Abstract
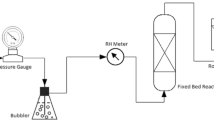
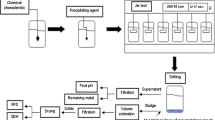
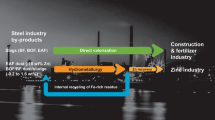
The oxidation behavior of sulfur in desulfurization slag generated from the secondary steelmaking process with air has been investigated in the temperature range of 973 K to 1373 K (700 °C to 1100 °C). Although a high removal rate of sulfur is not achieved at temperatures lower than 1273 K (1000 °C) because of the formation of CaSO4, most of the sulfur is rapidly removed from slag as SO2 gas in the 1273 K to 1373 K (700 °C to 1100 °C) range. This finding indicates that the desulfurization slag generated from the secondary steelmaking process can be reused as a desulfurized flux through air oxidation, making it possible to reduce significantly the amount of desulfurization slag for disposal.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.J. Fincham and F.D. Richardson: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1954, vol. 178, pp. 4–15.
Slag Atlas, 2nd ed., VDEh, Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Dusseldorf, Germany, 1995, pp. 90.
A.K. Chatterjee and G.I. Zhmoidin: J. Mater. Sci., 1972, vol. 7, pp. 93–97.
A.I. Zaitsev, N.V. Korolyov, and B.M. Mogutnov: J. Mater. Sci., 1991, vol. 26, pp.1588–1600.
M. Hino, S. Kitagawa, and S. Ban-Ya: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 35–41.
M. Ohta, T. Kubo, and K Morita: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 2003, vol. 89, pp. 742–49.
Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) K 0058, 2005.
R. Inoue and H. Suito: ISIJ Int., 2002, vol. 42, pp. 785–93.
A.B. Fox, K.C. Mills, D. Lever, M.C.C. Bezerra, C. Valadares, I. Inamuno, J. J. Laraudogoitia, and J. Gisby: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 1051–58.
T. Nagasaka and K. Yokoyama: Japanese Patent 2010-095793.
K. Kobayashi, T. Hiraki, K. Matsubae, and T. Nagasaka: Int. J. High Temp. Mater. Proc., in press.
Landolt-Börnstein: Thermodynamic Properties of Inorganic Material, Scientific Group Thermodata Europe (SGTE), Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg, Germany, 1999.
G. Marbân, M. García-Calzada, and A.B. Fuertes: Chem. Eng. Sci., 1999, vol. 54, pp. 77–90.
D.C. Lynch and J.F. Elliott: Metall. Trans. B, 1980, vol. 11B, pp. 415–25.
B. García, Y. Yamazaki, and T. Takarada: Fuel, 1999, vol. 78, pp. 883–90.
V.P. Glushko: Thermocenter of the Russian Academy of Sciences, IVTAN Association, Izhorskaya 13/19, 127412 Moscow, Russia, 1994.
I. Barin: Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, VCH Verlags Gesellschaft, Weinheim, Germany, 1989.
A.D. Pelton, J.B. See, and J.F. Elliott: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1163–71.
B. Agrawal, G.J. Yurek, and J.F. Elliott: Metall. Trans. B, 1983, vol. 14B, pp. 221–30.
T. Takahashi, S. Kashiwakura, K. Kanehashi, and T. Nagasaka: Energy Fuels, 2009, vol. 23, pp. 1778–80.
T. Takahashi, S. Kashiwakura, K. Kanehashi, S. Hayashi, and T. Nagasaka: Env. Sci. Tech., 2011, vol. 45, pp. 890–95.
S.R. Kelemen, G.N. George, and M.L. Gorbaty: Fuel, 1990, vol. 69, pp. 939–44.
J. Fukumi, C. Taki, T. Hatanaka, and H. Ogura: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1990, vol. 76, pp. 1956–63.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Grant-In-Aid for scientific research (The Japan Society for Promotion of Science in 2009-2012, contract Number 21246114) and an ISIJ Research Promotion Grant (The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan in 2009–2010). T.N. deeply appreciates the great guidance, support, and encouragement given by Professor R.J. Fruehan, Professor A.W. Cramb (now Provost of Illinois Institute of Technology), Professor and Mrs. I. Jimbo (now Tokai University, Japan), Dr. Naoki Kikuchi (now JFE Steel, Japan), and Ms. M. Lesko, Center for Iron and Steelmaking Research, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA. Careful correction of manuscript by Ms. Liz Webeck is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 14, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiraki, T., Kobayashi, J., Urushibata, S. et al. Removal of Sulfur from CaF2 Containing Desulfurization Slag Exhausted from Secondary Steelmaking Process by Oxidation. Metall Mater Trans B 43, 703–709 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-012-9685-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-012-9685-8