Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effect of Nigella sativa (NS) extract on memory performance and its possible mechanisms in scopolamine (Sco)-induced spatial memory impairment model using Morris water maze test.
Methods
Thirty-two male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups. The control group received saline instead of both NS extract and Sco. The Sco group was treated by saline for two weeks, and was injected by Sco (2 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) 30 min before each trail in Morris water maze test. Sco+NS 200 and Sco+NS 400 groups were daily treated by 200 or 400 mg/kg of NS (intraperitoneally) for two weeks, respectively, and were finally injected by Sco 30 min before Morris water maze test. The brains of animals were removed to determine the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity and oxidative stress criteria in cortical tissues.
Results
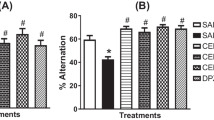
Time latency and path length in the Sco group were significantly higher than in the control group (P<0.01), while the Sco+NS 400 group showed a significantly shorter traveled path length and time latency compared with the Sco group (P<0.01). AChE activity in the cortical tissues of the Sco group was significantly higher than the control group (P<0.01), while AChE activity in the Sco+NS 200 and Sco+NS 400 groups was lower than the Sco group (P<0.01). Following Sco administration, malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations were increased (P<0.01) in comparison with the control group, while cortical total thiol content decreased (P<0.01). Pretreatment with extracts caused a significant elevation in cortical total thiol content (P<0.01) and reduction in cortical MDA concentration (P<0.01) compared with the Sco group.
Conclusions
Hydro-alcoholic extract of NS prevents Sco-induced spatial memory deficits and decreases the AChE activity as well as oxidative stress of brain tissues in rats. Our results support the traditional belief about the beneficial effects of NS in nervous system. Moreover, further investigations are needed for better understanding of this protective effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang JZ, Wang ZF. Role of melatonin in Alzheimer-like neurodegeneration. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2006;27:41–49.
Halliwell B. Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem 1992;59:1609–1623.
Frlich L, Riederer P. Free radical mechanisms in dementia of Alzheimer type and the potential for antioxidative treatment. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1995;45:443–446.
Qureshi GA, Baig S, Sarwar M, Parvez SH. Neurotoxicity, oxidative stress and cerebrovascular disorders. Neurotoxicology 2004;25:121–138.
Bickford PC, Gould T, Briederick L, Chadman K, Pollock A, Young D, et al. Antioxidant-rich diets improve cerebellar physiology and motor learning in aged rats. Brain Res 2000;866:211–217.
Drachman DA. Memory and cognitive function in man: does the cholinergic system have a specific role? Neurology 1977;27:783–790.
Perry EK, Tomlinson BE, Blessed G, Bergmann K, Gibson PH, Perry RH. Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental test scores in senile dementia. Br Med J 1978;2:1457–1459.
Glick SD, Zimmerberg B. Amnesic effects of scopolamine. Behav Biol 1972;7:245–254.
Fan Y, Hu J, Li J, Yang Z, Xin X, Wang J, et al. Effect of acidic oligosaccharide sugar chain on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats and its related mechanisms. Neurosci Lett 2005;374:222–226.
Khalifa AE. Pro-oxidant activity of zuclopenthixol in vivo: differential effect of the drug on brain oxidative status of scopolamine-treated rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 2004;23:439–445.
Bartus RT. Evidence for a direct cholinergic involvement in the scopolamine-induced amnesia in monkeys: effects of concurrent administration of physostigmine and methylphenidate with scopolamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1978;9:833–836.
Mewaldt SP, Ghoneim MM. The effects and interactions of scopolamine, physostigmine and methamphetamine on human memory. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1979;10:205–210.
Yang MH, Yoon KD, Chin YW, Park JH, Kim SH, Kim YC, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Dioscorea opposita on scopolamineinduced memory impairment in in vivo behavioral tests and in vitro assays. J Ethnopharmacol 2009;121:130–134.
Boskabady MH, Farhadi J. The possible prophylactic effect of Nigella sativa seed aqueous extract on respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function tests on chemical war victims: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med 2008;14:1137–1144.
Boskabady MH, Javan H, Sajady M, Rakhshandeh H. The possible prophylactic effect of Nigella sativa seed extract in asthmatic patients. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2007;21:559–566.
Boskabady MH, Keyhanmanesh R, Saadatloo MA. Relaxant effects of different fractions from Nigella sativa L. on guinea pig tracheal chains and its possible mechanism(s). Indian J Exp Biol 2008;46:805–810.
Boskabady MH, Mohsenpoor N, Takaloo L. Antiasthmatic effect of Nigella sativa in airways of asthmatic patients. Phytomedicine 2010;17:707–713.
Boskabady MH, Shafei MN, Parsaee H. Effects of aqueous and macerated extracts from Nigella sativa on guinea pig isolated heart activity. Pharmazie 2005;60:943–948.
Boskabady MH, Shirmohammadi B, Jandaghi P, Kiani S. Possible mechanism(s) for relaxant effect of aqueous and macerated extracts from Nigella sativa on tracheal chains of guinea pig. BMC Pharmacol 2004;4:3–8.
Keyhanmanesh R, Boskabady MH, Ebrahimi Saadatloo MA, Saeed khamnei. The contribution of water and lipid soluble substances in the relaxant effects of Nigella sativa extract on guinea pig tracheal smooth muscle (in vitro ). Iranian J Basic Med Sci 2007;10:154–161.
Ali BH, Blunden G. Pharmacological and toxicological properties of Nigella sativa. Phytother Res 2003;17:299–305.
Mahmood MS, Gilani AH, Khwaja A, Rashid A, Ashfaq MK. The in vitro effect of aqueous extract of Nigella sativa seeds on nitric oxide production. Phytother Res 2003;17:921–924.
El-Mahmoudy A, Matsuyama H, Borgan MA, Shimizu Y, El-Sayed MG, Minamoto N, et al. Thymoquinone suppresses expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 2002;2:1603–1611.
Kanter M, Coskun O, Uysal H. The antioxidative and antihistaminic effect of Nigella sativa and its major constituent, thymoquinone on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage. Arch Toxicol 2006;80:217–224.
Mansour MA, Ginawi OT, El-Hadiyah T, El-Khatib AS, Al-Shabanah OA, Al-Sawaf HA. Effects of volatile oil constituents of Nigella sativa on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice: evidence for antioxidant effects of thymoquinone. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 2001;110:239–251.
Ismail M, Al-Naqeep G, Chan KW. Nigella sativa thymoquinonerich fraction greatly improves plasma antioxidant capacity and expression of antioxidant genes in hypercholesterolemic rats. Free Radic Biol Med 2010;48:664–672.
Yaman I, Balikci E. Protective effects of Nigella sativa against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2010;62:183–190.
Uz E, Bayrak O, Kaya A, Bayrak R, Uz B, Turgut FH, et al. Nigella sativa oil for prevention of chronic cyclosporine nephrotoxicity: an experimental model. Am J Nephrol 2008;28:517–522.
Dollah MA, Parhizkar S, Izwan M. Effect of Nigella sativa on the kidney function in rats. Avicenna J Phytomed 2012;3:152–158.
Hosseinzadeh H, Parvardeh S, Asl MN, Sadeghnia HR, Ziaee T. Effect of thymoquinone and Nigella sativa seeds oil on lipid peroxidation level during global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat hippocampus. Phytomedicine 2007;14:621–627.
Mousavi SH, Tayarani-Najaran Z, Asghari M, Sadeghnia HR. Protective effect of Nigella sativa extract and thymoquinone on serum/glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cells death. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2010;30:591–598.
Hosseini M, Headari R, Oryan S, Hadjzadeh MA, Saffarzadeh F, Khazaei M. The effect of chronic administration of L-arginine on the learning and memory of estradiol-treated ovariectomized rats tested in the Morris water maze. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2010;65:803–807.
Hosseini M, Dastghaib SS, Rafatpanah H, Hadjzadeh MA, Hossein H, Farrokhi I. Nitric oxide contributes in learning and memory deficit in offspring of hypothyroid female rats. Clinics 2010;65:1–7.
Azizi-Malekabadi H, Hosseini M, Saffarzadeh F, Karami R, Khodabandehloo F. Chronic treatment with the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, L-NAME, attenuates estradiol-mediated improvement of learning and memory in ovariectomized rats. Clinics 2011;66:1–7.
Hosseini M, Nemati-Karimooy HA, Hadjzadeh MA, Safari V. Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor aminoguanidine, differently affects Morris water maze tasks of ovariectomized and naïve female rats. Acta Physiol Hung 2011;98:421–432.
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 1961;7:88–95.
Isoma K, Ishikawa M, Ohta M, Ogawa Y, Hasegawa H, Kohda T, et al. Effects of T-82, a new quinoline derivative, on cholinesterase activity and extracellular acetylcholine concentration in rat brain. Jpn J Pharmacol 2002;88:206–212.
Zhong SZ, Ge QH, Qu R, Li Q, Ma SP. Paeonol attenuates neurotoxicity and ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose in ICR mice. J Neurol Sci 2009;277:58–64.
Hosseinzadeh H, Sadeghnia HR. Safranal, a constituent of Crocus sativus (saffron), attenuated cerebral ischemia induced oxidative damage in rat hippocampus. J Pharm Pharm Sci 2005;8:394–399.
Janero DR. Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and peroxidative tissue injury. Free Radical Bio Med 1990;9:515–540.
Hall ED, Andrus PK. Measurement of oxygen radicals and lipid peroxidation in neural tissues. Curr Protoc Neurosci 2009;17:1–51.
Kanter M, Coskun O, Korkmaz A, Oter S. Effects of Nigella sativa on oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 2004;279:685–691.
Kanter M, Coskun O, Budancamanak M. Hepatoprotective effects of Nigella sativa L and Urtica dioica L on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzyme systems and liver enzymes in carbon tetrachloride-treated rats. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:6684–6688.
Kanter M, Demir H, Karakaya C, Ozbek H. Gastroprotective activity of Nigella sativa L oil and its constituent, thymoquinone against acute alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:6662–6666.
Bonin-Guillaume S, Zekry D, Giacobini E, Gold G, Michel JP. The economical impact of dementia. Presse Med 2005;34:35–41.
Keyhanmanesh R, Boskabady MH, Eslamizadeh MJ, Khamneh S, Ebrahimi MA. The effect of thymoquinone, the main constituent of Nigella sativa on tracheal responsiveness and white blood cell count in lung lavage of sensitized guinea pigs. Planta Med 2010;76:218–22.
Shafei MN, Boskabady MH, Parsaee H. Effect of aqueous extract from Nigella sativa L. on guinea pig isolated heart. Indian J Exp Biol 2005;43:635–639.
Rakhshandeh H, Vahdati-Mashhadian N, Khajekaramadini M. in vitro and in vivo study of the antibacterial effects of Nigella sativa methanol extract in dairy cow mastitis. Avicenna J Phytomed 2011;1:29–35.
Bashir MU, Qureshi HJ. Analgesic effect of Nigella sativa seeds extract on experimentally induced pain in albino mice. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2010;20:464–467.
Dirjomuljono M, Kristyono I, Tjandrawinata RR, Nofiarny D. Symptomatic treatment of acute tonsillo-pharyngitis patients with a combination of Nigella sativa and Phyllanthus niruri extract. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2008;46:295–306.
Ghannadi A, Hajhashemi V, Jafarabadi H. An investigation of the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Nigella sativa seed polyphenols. J Med Food 2005;8:488–493.
Hall ST, Puech A, Schaffler K, Wesnes K, Gamzu ER. Early clinical testing of cognition enhancers: prediction of efficacy. Pharmacopsychiatry 1990;23:57–58.
Babazadeh B, Sadeghnia HR, Safarpour-Kapurchal E, Parsaee H, Nasri S. Protective effect of Nigella sativa and thymoquinone on serum/glucose deprivation-induced DNA damage in PC12 cells. Avicenna J Phytomed 2012;2:125–132.
Hamdy NM, Taha RA. Effects of Nigella sativa oil and thymoquinone on oxidative stress and neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmacology 2009;84:127–134.
Chui MH, Greenwood CE. Antioxidant vitamins reduce acute meal-induced memory deficits in adults with type 2 diabetes. Nutr Res 2008;28:423–429.
Hasanein P, Shahidi S. Effects of combined treatment with vitamins C and E on passive avoidance learning and memory in diabetic rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2010;93:472–478.
Ilhan A, Gurel A, Armutcu F, Kamisli S, Iraz M. Antiepileptogenic and antioxidant effects of Nigella sativa oil against pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in mice. Neuropharmacology 2005;49:456–464.
Kanter M, Coskun O, Kalayci M, Buyukbas S, Cagavi F. Neuroprotective effects of Nigella sativa on experimental spinal cord injury in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 2006;25:127–133.
Kwon SH, Lee HK, Kim JA, Hong SI, Kim HC, Jo TH, et al. Neuroprotective effects of chlorogenic acid on scopolamineinduced amnesia via anti-acetylcholinesterase and antioxidative activities in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2010;649:210–7.
Shi J, Liu Q, Wang Y, Luo G. Coadministration of huperzine A and ligustrazine phosphate effectively reverses scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2010;96:449–453.
Jukic M, Politeo O, Maksimovic M, Milos M. in vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibitory properties of thymol, carvacrol and their derivatives thymoquinone and thymohydroquinone. Phytother Res 2007;21:259–261.
el Tahir KE, Ashour MM, al-Harbi MM. The respiratory effects of the volatile oil of the black seed (Nigella sativa) in guinea-pigs: elucidation of the mechanism(s) of action. Gen Pharmacol 1993;24:1115–1122.
Wienkotter N, Hopner D, Schutte U, Bauer K, Begrow F, El-Dakhakhny M, et al. The effect of nigellone and thymoquinone on inhibiting trachea contraction and mucociliary clearance. Planta Med 2008;74:105–108
Masuoka T, Kamei C. The role of nicotinic receptors in the amelioration of cholinesterase inhibitors in scopolamineinduced memory deficits. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2009;206:259–265.
Ahmed T, Gilani AH. Inhibitory effect of curcuminoids on acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuation of scopolamine-induced amnesia may explain medicinal use of turmeric in Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2009;91:554–559.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, M., Mohammadpour, T., Karami, R. et al. Effects of the hydro-alcoholic extract of Nigella sativa on scopolamine-induced spatial memory impairment in rats and its possible mechanism. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 21, 438–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1742-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1742-5