Abstract
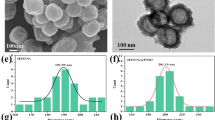
The cancer treatment by laser-conjugated nanomaterials has become a new developing trend due of their unique physicochemical performance. In this paper, two-phase colloidal method has been used to synthesize a novel Mn-doped CuS (Mn-CuS) nanoprism with high-surface area with different Mn concentrations (0%, 1%, 3% and 5%) for first time. The characterization of synthesized Mn-CuS involved the structural, compositional, surface charges, optical and morphological properties analysis. XRD showed that the Mn-doped covellite copper sulfide nanoparticles have hexagonal structure and additional diffraction peaks, which are assigned to orthorhombic chalcocite CuS were appeared. FTIR confirmed that the CuS and Mn-CuS have been prepared by two-phase colloidal synthesis method at 180 °C. The absolute values of zeta potential were indicated the suspension of CuS and Mn-doped CuS nanoprisms was electrostatically stabilized and the nanoparticles were stable and mono-dispersed. From UV–visible analysis, the absorption spectrum of Mn-doped CuS has two peaks: the first in UV–visible wavelength range and the second in NIR range. The optical band gap of Mn-CuS decreased as the Mn concentration increased. The TEM images showed that the 1% is best percentage of Mn to produce Mn-doped CuS nanoprism with uniform shape and size distribution and less average edge lengths. The best sample nanoprism (Mn-CuS 1% nanoprisms) was modified with gum Arabic for first time to decrease the cytotoxicity and increase the biocompatibility and investigated as photothermal agent in MDA-MB-231 cancer treatment. The results showed that the cancer cells were killed effectively by GA@Mn-CuS 1% nanoprisms. This indicated that GA@Mn-CuS nanoprisms are able to be used as an efficient theranostic agent for tumor photothermal therapy in the future.Affiliations: Journal instruction requires a city and country for affiliations; however, city is missing in affiliations 1 and 2. Please verify if the provided city is correct and amend if necessary.I verified the provided city, it is correct.Please check the edit made in the article title.I am checked the edit made in the article title , It is correct.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadeer NS, Murphy CJ (2016) Recent progress in cancer thermal therapy using gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 120(9):4691–4716
Abdullaeva Z, Omurzak E, Mashimo T (2013) Synthesis of copper sulfide nanoparticles by pulsed plasma in liquid method. World Acad Int Sch Sci Res Innov 7:422–425
AL-Barram LF, AL-Jawad SM, Taha AA, Imran NJ (2020) Photothermal therapy of cancer cells enhanced by glutathione (GSH) modified small-sized gold nanoparticles. J Electromagn Waves Appl 34(18):2467–2487
Al-Jawad SM, Rafic SN, Muhsen MM (2017) Preparation and characterization of polyaniline–cadmium sulfide nanocomposite for gas sensor application. Mod Phys Lett B 31(26):1750234
Al-Jawad SM, Sabeeh SH, Taha AA, Jassim HA (2018) Studying structural, morphological and optical properties of nanocrystalline ZnO: Ag films prepared by sol–gel method for antimicrobial activity. J. Sol–gel Sci. Technol. 87(2):362–371
Al-Jawad SM, Sabeeh SH, Taha AA, Jassim HA (2019a) Synthesis and characterization of Fe–ZnO thin films for antimicrobial activity. Surf Rev Lett 26(05):1850197
AL-Jawad SM, Taha AA, Redha AM (2019b) Studying the structural, morphological, and optical properties of CuS: Ni nanostructure prepared by a hydrothermal method for biological activity. J. Sol–gel Sci. Technol. 91(2):310–323
Al-Jawad SM, Taha AA, Redha AM, Imran NJ (2021) Influence of nickel doping concentration on the characteristics of nanostructure CuS prepared by hydrothermal method for antibacterial activity. Surf Rev Lett 28(01):2050031
Alzahrani E (2014) Gum Arabic-coated magnetic nanoparticles for methylene blue removal. Int J Innov Res Sci Technol 3(8):15118–15129
Ayodhya D, Venkatesham M, Santoshi Kumari A, Reddy GB, Ramakrishna D, Veerabhadram G (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of dye pollutants under solar, visible and UV lights using green synthesised CuS nanoparticles. J Exp Nanosci 11(6):418–432
Bilgili O (2019) The effects of mn doping on the structural and optical properties of ZnO. Acta Phys Pol A 136(3):460–466
Callister WD, Rethwisch DG (2018) Materials science and engineering: an introduction. Wiley, New York
Castillón-Barraza FF, Farías MH, Coronado-López JH, Encinas-Romero MA, Pérez-Tello M, Herrera-Urbina R, Posada-Amarillas A (2011) Synthesis and characterization of copper sulfide nanoparticles obtained by the polyol method. Adv Sci Lett 4(2):596–601
Chaki SH, Tailor JP, Deshpande MP (2014) Synthesis and characterizations of undoped and Mn doped CuS nanoparticles. Adv Sci Lett 20(5–6):959–965
Chakraborty P, Adhikary J, Chatterjee S, Biswas B, Chattopadhyay T (2016) Facile synthesis of copper sulfide nanoparticles: antibacterial and antifungal activity study. Rasayan J Chem 9(1):77–83
Dehimi M, Touam T et al (2015) (2015) Effects of low Ag doping on physical and optical waveguide properties of highly oriented sol–gel ZnO thin films. Adv Condens Matter Phys. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/740208
Deng X, Li K et al (2017) A hollow-structured CuS@Cu2S@Au nanohybrid: synergistically enhanced photothermal efficiency and photoswitchable targeting effect for cancer theranostics. Adv Mater 29(36):1701266
Fathima AS, Sivaguru N, Kumar VS (2016) Investigation on optical properties of CuS and Zn doped CuS thin films by chemical bath deposition method. Strain 10:3M
Foecke T, Iadicola MA, Lin A, Banovic SW (2007) A method for direct measurement of multiaxial stress-strain curves in sheet metal. Metall Mater Trans A 38(2):306–313
Freeda MA, Mahadevan CK (2013) Effect of Zn2+ dopping on CuS nanocrystals. Mater Sci Ind J 9(8):283–288
Ghosh R, Basak D, Fujihara S (2004) Effect of substrate-induced strain on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of polycrystalline ZnO thin films. J Appl Phys 96(5):2689–2692
Gondal MA, Drmosh QA, Yamani ZH, Saleh TA (2009) Synthesis of ZnO2 nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid and their annealing transformation into ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 256(1):298–304
Guo Y, Cao X, Lan X, Zhao C, Xue X, Song Y (2008) Solution-based doping of manganese into colloidal ZnO nanorods. J Phys Chem C 112(24):8832–8838
Heiba ZK, Mohamed MB (2018) Changes in structural, optical and magnetic properties of nano-CuS upon doping with Mn and Fe: a comparative study. Appl Phys A 124(6):1–11
Hsu SW, Ngo C, Bryks W, Tao AR (2015) Shape focusing during the anisotropic growth of CuS triangular nanoprisms. Chem Mater 27(14):4957–4963
Hubenthal F, Hendrich C, Träger F (2010) Damping of the localized surface plasmon polariton resonance of gold nanoparticles. Appl Phys B 100(1):225–230
Kandasamy N, Saravanan S (2013, July) Synthesis and optical properties of Vanadium doped Covellite nanostructure by wet chemical method. In: International conference on advanced nanomaterials and emerging engineering technologies (pp 52–54). IEEE
Karmakar R, Neogi SK, Banerjee A, Bandyopadhyay S (2012) Structural; morphological; optical and magnetic properties of Mn doped ferromagnetic ZnO thin film. Appl Surf Sci 263:671–677
Kriegel I, Scotognella F, Manna L (2017) Plasmonic doped semiconductor nanocrystals: properties, fabrication, applications and perspectives. Phys Rep 674:1–52
Kundu J, Pradhan D (2013) Influence of precursor concentration, surfactant and temperature on the hydrothermal synthesis of CuS: structural, thermal and optical properties. New J Chem 37(5):1470–1478
Lesyuk R, Klein E, Yaremchuk I, Klinke C (2018) Copper sulfide nanosheets with shape-tunable plasmonic properties in the NIR region. Nanoscale 10(44):20640–20651
Liao G, He F et al (2020) Emerging graphitic carbon nitride-based materials for biomedical applications. Prog Mater Sci 112:100666
Mo Z, Qiu M et al (2022) Multifunctional phototheranostic nanoplatform based on polydopamine-manganese dioxide-IR780 iodide for effective magnetic resonance imaging-guided synergistic photodynamic/photothermal therapy. J Colloid Interface Sci 611:193–204
Mo Z, Li Q et al (2022) A nanoarchitectonic approach enables triple modal synergistic therapies to enhance antitumor effects. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14(8):10001–10014
Narayanan N, Deepak K (2018) Ga Dopant induced band gap broadening and conductivity enhancement in spray pyrolysed Zn0·85Ca0·15O thin films. Mater Res. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2018-0034
Nduna M, Rodriguez-Pascual M, Lewis AE (2013) Effect of dissolved precipitating ions on the settling characteristics of copper sulphide. J South Afr Inst Min Metall 113(5):00–00
Nemade KR, Waghuley DS (2015) Band gap engineering of CuS nanoparticles for artificial photosynthesis. Mater Sci Semicond Process 39:781–785
Pal M, Pal U, Jiménez JMGY, Pérez-Rodríguez F (2012) Effects of crystallization and dopant concentration on the emission behavior of TiO2: Eu Nanophosphors. Nanoscale Res Lett 7(1):1–12
Pei LZ, Wang JF, Tao XX, Wang SB, Dong YP, Fan CG, Zhang QF (2011) Synthesis of CuS and Cu1·1Fe1·1S2 crystals and their electrochemical properties. Mater Charact 62(3):354–359
Podili S, Geetha D, Ramesh PS (2017) One-pot synthesis of CTAB stabilized mesoporous cobalt doped CuS nano flower with enhanced pseudocapacitive behavior. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28(20):15387–15397
Podili S, Geetha D, Ramesh PS (2018) Electrochemical studies on Ni doped CuS nanostructures with cationic surfactant synthesized through a hydrothermal route. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29(13):11167–11177
Poulose AC, Veeranarayanan S et al (2015) Multi-stimuli responsive Cu2S nanocrystals as trimodal imaging and synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy agents. Nanoscale 7(18):8378–8388
Qin Z, Qiu M, Zhang Q, Yang S, Liao G, Xiong Z, Xu Z (2021) Development of copper vacancy defects in a silver-doped CuS nanoplatform for high-efficiency photothermal–chemodynamic synergistic antitumor therapy. J Mater Chem 9(42):8882–8896
Quintana PV, Arenas-Arrocena MC et al (2014) Growth evolution and phase transition from chalcocite to digenite nanocrystalline copper sulphide: Morphological, optical and electrical properties. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 5:1542–1552
Shinde VR, Gujar TP, Lokhande CD, Mane RS, Han SH (2006) Mn doped and undoped ZnO films: A comparative structural, optical and electrical properties study. Mater Chem Phys 96(2–3):326–330
Singh M, Goyal M, Devlal K (2018) Size and shape effects on the band gap of semiconductor compound nanomaterials. J Taibah Univ Sci 12(4):470–475
Sokolov VI, Druzhinin AV et al (2010) Optical evidence of strong coupling between valence-band holes and d-localized spins in Zn1−x MnxO. Phys Rev B 81(15):153104
Soni BH, Deshpande MP, Bhatt SV, Chaki SH, Sathe V (2013) X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and raman spectroscopy of undoped and Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by microwave irradiation. J Appl Spectrosc 79(6):901–907
Sreelekha N, Subramanyam K, Reddy DA, Murali G, Ramu S, Varma KR, Vijayalakshmi RP (2016a) Structural, optical, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of Co doped CuS diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 378:330–340
Sreelekha N, Subramanyam K, Reddy DA, Murali G, Varma KR, Vijayalakshmi RP (2016b) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B by Fe doped CuS diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles under the simulated sunlight irradiation. Solid State Sci 62:71–81
Taha AA, Al-Jawad SM, Salim MM (2018) Influence of titanium tetraisopropoxide concentration on the antibacterial activity of TiO2 thin films. Surf Rev Lett 25(06):1850111
Wang ZH, Geng DY, Zhang YJ, Zhang ZD (2010) CuS: Ni flowerlike morphologies synthesized by the solvothermal route. Mater Chem Phys 122(1):241–245
Xie Y, Carbone L et al (2013) Metallic-like stoichiometric copper sulfide nanocrystals: phase-and shape-selective synthesis, near-infrared surface plasmon resonance properties, and their modeling. ACS Nano 7(8):7352–7369
Yildirim MA, Ateş A, Astam A (2009) Annealing and light effect on structural, optical and electrical properties of CuS, CuZnS and ZnS thin films grown by the SILAR method. Physica E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct 41(8):1365–1372
Yu W, Yu N et al (2019) Chitosan-mediated green synthesis and folic-acid modification of CuS quantum dots for photoacoustic imaging guided photothermal therapy of tumor. J Colloid Interface Sci 555:480–488
Zaman MS, Moon CH, Bozhilov KN, Haberer ED (2013) Phage-directed synthesis of copper sulfide: structural and optical characterization. Nanotechnology 24(32):325602
Zhang M, Zou Y, Zhong Y, Liao G, Yu C, Xu Z (2019) Polydopamine-based tumor-targeted multifunctional reagents for computer tomography/fluorescence dual-mode bioimaging-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2(2):630–637
Zhao R, Sun X, Sun J, Wang L, Han J (2017) Polypyrrole-modified CuS nanoprisms for efficient near-infrared photothermal therapy. RSC Adv 7(17):10143–10149
Zou Y, Jin H, Sun F, Dai X, Xu Z, Yang S, Liao G (2018) Design and synthesis of a lead sulfide based nanotheranostic agent for computer tomography/magnetic resonance dual-mode-bioimaging-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1(5):2294–2305
Zou Y, Sun F et al (2019) A novel nanotheranostic agent for dual-mode imaging-guided cancer therapy based on europium complexes-grafted-oxidative dopamine. Chem Eng J 357:237–247
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Ethics approval
None required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muhsen, M.M., Al-Jawad, S.M.H. & Taha, A.A. Gum Arabic-modified Mn-doped CuS nanoprisms for cancer photothermal treatment. Chem. Pap. 76, 6821–6838 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02364-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02364-0