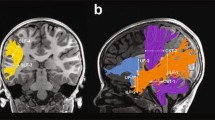
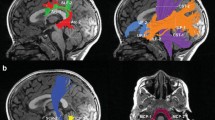
Abstract
Development of reading skills is vulnerable to disruption in children treated for brain tumors. Interventions, remedial and prophylactic, are needed to mitigate reading and other learning difficulties faced by survivors. A functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study was conducted to investigate long-term effects of a prophylactic reading intervention administered during radiation therapy in children treated for medulloblastoma. The fMRI study included 19 reading-intervention (age 11.7 ± 0.6 years) and 21 standard-of-care (age 12.1 ± 0.6 years) medulloblastoma survivors, and 21 typically developing children (age 12.3 ± 0.6 years). The survivors were 2.5 [1.2, 5.4] years after completion of tumor therapies and reading-intervention survivors were 2.9 [1.6, 5.9] years after intervention. Five fMRI tasks (Rapid Automatized Naming, Continuous Performance Test using faces and letters, orthographic and phonological processing of letter pairs, implicit word reading, and story reading) were used to probe reading-related neural activation. Woodcock-Johnson Reading Fluency, Word Attack, and Sound Awareness subtests were used to evaluate reading abilities. At the time of fMRI, Sound Awareness scores were significantly higher in the reading-intervention group than in the standard-of-care group (p = 0.046). Brain activation during the fMRI tasks was detected in left inferior frontal, temporal, ventral occipitotemporal, and subcortical regions, and differed among the groups (p < 0.05, FWE). The pattern of group activation differences, across brain areas and tasks, was a normative trend in the reading-intervention group. Standardized reading scores and patterns of brain activation provide evidence of long-term effects of prophylactic reading intervention in children treated for medulloblastoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitan, T., Burman, D. D., Lu, D., Cone, N. E., Gitelman, D. R., Mesulam, M. M., et al. (2006). Weaker top-down modulation from the left inferior frontal gyrus in children. NeuroImage, 33, 991–998.
Booth, J. R., Wood, L., Lu, D., Houk, J. C., & Bitan, T. (2007). The role of the basal ganglia and cerebellum in language processing. Brain Research, 1133, 136–144.
Butler, R. W., & Haser, J. K. (2006). Neurocognitive effects of treatment for childhood cancer. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 12, 184–191.
Butler, R. W., Copeland, D. R., Fairclough, D. L., Mulhern, R. K., Katz, E. R., Kazak, A. E., et al. (2008). A multicenter, randomized clinical trial of a cognitive remediation program for childhood survivors of a pediatric malignancy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 76, 367–378.
Cohen, L., Martinaud, O., Lemer, C., Lehericy, S., Samson, Y., Obadia, M., et al. (2003). Visual word recognition in the left and right hemispheres: anatomical and functional correlates of peripheral alexias. Cerebral Cortex, 13, 1313–1333.
Conklin, H. M., Li, C., Xiong, X., Ogg, R. J., & Merchant, T. E. (2008). Predicting change in academic abilities after conformal radiation therapy for localized ependymoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 26, 3965–3970.
Conklin, H. M., Lawford, J., Jasper, B. W., Morris, E. B., Howard, S. C., Ogg, S. W., et al. (2009). Side effects of methylphenidate in childhood cancer survivors: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics, 124, 226–233.
Conklin, H. M., Helton, S., Ashford, J., Mulhern, R. K., Reddick, W. E., Brown, R., et al. (2010a). Predicting methylphenidate response in long-term survivors of childhood cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 35, 144–155.
Conklin, H. M., Reddick, W. E., Ashford, J., Ogg, S., Howard, S. C., Morris, E. B., et al. (2010b). Long-term efficacy of methylphenidate in enhancing attention regulation, social skills, and academic abilities of childhood cancer survivors. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 28, 4465–4472.
Dennis, M., Spiegler, B. J., Hetherington, C. R., & Greenberg, M. L. (1996). Neuropsychological sequelae of the treatment of children with medulloblastoma. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 29, 91–101.
Friederici, A. D. (2006). What’s in control of language? Nature Neuroscience, 9, 991–992.
Gajjar, A., Packer, R. J., Foreman, N. K., Cohen, K., Haas-Kogan, D., & Merchant, T. E. (2013). Children’s Oncology Group’s 2013 blueprint for research: central nervous system tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer, 60, 1022–1026.
Gebauer, D., Fink, A., Kargl, R., Reishofer, G., Koschutnig, K., Purgstaller, C., et al. (2012). Differences in brain function and changes with intervention in children with poor spelling and reading abilities. PLoS ONE, 7, e38201.
Gibson, P., Tong, Y., Robinson, G., Thompson, M. C., Currle, D. S., Eden, C., et al. (2010). Subtypes of medulloblastoma have distinct developmental origins. Nature, 468, 1095–1099.
Gillam, R. B., Loeb, D. F., Hoffman, L. M., Bohman, T., Champlin, C. A., Thibodeau, L., et al. (2008). The efficacy of fast ForWord language intervention in school-age children with language impairment: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 51, 97–119.
Glauser, T. A., & Packer, R. J. (1991). Cognitive deficits in long-term survivors of childhood brain tumors. Childs Nervous System, 7, 2–12.
Hardy, K. K., Willard, V. W., Allen, T. M., & Bonner, M. J. (2013). Working memory training in survivors of pediatric cancer: a randomized pilot study. Psychooncology, 22, 1856–1865.
Ketteler, D., Kastrau, F., Vohn, R., & Huber, W. (2008). The subcortical role of language processing. High level linguistic features such as ambiguity-resolution and the human brain; an fMRI study. NeuroImage, 39, 2002–2009.
Kherif, F., Josse, G., & Price, C. J. (2011). Automatic top-down processing explains common left occipito-temporal responses to visual words and objects. Cerebral Cortex, 21, 103–114.
Liang, K. Y., & Zeger, S. L. (1986). Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika, 73, 13–22.
Liu, T. T. (2004). Efficiency, power, and entropy in event-related fMRI with multiple trial types part II: design of experiments. NeuroImage, 21, 401–413.
Loeb, D. F., Gillam, R. B., Hoffman, L., Brandel, J., & Marquis, J. (2009). The effects of fast ForWord language on the phonemic awareness and reading skills of school-age children with language impairments and poor reading skills. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 18, 376–387.
Maddrey, A. M., Bergeron, J. A., Lombardo, E. R., McDonald, N. K., Mulne, A. F., Barenberg, P. D., et al. (2005). Neuropsychological performance and quality of life of 10 year survivors of childhood medulloblastoma. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 72, 245–253.
Merchant, T. E., Happersett, L., Finlay, J. L., & Leibel, S. A. (1999). Preliminary results of conformal radiation therapy for medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology, 1, 177–187.
Misra, M., Katzir, T., Wolf, M., & Poldrack, R. A. (2004). Neural Systems for rapid automatized naming in skilled readers: unraveling the RAN-reading relationship. Scientific Studies of Reading, 8, 241–256.
Mulhern, R. K., Kepner, J. L., Thomas, P. R., Armstrong, F. D., Friedman, H. S., & Kun, L. E. (1998). Neuropsychologic functioning of survivors of childhood medulloblastoma randomized to receive conventional or reduced-dose craniospinal irradiation: a pediatric oncology group study. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 16, 1723–1728.
Mulhern, R. K., Reddick, W. E., Palmer, S. L., Glass, J. O., Elkin, T. D., Kun, L. E., et al. (1999). Neurocognitive deficits in medulloblastoma survivors and white matter loss. Annals of Neurology, 46, 834–841.
Mulhern, R. K., Khan, R. B., Kaplan, S., Helton, S., Christensen, R., Bonner, M., et al. (2004). Short-term efficacy of methylphenidate: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial among survivors of childhood cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 22, 4795–4803.
Mulhern, R. K., Palmer, S. L., Merchant, T. E., Wallace, D., Kocak, M., Brouwers, P., et al. (2005). Neurocognitive consequences of risk-adapted therapy for childhood medulloblastoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23, 5511–5519.
Norton, E. S., & Wolf, M. (2012). Rapid automatized naming (RAN) and reading fluency: implications for understanding and treatment of reading disabilities. Annual Review of Psychology, 63, 427–452.
Ogg, R. J., Zou, P., Allen, D. N., Hutchins, S. B., Dutkiewicz, R. M., & Mulhern, R. K. (2008). Neural correlates of a clinical continuous performance test. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 26, 504–512.
Palmer, S. L., Leigh, L., Ellison, S. C., Onar-Thomas, A., Wu, S., Qaddoumi, I., et al. (2014). Feasibility and efficacy of a computer-based intervention aimed at preventing reading decoding deficits among children undergoing active treatment for medulloblastoma: results of a randomized trial. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 39, 450–458.
Price, C. J. (2012). A review and synthesis of the first 20 years of PET and fMRI studies of heard speech, spoken language and reading. NeuroImage, 62, 816–847.
Price, C. J. (2013). Current themes in neuroimaging studies of reading. Brain and Language, 125, 131–133.
Price, C. J., & Devlin, J. T. (2011). The interactive account of ventral occipitotemporal contributions to reading. Trends in Cognitive Science, 15, 246–253.
Pugh, K. R., Landi, N., Preston, J. L., Mencl, W. E., Austin, A. C., Sibley, D., et al. (2013). The relationship between phonological and auditory processing and brain organization in beginning readers. Brain and Language, 125, 173–183.
Ramsden, S., Richardson, F. M., Josse, G., Shakeshaft, C., Seghier, M. L., & Price, C. J. (2013). The influence of reading ability on subsequent changes in verbal IQ in the teenage years. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 6, 30–39.
Raschle, N. M., Zuk, J., & Gaab, N. (2012). Functional characteristics of developmental dyslexia in left-hemispheric posterior brain regions predate reading onset. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 2156–2161.
Ries, M. L., Boop, F. A., Griebel, M. L., Zou, P., Phillips, N. S., Johnson, S. C., et al. (2004). Functional MRI and Wada determination of language lateralization: a case of crossed dominance. Epilepsia, 45, 85–89.
Rodgers, S. P., Trevino, M., Zawaski, J. A., Gaber, M. W., & Leasure, J. L. (2013). Neurogenesis, exercise, and cognitive late effects of pediatric radiotherapy. Neural Plasticity, 2013, 698528.
Romine, C. B., & Reynolds, C. R. (2005). A model of the development of frontal lobe functioning: findings from a meta-analysis. Applied Neuropsychology, 12, 190–201.
Schreiber, J. E., Gurney, J. G., Palmer, S. L., Bass, J. K., Wang, M., Chen, S., et al. (2014). Examination of risk factors for intellectual and academic outcomes following treatment for pediatric medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology, 16(8), 1129–36.
Seghier, M. L., & Price, C. J. (2010). Reading aloud boosts connectivity through the putamen. Cerebral Cortex, 20, 570–582.
Seghier, M. L., & Price, C. J. (2011). Explaining left lateralization for words in the ventral occipitotemporal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 14745–14753.
Shaywitz, B. A., Shaywitz, S. E., Blachman, B. A., Pugh, K. R., Fulbright, R. K., Skudlarski, P., et al. (2004). Development of left occipitotemporal systems for skilled reading in children after a phonologically- based intervention. Biological Psychiatry, 55, 926–933.
Simos, P. G., Fletcher, J. M., Bergman, E., Breier, J. I., Foorman, B. R., Castillo, E. M., et al. (2002). Dyslexia-specific brain activation profile becomes normal following successful remedial training. Neurology, 58, 1203–1213.
Temple, E., Poldrack, R. A., Salidis, J., Deutsch, G. K., Tallal, P., Merzenich, M. M., et al. (2001). Disrupted neural responses to phonological and orthographic processing in dyslexic children: an fMRI study. Neuroreport, 12, 299–307.
Temple, E., Deutsch, G. K., Poldrack, R. A., Miller, S. L., Tallal, P., Merzenich, M. M., et al. (2003). Neural deficits in children with dyslexia ameliorated by behavioral remediation: evidence from functional MRI. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 2860–2865.
Turkeltaub, P. E., Gareau, L., Flowers, D. L., Zeffiro, T. A., & Eden, G. F. (2003). Development of neural mechanisms for reading. Nature Neuroscience, 6, 767–773.
Turkeltaub, P. E., Flowers, D. L., Lyon, L. G., & Eden, G. F. (2008). Development of ventral stream representations for single letters. Ann NY Acad Sci, 1145, 13–29.
Wolfe, K. R., Madan-Swain, A., Hunter, G. R., Reddy, A. T., Banos, J., & Kana, R. K. (2013). An fMRI investigation of working memory and its relationship with cardiorespiratory fitness in pediatric posterior fossa tumor survivors who received cranial radiation therapy. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 60, 669–675.
Woodcock, R. W., McGrew, K. S., & Mather, N. (2001). Woodcock-Johnson tests of achivement (3rd ed.). Rolling Meadows: Riverside Publishing.
Zou, P., Mulhern, R. K., Butler, R. W., Li, C. S., Langston, J. W., & Ogg, R. J. (2005). BOLD responses to visual stimulation in survivors of childhood cancer. NeuroImage, 24, 61–69.
Zou, P., Li, Y., Conklin, H. M., Mulhern, R. K., Butler, R. W., & Ogg, R. J. (2012). Evidence of change in brain activity among childhood cancer survivors participating in a cognitive remediation program. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 27, 915–929.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Cancer Center Support (CORE) grant CA21765 from the National Cancer Institute, grant HD049888 from the National Institute for Child Health and Human Development, grant RR029005 from the National Center for Research Resources, and by ALSAC.
Conflict of interest
Ping Zou, Heather M. Conklin, Matthew A. Scoggins, Yimei Li, Xingyu Li, Melissa M. Jones, Shawna L. Palmer, Amar Gaggar, and Robert J. Ogg declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, P., Conklin, H.M., Scoggins, M.A. et al. Functional MRI in medulloblastoma survivors supports prophylactic reading intervention during tumor treatment. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 258–271 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9390-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9390-8