Abstract
Background
Analysis of the expression of genes related to the energy metabolism can elucidate the understanding of physiological and genetic factors that contribute to obesity. This study aimed to evaluate the expression of genes and its influence on resting metabolic rate and weight loss in obese patients before and after bariatric surgery.
Methods
This study was conducted on 23 women, who were divided into two groups: bariatric surgery (preoperative and 6 months after surgery) and control. Abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue samples were collected to analyze the gene expression, and the resting metabolic rate (RMR) was measured by indirect calorimetry.
Results
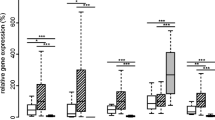
Significant differences were observed in weight reduction (22 %, p = 0.01), BMI (22.5 %, p = 0.01), and RMR values (10.5 %, p = 0.01) after the bariatric surgery, while the weight-adjusted RMR increased (15.8 %, p = 0.01). Increased UCP2 expression after 6 months of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) as compared to preoperative period (0.764 to 1.268, p = 0.01) was observed. Analysis with weight-adjusted RMR as dependent variable revealed that UCP2 (r 2 = 0.517, p = 0.01) and PLIN1 (r 2 = 0.420, p = 0.04) expression determine the RMR values in preoperative period. Moreover, UCP2 and PLIN1 expression in preoperative period influenced the percentage of weight loss, even when adjusted for age and BMI.
Conclusions
We have demonstrated that after 6 months of bariatric surgery, there is significant increase in the UCP2 expression. Additionally, the expression of UCP2 and PLIN1 genes influences the resting metabolic rate in obese individuals and could predict the weight loss after bariatric surgery.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haidar YM, Cosman BC. Obesity epidemiology. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24(4):205–10.
BRASIL. Vigilância de fatores de risco e proteção para doenças crônicas por inquérito telefônico (VIGITEL). In: Saúde Md, editor. 2015. p. Disponível em: http://portalsaude.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2015/abril/15/PPT-Vigitel-14-.pdf acesso 05 de agosto de 2015.
Nicoletti CF, de Oliveira BA, de Pinhel MA, Donati B, Marchini JS, Salgado Junior W, et al. Influence of excess weight loss and weight regain on biochemical indicators during a 4-year follow-up after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2015;25(2):279–84.
Carrasco F, Papapietro K, Csendes A, Salazar G, Echenique C, Lisboa C, et al. Changes in resting energy expenditure and body composition after weight loss following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2007;17(5):608–16.
Hasson RE, Howe CA, Jones BL, Freedson PS. Accuracy of four resting metabolic rate prediction equations: effects of sex, body mass index, age, and race/ethnicity. J Sci Med Sport/Sports Med Aust. 2011;14(4):344–51.
Smith CE, Ordovas JM. Update on perilipin polymorphisms and obesity. Nutr Rev. 2012;70(10):611–21.
Deram S, Villares SM. Genetic variants influencing effectiveness of weight loss strategies. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2009;53(2):129–38.
Brondani LA, Assmann TS, de Souza BM, Boucas AP, Canani LH, Crispim D. Meta-analysis reveals the association of common variants in the uncoupling protein (UCP) 1-3 genes with body mass index variability. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96411. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096411.
Diano S, Horvath TL. Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) in glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Mol Med. 2012;18(1):52–8.
Toda C, Diano S. Mitochondrial UCP2 in the central regulation of metabolism. Best practice & research. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;28(5):757–64.
Ruiz JR, Larrarte E, Margareto J, Ares R, Alkorta P, Labayen I. Preliminary findings on the role of PLIN1 polymorphisms on body composition and energy metabolism response to energy restriction in obese women. Br J Nutr. 2011;106(4):486–90.
Kern PA, Di Gregorio G, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G. Perilipin expression in human adipose tissue is elevated with obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(3):1352–8.
Deram S, Nicolau CY, Perez-Martinez P, Guazzelli I, Halpern A, Wajchenberg BL, et al. Effects of perilipin (PLIN) gene variation on metabolic syndrome risk and weight loss in obese children and adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(12):4933–40.
Weijs PJ, Vansant GA. Validity of predictive equations for resting energy expenditure in Belgian normal weight to morbid obese women. Clin Nutr. 2010;29(3):347–51.
Weir JB. New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol. 1949;109(1-2):1–9.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162(1):156–9.
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, Mathieu C. An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods. 2001;25(4):386–401.
Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Engeli S, Sharma AM. Validation of endogenous controls for gene expression studies in human adipocytes and preadipocytes. Horm Metab Res. 2001;33:625–7.
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, et al. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 2009;55(4):611–22.
Berisha SZ, Serre D, Schauer P, Kashyap SR, Smith JD. Changes in whole blood gene expression in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes following bariatric surgery: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e16729. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016729.
Pedrosa IV, Burgos MG, Souza NC, Morais CN. Nutrition aspects in obese before and after bariatric surgery. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2009;36(4):316–22.
Nassif PAN, Lopes AD, Lopes GL, Martins PR, Pedri LE, Varaschim M, et al. Alterações nos parâmetros pré e pós-operatórios de pacientes com síndrome metabólica, submetidos a bypass gastrointestinal em Y de Roux. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2009;22(3):165–70.
Pinhel MAS, Nicoletti CF, de Oliveira BAP, Chaves RCP, Parreiras LT, Sivieri T, et al. Weight loss and metabolic outcomes 12 months after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in a population of Southeastern Brazil. Nutr Hosp. 2015;32(3):1017–21.
Nicoletti CF, Nonino CB, de Oliveira BA, Pinhel MA, Mansego ML, Milagro FI, et al. DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Levels in Relation to Two Weight Loss Strategies: Energy-Restricted Diet or Bariatric Surgery. Obes Surg. 2015;26(3):603–11.
Tamboli RA, Hossain HA, Marks PA, Eckhauser AW, Rathmacher JA, Phillips SE, et al. Body composition and energy metabolism following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Obesity. 2010;18(9):1718–24.
Oliveira BAP, Pinhel MAS, Nicoletti CF, Oliveira CC, Quinhoneiro DCG, Noronha NY, et al. UCP1 and UCP3 expression is associated with lipid and carbohydrate oxidation and body composition. Plos One. 2016;11(3):e0150811. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150811.
de Castro Cesar M, de Lima Montebelo MI, Rasera Jr I, De Oliveira Jr AV, Gomes Gonelli PR, Aparecida Cardoso G. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on resting energy expenditure in women. Obes Surg. 2008;18(11):1376–80.
Faria SL, Faria OP, Buffington C, de Almeida CM. Rodrigues de Gouvea H. Energy expenditure before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2012;22(9):1450–5.
Mingrone G, Rosa G, Greco AV, Manco M, Vega N, Hesselink MK, et al. Decreased uncoupling protein expression and intramyocytic triglyceride depletion in formerly obese subjects. Obes Res. 2003;11(5):632–40.
Mahadik SR, Lele RD, Saranath D, Seth A, Parikh V. Uncoupling protein-2 (UCP2) gene expression in subcutaneous and omental adipose tissue of Asian Indians: Relationship to adiponectin and parameters of metabolic syndrome. Adipocyte. 2012;1(2):101–7.
Ray H, Pinteur C, Frering V, Beylot M, Large V. Depot-specific differences in perilipin and hormone-sensitive lipase expression in lean and obese. Lipids Health Dis. 2009;8:58.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant nos. 2013/06563-7 and 2013/08916-4 from the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, B.A.P., de Souza Pinhel, M.A., Nicoletti, C.F. et al. UCP2 and PLIN1 Expression Affects the Resting Metabolic Rate and Weight Loss on Obese Patients. OBES SURG 27, 343–348 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-016-2275-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-016-2275-0