hendriks, A. T., & Zeeman, G. (2009). Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresource Technology, 99(1), 10–18.
Mouthier, T., Appeldoorn, M. M., Pel, H., Schols, H. A., Gruppen, H., & Kabel, M. A. (2018). Corn stover lignin is modified differently by acetic acid compared to sulfuric acid. Industrial Crops and Products, 121, 160–168.
Taherzadeh, M. J., & Karimi, K. (2008). Pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve ethanol and biogas production: a review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 9(9), 1621–1651.
Zhao, X., Cheng, K., & Liu, D. (2009). Organosolv pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 82(5), 815–827.
Alizadeh, H., Teymouri, F., Gilbert, T. I., et al. (2005). Pretreatment of switchgrass by ammonia fiber explosion (AFEX). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 121-124(1–3), 1133.
Pielhop, T., Amgarten, J., Rohr, P. R. V., et al. (2016). Steam explosion pretreatment of softwood: the effect of the explosive decompression on enzymatic digestibility. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 9(1), 152.
Zheng, Y., Lin, H. M., Wen, J., Cao, N., Yu, X., & Tsao, G. T. (1995). Supercritical carbon dioxide explosion as a pretreatment for cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnology Letters, 17(8), 845–850.
Zheng, Y., Lin, H. M., & Tsao, G. T. (1998). Pretreatment for cellulose hydrolysis by carbon dioxide explosion. Biotechnology Progress, 14(6), 890–896.
Kim, K. H., & Hong, J. (2001). Supercritical CO2 pretreatment of lignocellulose enhances enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. Bioresource Technology, 77(2), 139–144.
Narayanaswamy, N., Faik, A., Goetz, D. J., & Gu, T. (2011). Supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment of corn stover and switchgrass for lignocellulosic ethanol production. Bioresource Technology, 102(13), 6995–7000.
Srinivasan, N., & Ju, L. K. (2010). Pretreatment of guayule biomass using supercritical carbon dioxide-based method. Bioresource Technology, 101(24), 9785–9791.
Zhao, W., Zong, Z.-M., Lin, J., Song, Y. M., Guo, X. F., Yao, Z. S., Zhang, L. N., He, R. L., Cao, J. P., & Wei, X. Y. (2007). Dewaxing from stalks with petroleum ether by different methods. Energy & Fuels, 21(2), 1165–1168.
Sul’man, E. M., Sul’man, M. G., & Prutenskaya, E. A. (2011). Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on the composition of lignocellulosic material in biotechnological processes. Catalysis in Industry, 3(1), 28–33.
Yu, J., Zhang, J., He, J., Liu, Z., & Yu, Z. (2009). Combinations of mild physical or chemical pretreatment with biological pretreatment for enzymatic hydrolysis of rice hull. Bioresource Technology, 100(2), 903–908.
Yin, J., Hao, L., Yu, W., Wang, E., Zhao, M., Xu, Q., & Liu, Y. (2014). Enzymatic hydrolysis enhancement of corn lignocellulose by supercritical CO2 combined with ultrasound pretreatment. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 35(5), 763–769.
Moharreri, E., Jafari, T., Suib, S. L., et al. (2017). Improved understanding of CO2–water pretreatment of guayule biomass by high solids ratio experiments, rapid physical expansion, and examination of textural properties. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 56(3) 645–652.
Adney, B., & Baker, J. (1996). Measurement of cellulase activities. LAP-006 NREL analytical procedure, 6(645).
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Biochemistry, 31(3), 426–428.
Tang A. (2000). The structure and properties of cellulose fibers treated with ultrasonic wave. South China University of Technology.
Bussemaker, M. J., & Zhang, D. (2013). Effect of ultrasound on lignocellulosic biomass as a pretreatment for biorefinery and biofuel applications. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 52(10), 3563–3580.
Miao, G., Feng, X., Li, S. R., et al. (2010). Effect of SC-CO2 pretreatment in increasing rice straw biomass conversion. Biosystems Engineering, 106(4), 470–475.
Liu, G., Ma, L., & Xiang, S. (2013). Chemical properties data manual, inorganic volume. Chemical Industry Press.
Zhao, M. J., Xu, Q. Q., Li, G. M., et al. (2018). Pretreatment of agricultural residues by supercritical CO 2 at 50–80 °C to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis. Journal of Energy Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2018.05.003
Ninomiya, K., Takamatsu, H., Onishi, A., Takahashi, K., & Shimizu, N. (2013). Sonocatalytic–Fenton reaction for enhanced OH radical generation and its application to lignin degradation. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20(4), 1092–1097.
Segal, L. C., Creely, J., Martin, A. E. J., et al. (1959). An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Textile Research Journal, 29(10), 786–794.
Mat Zain, N. F. (2014). Preparation and characterization of cellulose and nanocellulose from pomelo (Citrus grandis) albedo. Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences, 05(01), 334.
Wang, S., Li, F., Zhang, P., Jin, S., Tao, X., Tang, X., Ye, J., Nabi, M., & Wang, H. (2017). Ultrasound assisted alkaline pretreatment to enhance enzymatic saccharification of grass clipping. Energy Conversion and Management, 149, 409–415.
Daza Serna, L. V., Orrego Alzate, C. E., & Cardona Alzate, C. A. (2016). Supercritical fluids as a green technology for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresource Technology, 199, 113–120.
Funding
The work was financially supported by the Petrochemicals Joint Fund between National Natural Science Foundation of China and China National Petroleum Corporation (U1662130), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21506027), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DUT17JC34).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhao, M., Xu, Q. et al. Enhanced Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Sorghum Stalk by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide and Ultrasonic Pretreatment. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 188, 101–111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2909-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2909-x