Abstract
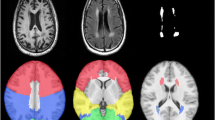
The APOE ε4 allele is associated with cognitive deficits and brain atrophy in older adults, but studies in younger adults are mixed. We examined APOE genotype effects on cognition and brain structure in younger adults and whether genotype effects differed by age and with presence of depression. 157 adults (32 % ε4 carriers, 46 % depressed) between 20 and 50 years of age completed neuropsychological testing, 131 of which also completed 3 T cranial MRI. We did not observe a direct effect of APOE genotype on cognitive performance or structural MRI measures. A significant genotype by age interaction was observed for executive function, where age had less of an effect on executive function in ε4 carriers. Similar interactions were observed for the entorhinal cortex, rostral and caudal anterior cingulate cortex and parahippocampal gyrus, where the effect of age on regional volumes was reduced in ε4 carriers. There were no significant interactions between APOE genotype and depression diagnosis. The ε4 allele benefits younger adults by allowing them to maintain executive function performance and volumes of cingulate and temporal cortex regions with aging, at least through age fifty years.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, D. M., Williams, L. M., Gatt, J. M., Dobson-Stone, C., Kuan, S. A., Todd, E. G., et al. (2007). The contribution of apolipoprotein E alleles on cognitive performance and dynamic neural activity over six decades. Biological Psychology, 75(3), 229–238.
Alexander, G. E., Bergfield, K. L., Chen, K., Reiman, E. M., Hanson, K. D., Lin, L., et al. (2012). Gray matter network associated with risk for alzheimer’s disease in young to middle-aged adults. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(12), 2723–2732.
Bunce, D., Anstey, K. J., Burns, R., Christensen, H., & Easteal, S. (2011). Does possession of apolipoprotein E varepsilon4 benefit cognitive function in healthy young adults? Neuropsychologia, 49(7), 1693–1697.
Byers, A. L., Covinsky, K. E., Barnes, D. E., & Yaffe, K. (2012). Dysthymia and depression increase risk of dementia and mortality among older veterans. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 20(8), 664–672.
Caselli, R. J., Reiman, E. M., Osborne, D., Hentz, J. G., Baxter, L. C., Hernandez, J. L., & Alexander, G. G. (2004). Longitudinal changes in cognition and behavior in asymptomatic carriers of the APOE e4 allele. Neurology, 62(11), 1990–1995.
Corder, E. H., Saunders, A. M., Strittmatter, W. J., Schmechel, D. E., Gaskell, P. C., Small, G. W., et al. (1993). Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science, 261(5123), 921–923.
Corsentino, E. A., Sawyer, K., Sachs-Ericsson, N., & Blazer, D. G. (2009). Depressive symptoms moderate the influence of the apolipoproteine epsilon4 allele on cognitive decline in a sample of community dwelling older adults. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 17(2), 155–165.
Crary, J. F., Trojanowski, J. Q., Schneider, J. A., Abisambra, J. F., Abner, E. L., Alafuzoff, I., et al. (2014). Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): a common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathologica, 128(6), 755–766.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage, 9(2), 179–194.
Desikan, R. S., Segonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., et al. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980.
DiBattista, A. M., Stevens, B. W., Rebeck, G. W., & Green, A. E. (2014). Two alzheimer’s disease risk genes increase entorhinal cortex volume in young adults. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 779.
Diniz, B.S., Butters, M.A., Albert, S.M., Dew, M.A., Reynolds, C.F.,3rd. (2013). Late-life depression and risk of vascular dementia and alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of community-based cohort studies. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 202(5), 329–335.
Donix, M., Burggren, A. C., Suthana, N. A., Siddarth, P., Ekstrom, A. D., Krupa, A. K., et al. (2010). Longitudinal changes in medial temporal cortical thickness in normal subjects with the APOE-4 polymorphism. NeuroImage, 53(1), 37–43.
Dowell, N. G., Ruest, T., Evans, S. L., King, S. L., Tabet, N., Tofts, P. S., & Rusted, J. M. (2013). MRI of carriers of the apolipoprotein E e4 allele-evidence for structural differences in normal-appearing brain tissue in e4+ relative to e4- young adults. NMR in Biomedicine, 26(6), 674–682.
Evans, S., Dowell, N. G., Tabet, N., Tofts, P. S., King, S. L., & Rusted, J. M. (2014). Cognitive and neural signatures of the APOE E4 allele in mid-aged adults. Neurobiology of Aging, 35(7), 1615–1623.
Fennema-Notestine, C., Panizzon, M. S., Thompson, W. R., Chen, C. H., Eyler, L. T., Fischl, B., et al. (2011). Presence of ApoE epsilon4 allele associated with thinner frontal cortex in middle age. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 26(Suppl 3), 49–60.
Filippini, N., Ebmeier, K. P., MacIntosh, B. J., Trachtenberg, A. J., Frisoni, G. B., Wilcock, G. K., et al. (2011). Differential effects of the APOE genotype on brain function across the lifespan. NeuroImage, 54(1), 602–610.
First, M. B., Gibbon, M., Spitzer, R. L., Williams, J. B., & Benjamin, L. S. (1997). Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis II personality disorders (SCID-II). Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Press, Inc..
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 11050–11055.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., van der Kouwe, A. J., Makris, N., Segonne, F., Quinn, B. T., & Dale, A. M. (2004a). Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage, 23(Suppl 1), S69–S84.
Fischl, B., van der Kouwe, A., Destrieux, C., Halgren, E., Segonne, F., Salat, D. H., et al. (2004b). Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 14(1), 11–22.
Han, S. D., & Bondi, M. W. (2008). Revision of the apolipoprotein E compensatory mechanism recruitment hypothesis. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: the Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, 4(4), 251–254.
Honea, R. A., Vidoni, E., Harsha, A., & Burns, J. M. (2009). Impact of APOE on the healthy aging brain: a voxel-based MRI and DTI study. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 18(3), 553–564.
Hostage, C. A., Choudhury, K. R., Murali Doraiswamy, P., Petrella, J. R., & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. (2014). Mapping the effect of the apolipoprotein E genotype on 4-year atrophy rates in an Alzheimer disease-related brain network. Radiology, 271(1), 211–219.
Ihle, A., Bunce, D., & Kliegel, M. (2012). APOE epsilon4 and cognitive function in early life: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychology, 26(3), 267–277.
Jack Jr., C. R., Knopman, D. S., Jagust, W. J., Petersen, R. C., Weiner, M. W., Aisen, P. S., et al. (2013). Tracking pathophysiological processes in alzheimer’s disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurology, 12(2), 207–216.
Jack Jr., C. R., Wiste, H. J., Weigand, S. D., Knopman, D. S., Vemuri, P., Mielke, M. M., et al. (2015). Age, sex, and APOE epsilon4 effects on memory, brain structure, and beta-amyloid across the adult life span. JAMA Neurology, 72(5), 511–519.
Jagust, W. (2013). Vulnerable neural systems and the borderland of brain aging and neurodegeneration. Neuron, 77(2), 219–234.
Jorm, A. F., Mather, K. A., Butterworth, P., Anstey, K. J., Christensen, H., & Easteal, S. (2007). APOE genotype and cognitive functioning in a large age-stratified population sample. Neuropsychology, 21(1), 1–8.
Karlsson, I. K., Bennet, A. M., Ploner, A., Andersson, T. M., Reynolds, C. A., Gatz, M., & Pedersen, N. L. (2015). Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 genotype and the temporal relationship between depression and dementia. Neurobiology of Aging, 36(4), 1751–1756.
Kempton, M. J., Salvador, Z., Munafo, M. R., Geddes, J. R., Simmons, A., Frangou, S., & Williams, S. C. (2011). Structural neuroimaging studies in major depressive disorder: meta-analysis and comparison with bipolar disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68(7), 675–690.
Kim, D. H., Payne, M. E., Levy, R. M., MacFall, J. R., & Steffens, D. C. (2002). APOE genotype and hippocampal volume change in geriatric depression. Biological Psychiatry, 51, 426–429.
Lavretsky, H., Ercoli, L., Siddarth, P., Bookheimer, S., Miller, K., & Small, G. (2003). Apolipoprotein epsilon4 allele status, depressive symptoms, and cognitive decline in middle-aged and elderly persons without dementia. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 11(6), 667–673.
Lind, J., Larsson, A., Persson, J., Ingvar, M., Nilsson, L. G., Backman, L., et al. (2006). Reduced hippocampal volume in non-demented carriers of the apolipoprotein E epsilon4: relation to chronological age and recognition memory. Neuroscience Letters, 396(1), 23–27.
Mahley, R. W., & Huang, Y. (2012). Apolipoprotein e sets the stage: response to injury triggers neuropathology. Neuron, 76(5), 871–885.
Marchant, N. L., King, S. L., Tabet, N., & Rusted, J. M. (2010). Positive effects of cholinergic stimulation favor young APOE epsilon4 carriers. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(5), 1090–1096.
Matura, S., Prvulovic, D., Jurcoane, A., Hartmann, D., Miller, J., Scheibe, M., et al. (2014). Differential effects of the ApoE4 genotype on brain structure and function. NeuroImage, 89, 81–91.
McClintock, S. M., Husain, M. M., Greer, T. L., & Cullum, C. M. (2010). Association between depression severity and neurocognitive function in major depressive disorder: a review and synthesis. Neuropsychology, 24(1), 9–34.
Mondadori, C. R., de Quervain, D. J., Buchmann, A., Mustovic, H., Wollmer, M. A., Schmidt, C. F., et al. (2007). Better memory and neural efficiency in young apolipoprotein E epsilon4 carriers. Cerebral Cortex, 17(8), 1934–1947.
Montgomery, S. A., & Asberg, M. (1979). A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 134, 382–389.
Nathan, B. P., Bellosta, S., Sanan, D. A., Weisgraber, K. H., Mahley, R. W., & Pitas, R. E. (1994). Differential effects of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 on neuronal growth in vitro. Science, 264(5160), 850–852.
Niti, M., Yap, K. B., Kua, E. H., & Ng, T. P. (2009). APOE-epsilon4, depressive symptoms, and cognitive decline in Chinese older adults: Singapore longitudinal aging studies. The Journals of Gerontology Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 64(2), 306–311.
O’Dwyer, L., Lamberton, F., Matura, S., Tanner, C., Scheibe, M., Miller, J., et al. (2012). Reduced hippocampal volume in healthy young ApoE4 carriers: an MRI study. PloS One, 7(11), e48895.
Pizzagalli, D. A. (2011). Frontocingulate dysfunction in depression: toward biomarkers of treatment response. Neuropsychopharmacology, 36, 183–206.
Protas, H. D., Chen, K., Langbaum, J. B., Fleisher, A. S., Alexander, G. E., Lee, W., et al. (2013). Posterior cingulate glucose metabolism, hippocampal glucose metabolism, and hippocampal volume in cognitively normal, late-middle-aged persons at 3 levels of genetic risk for Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurology, 70(3), 320–325.
Qiu, A., Taylor, W. D., Zhao, Z., MacFall, J. R., Miller, M. I., Key, C. R., et al. (2009). APOE related hippocampal shape alteration in geriatric depression. NeuroImage, 44, 620–626.
Rajan, K. B., Wilson, R. S., Skarupski, K. A., Mendes de Leon, C. F., & Evans, D. A. (2014). Gene-behavior interaction of depressive symptoms and the apolipoprotein E {varepsilon}4 allele on cognitive decline. Psychosomatic Medicine, 76(2), 101–108.
Reinvang, I., Espeseth, T., & Westlye, L. T. (2013). APOE-related biomarker profiles in non-pathological aging and early phases of alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(8), 1322–1335.
Richter-Schmidinger, T., Alexopoulos, P., Horn, M., Maus, S., Reichel, M., Rhein, C., et al. (2011). Influence of brain-derived neurotrophic-factor and apolipoprotein E genetic variants on hippocampal volume and memory performance in healthy young adults. Journal of Neural Transmission, 118(2), 249–257.
Risacher, S. L., & Saykin, A. J. (2013). Neuroimaging and other biomarkers for alzheimer’s disease: the changing landscape of early detection. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9, 621–648.
Risacher, S. L., Shen, L., West, J. D., Kim, S., McDonald, B. C., Beckett, L. A., et al. (2010). Longitudinal MRI atrophy biomarkers: relationship to conversion in the ADNI cohort. Neurobiology of Aging, 31(8), 1401–1418.
Rusted, J. M., Evans, S. L., King, S. L., Dowell, N., Tabet, N., & Tofts, P. S. (2013). APOE e4 polymorphism in young adults is associated with improved attention and indexed by distinct neural signatures. NeuroImage, 65, 364–373.
Schultz, M. R., Lyons, M. J., Franz, C. E., Grant, M. D., Boake, C., Jacobson, K. C., et al. (2008). Apolipoprotein E genotype and memory in the sixth decade of life. Neurology, 70(19 Pt 2), 1771–1777.
Sheehan, D. V., Lecrubier, Y., Sheehan, K. H., Amorim, P., Janavs, J., Weiller, E., et al. (1998). The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Inventory (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, Suppl 20, 22–33.
Sheline, Y. I., Pieper, C. F., Barch, D. M., Welsh-Boehmer, K., McKinstry, R. C., MacFall, J. R., et al. (2010). Support for the vascular depression hypothesis in late-life depression: results of a 2-site, prospective, antidepressant treatment trial. Archives of General Psychiatry, 67(3), 277–285.
Skoog, I., Waern, M., Duberstein, P., Blennow, K., Zetterberg, H., Borjesson-Hanson, A., et al. (2015). A 9-year prospective population-based study on the association between the APOE*E4 allele and late-life depression in Sweden. Biological Psychiatry, 78(10), 730–736.
Steffens, D. C., Norton, M. C., Hart, A. D., Skoog, I., Corcoran, C., & Breitner, J. C. (2003). Apolipoprotein E genotype and major depression in a community of older adults. The cache county study. Psychological Medicine, 33, 541–547.
Strittmatter, W. J., Saunders, A. M., Schmechel, D., Pericak-Vance, M., Enghild, J., Salvesen, G. S., & Roses, A. D. (1993). Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90, 1977–1981.
Suri, S., Heise, V., Trachtenberg, A. J., & Mackay, C. E. (2013). The forgotten APOE allele: a review of the evidence and suggested mechanisms for the protective effect of APOE varepsilon2. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(10 Pt 2), 2878–2886.
Taylor, J. L., Scanlon, B. K., Farrell, M., Hernandez, B., Adamson, M. M., Ashford, J. W., et al. (2014). APOE-epsilon4 and aging of medial temporal lobe gray matter in healthy adults older than 50 years. Neurobiology of Aging, 35(11), 2479–2485.
Wishart, H. A., Saykin, A. J., McAllister, T. W., Rabin, L. A., McDonald, B. C., Flashman, L. A., et al. (2006). Regional brain atrophy in cognitively intact adults with a single APOE epsilon4 allele. Neurology, 67(7), 1221–1224.
Yu, Y. W., Lin, C. H., Chen, S. P., Hong, C. J., & Tsai, S. J. (2000). Intelligence and event-related potentials for young female human volunteer apolipoprotein E epsilon4 and non-epsilon4 carriers. Neuroscience Letters, 294(3), 179–181.
Yuan, Y., Zhang, Z., Bai, F., You, J., Yu, H., Shi, Y., & Liu, W. (2010). Genetic variation in apolipoprotein E alters regional gray matter volumes in remitted late-onset depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 121(3), 273–277.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) grant R01 MH077745. It was further supported by CTSA award UL1TR000445 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) and conducted in part using the resources of the Advanced Computing Center for Research and Education at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
All authors (including Dr. Taylor, Mr. Boyd, Ms. Turner, Mr. McQuoid, Dr. Ashley-Koch, Dr. MacFall, Dr. Saleh, and Dr. Potter) declare they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Table 1
(DOCX 90 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, W.D., Boyd, B., Turner, R. et al. APOE ε4 associated with preserved executive function performance and maintenance of temporal and cingulate brain volumes in younger adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 194–204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9522-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9522-9