Abstract
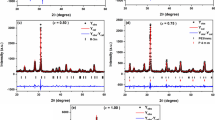
N-type Cu-doped Bi2Te2.85Se0.15 thermoelectric materials were prepared by pulse-current sintering under cyclic uniaxial pressure, and the effect of the cyclic uniaxial pressure on texture and thermoelectric properties was investigated. Cu x Bi2Te2.85Se0.15 (x = 0−0.03) powder prepared by mechanical alloying was sintered at 673 K using pulse-current heating under 100 MPa of cyclic uniaxial pressure. X-ray diffraction patterns and electron backscattered diffraction analyses showed that the cyclic uniaxial pressure was effective for texture control. The flattened crystal grains were stacked in the thickness direction of the sintered materials and the hexagonal c-plane strongly tended to align in the direction perpendicular to the uniaxial pressure. As a result of this crystal alignment, the electrical resistivity in the direction perpendicular to the uniaxial pressure became smaller than that of equivalent samples prepared with a constant uniaxial pressure. The smaller resistivity led to a larger power factor, and the figure␣of merit was improved by the application of cyclic uniaxial pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.M. Yim and F.D. Rosi, Solid State Electron. 15, 1121 (1972).
J.R. Wiese and L. Muldawer, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 15, 13 (1960).
H. Kaibe, Y. Tanaka, M. Sakata, and I. Nishida, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 50, 945 (1989).
I.J. Ohsugi, T. Kojima, and I.A. Nishida, J. Appl. Phys. 68, 5692 (1990).
M. Carle, P. Pierrat, C.L. Graver, S. Scherrer, and H. Scherrer, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 56, 201 (1995).
R. Martin-Lopez, B. Lenoir, A. Dauscher, H. Scherrer, and S. Scherrer, Solid State Commun. 108, 285 (1998).
J. Yang, T. Aizawa, A. Yamamoto, and T. Ohta, Mater. Chem. Phys. 70, 90 (2001).
J.J. Shen, S.N. Zhang, S.H. Yang, Z.Z. Yin, T.J. Zhu, and X.B. Zhao, J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 161 (2011).
J.S. Dyck, B. Mao, J. Wang, S. Dorroh, and C. Burda, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 1408 (2012).
Z.A. Munirw, D.V. Quach, and M. Ohyanagi, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1 (2011).
R. Orrù, R. Licheri, A.M. Locci, A. Cincotti, and G. Cao, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 63, 127 (2009).
W. Zhu, W. Zhao, H. Zhou, J. Yu, D. Tang, Z. Liu, and Q. Zhang, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 1768 (2014).
H. Kim and S. Hong, J. Alloys Compd. 586, S428 (2014).
G. Delaizir, G. Bernard-Granger, J. Monnier, R. Grodzki, O. Kim-Hak, P.-D. Szkutnik, M. Soulier, S. Saunier, D. Goeuriot, O. Rouleau, J. Simon, C. Godart, and C. Navone, Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1954 (2012).
N. Bomshtein, G. Spiridonov, Z. Dashevsky, and Y. Gelbstein, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 1546 (2012).
Y. Pan, T.R. Wei, Q. Cao, and J.F. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng., B 197, 75 (2015).
D.H. Kim, C. Kim, S.H. Heo, and H. Kim, Acta Mater 59, 405 (2011).
H. Kitagawa, K. Nagao, N. Mimura, S. Morito, and K. Kikuchi, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 1574 (2014).
O.B. Sokolov, S.Y. Skipidarov, and N.I. Duvankov, J. Thermoelectr. 4, 48 (2003).
O.B. Sokolov, S.Y. Skipidarov, N.I. Duvankov, and G.G. Shabunina, J. Cryst. Growth 262, 442 (2004).
D.B. Hyun, J.S. Hwang, B.C. You, T.S. Oh, and C.W. Hwang, J. Mater. Sci. 33, 5595 (1998).
W.S. Liu, Q. Zhang, Y. Lan, S. Chen, X. Yan, Q. Zhang, H. Wang, D. Wang, G. Chen, and Z. Ren, Adv. Energy Mater. 1, 577 (2011).
T.E. Svechnikova, P.P. Konstantinov, and G.T. Alekseeva, Inorg. Mater. 36, 556 (2000).
H. Kitagawa, T. Matsuura, T. Kato, and K. Kamata, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 1870 (2015).
A.J. Schwartz, M. Kumar, and B.L. Adams, eds., Electron Backscatter Diffraction in Materials Science (New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum, 2000), pp. 51.
F. Izumi and K. Momma, Solid State Phenom. 130, 15 (2007).
D.L. Greenaway and G. Harbeke, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 26, 1585 (1965).
Acknowledgement
This work was partly supported by the “Supporting-Industry Project” of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitagawa, H., Mimura, N., Takimura, K. et al. Thermoelectric Properties of Cu-doped Bi2Te2.85Se0.15 Prepared by Pulse-Current Sintering Under Cyclic Uniaxial Pressure. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 1523–1528 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-015-4094-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-015-4094-9