Abstract
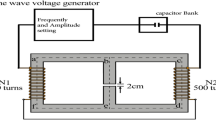
This investigation was performed to evaluate the influence of the static magnetic field up to 15 mT on the viability and proliferation rate of rat bone marrow stem cells. Cells from passage 5 were trypsinized, and a cell suspension was prepared. The cells were counted and cultured in 25-cm2 flasks. They were incubated for 1 d, washed with phosphate-buffered saline, and then exposed with different intensities of static magnetic field (4, 7, and 15 mT) at different exposure times (24, 48, 72, and 96 h). Cells were then washed with phosphate-buffered saline, trypsinized, and a cell suspension was prepared separately from each flask. To investigate the viability and proliferation rates of treated cells, staining with Trypan blue and counting were performed with an optical microscope. The mean number of whole cells and living cells was considered as proliferation and survival rates, respectively. Increasing of intensity and time of static magnetic field exposure decreased the viability percent and proliferation rate in treated groups compared with corresponded control. However, reduced cell viability, where this occurred, is exclusively due to apoptosis since necrosis is never observed by others.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolmaleki P.; Ghanati F.; Sahebjamei H.; Sabet-Sarvestani A. Peroxidase activity, lignification and promotion of cell death in tobacco cells exposed to static magnetic field. The Environmentalist 27: 435–440; 2007.
Albertini M. C.; Accorsi A.; Citterio B.; Burattini S.; Piacentini M. P.; Uguccioni F.; Piatti E. Morphological and biochemical modifications induced by a static magnetic field on Fusarium culmorum. Biochimie 85: 963–970; 2003.
Aldinucci C.; Garcia J. B.; Palm M.; Sgaragli G.; Benocchi A.; Meini A.; Pessina F.; Rossi C.; Bonechi C.; Pessina G. P. The effect of exposure to high flux density static and pulsed magnetic fields on lymphocyte function. Bioelectromagnetics 24: 373–379; 2003.
Alipov D. Y.; Belyaev I. Y.; Aizenberg O. A. Systemic reaction of E. coli cells to weak electromagnetic fields of extremely low frequency. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 34: 5–12; 1994.
Amara S.; Douki T.; Ravanat J. L.; Garrel C.; Guiraud P.; Favier A.; Sakly M.; Ben Rhouma K.; Abdelmelek H. Influence of a static magnetic field (250 mT) on the antioxidant response and DNA integrity in THP1 cells. Phys Med Biol 52: 889–898; 2007.
Antonopoulos A.; Yang B.; Stamm A.; Heller W. D.; Obe G. Cytological effects of 50 Hz electromagnetic fields on human lymphocytes in vitro. Mutat. Res. 346: 151–157; 1995.
Brighton C.; Lorich D.; Kupcha R.; Reilly T.; Jones A.; Woodbury R. N. The pericyte as a possible osteoblast progenitor cell. Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 275: 287–299; 1992.
Brune B. Nitric oxide: NO apoptosis or turning it ON? Cell Death Diff 10: 864–869; 2003.
Buemi M.; Marino D.; Di Pasquale G.; Floccari F.; Senatore M.; Aloisi C.; Grasso F.; Mondio G.; Perillo P.; Frisina N.; Corica F. Cell proliferation/cell death balance in renal cell cultures after exposure to a static magnetic field. Nephron 87: 269–673; 2001.
Chionna A.; Dwikat M.; Panzarini E.; Tenuzzo B.; Carla E. C.; Verri T.; Pagliar Abbro L.; Dini L. Cell shape and plasma membrane alterations after static magnetic fields exposure. Europ J Histoch 47: 299–308; 2003.
Conti P.; Gigante G. E.; Cifone M. G.; Alesse E.; Ianni G.; Reale M.; Angeletti P. U. Reduced mitogenic stimulation of human lymphocytes by extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. FEBS Lett 162: 156–160; 1983.
Cridland N. A.; Haylock R. G. E.; Saunders R. D. 50 Hz magnetic field exposure alters onset of S-phase in normal human fibroblasts. Bioelectromagnetics 20: 446–452; 1999.
Dini L.; Abbro L. Bioeffects of moderate-intensity static magnetic field on cell cultures. Micron 36: 195–217; 2005.
Diniz P.; Soejima K.; Ito G. Nitric oxide mediates the effects of pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation on the osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Nitric Oxide 7: 18–23; 2002.
Eslaminejad M. B.; Nikmahzar A.; Taghiyar L.; Nadri S.; Massumi M. Murine mesenchymal stem cells isolated by low density primary culture system. Dev Growth Differ 48: 361–370; 2006.
Fanelli C.; Coppola S.; Barone R.; Colussi C.; Gualaldi G.; Volpe P.; Ghibelli L. Magnetic fields increase cell survival by inhibiting apoptosis via modulation of CaCC influx. FASEB Journal 13: 95–102; 1999.
Gluck B.; Guntzschel V.; Berg H. Inhibition of proliferation of human lymphoma cells U937 by a 50 Hz electromagnetic field. Cellular Molecular Biology 47: 115–117; 2001.
Guo M.; Hay B. A. Cell proliferation and apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11(6): 745–752; 1999.
Ishisaka R.; Kanno T.; Inai Y.; Nakahara H.; Akiyama J.; Yoshioka T.; Utsumi K. Effect of a magnetic field on the various functions of subcellular organelles and cells. Pathophysiology 7: 149–152; 2000.
Jajte J.; Grzegorczyk J.; Zmy’s lony M.; Rajkowska E. Effect of 7 mT static magnetic field and iron ions on rat lymphocytes: apoptosis, necrosis and free radical processes. Bioelectrochemistry 57: 107–111; 2002.
Jajte J. M. Programmed cell death as a biological function of electromagnetic fields at a frequency of (50/60 Hz). Med Pr 51: 383–389; 2000.
Javani J. F.; Abdolmaleki P.; Ghanati F. Study the effect of static magnetic field on chromosomal aberrations on Vicia faba in area with high natural radioactivity. Environmentalist 31: 169–175; 2011.
Javani J. F.; Abdolmaleki P.; Ghanati F. Oxidative stress in broad bean (Vicia faba L.) induced by static magnetic field under natural radioactivity. Mutat. Res. 741: 116–121; 2012.
Kuznetsov S.; Mankani M.; Gronthos S.; Satomura K.; Bianco P.; Robey P. Circulating skeletal stem cells. J. Cell. Biol. 153: 1133–1140; 2001.
Lai H.; Singh N. P. Magnetic field induced DNA strand breaks in brain cells of the rat. Environ Health Perspect 112: 687–694; 2004.
Lee J.; Musgrave D.; Pelinkovic D. Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2-expressing muscle-derived cells on healing of critical-sized bone defects in mice. J. Bone Joint Surg. 83-A: 1032–1039; 2001.
Makoolati Z.; Movahedin M.; Forouzandeh-Moghadam M. Effects of different doses of bone morphogenetic protein 4 on viability and proliferation rates of mouse embryonic stem cells. Yakhteh Med J. 11: 29–34; 2009.
Marandi M.; Mowla S. J.; Tavallaei M.; Yaghoobi M. M.; Jafarnejad S. M. Proprotein convertases 1 and 2 (PC1 and PC2) are expressed in neutrally differentiated rat bone marrow stromal stem cells (BMSCs). Neurosci Lett 420: 198–203; 2007.
Marinelli F.; La Sala D.; Cicciotti G.; Cattini L.; Trimarchi C.; Putti S.; Zamparelli A.; Giuliani L.; Tommassetti G.; Cinti C. Exposure to 900 Mhz electromagnetic field induces an unbalance between pro-apoptotic and prosurvival signals in T-lymphoblastoid leukaemia CCRF-CEM cells. J Cell Physiol 198: 479–480; 2004.
Markov M. S. Angiogenesis, magnetic fields and 'window effects'. Cardiology 117: 54–56; 2010.
Mazaheri Z.; Movahedin M.; Rahbari Zadeh F.; Aman Pour S. Different doses of bone morphogenetic protein 4 promote the expression of early germ cell specific gene in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47: 521–525; 2011.
Miyakoshi J. Effects of static magnetic fields at the cellular level. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 87: 213–223; 2005.
Mizuno S.; Glowacki J. Chondroinduction of human dermal fibroblasts by demineralized bone in three-dimensional culture. Exp. Cell Res. 227: 89–97; 1996.
Niehaus M.; Bruggemeyer H.; Behre H. M.; Lerchl A. Growth retardation, testicular stimulation, and increased melatonin synthesis by weak magnetic fields (50 Hz) in Djungarian hamsters, Phodopus sungorus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 234: 707–711; 1997.
Ottaviani E.; Malagoli D.; Ferrari A.; Tagliazucchi D.; Conte A.; Gobba F. 50 Hz magnetic fields of varying flux intensity affect cell shape changes in invertebrate immunocytes: the role of potassium ion channels. Bioelectromagnetics 23: 292–297; 2002.
Paradisi S.; Donelli G.; Santini M. S.; Straface E.; Malorni W. A 50 Hz magnetic field induces structural and biophysical changes in membranes. Bioelectronmagnetics 14: 247–255; 1993.
Piacentini M. P.; Fraternale D.; Piatti E.; Ricci D.; Vetrano F. Senescence delay and change of antioxidant enzyme levels in Cucumis sativus L. etiolated seedling by ELF magnetic fields. Plant Sci 161: 45–53; 2001.
Peister A.; Mellad J. A.; Larson B. L.; Hall B. M.; Gibson L. F.; Prockop D. J. Adult stem cells from bone marrow (MSCs) isolated from different strains of inbred mice vary in surface epitopes, rates of proliferation, and differentiation potential. Blood 103: 1662–1668; 2004.
Potenza L.; Ubaldi L.; De Sanctis R.; De Bellis R.; Cucchiaini L.; Dacha M. Effects of a static magnetic field on cell growth and gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mutat Res 561: 53–62; 2004.
Raylman R. R.; Clavo A. C.; Wahl R. L. Exposure to strong static magnetic field slows the growth of human cancer cells in vitro. Bioelectromagnetics 17: 358–363; 1996.
Rosen A. D. Mechanism of action of moderate-intensity static magnetic fields. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1282: 149–155; 2003.
Sarvestani A. S.; Abdolmaleki P.; Mowla S. J.; Ghanati F.; Heshmati E.; Tavasoli Z.; Jahromi A. M. Static magnetic fields aggravate the effects of ionizing radiation on cell cycle progression in bone marrow stem cells. Micron 41: 101–104; 2010.
Scarfi M. R.; Lioi M. B.; Zeni O.; Della Noce M.; Franceschi C.; Bersani F. Micronucleus frequency and cell proliferation in human lymphocytes exposed to 50 Hz sinusoidal magnetic fields. Health Phys. 76: 244–250; 1999.
Stevens R.G. Electromagnetic fields and free radicals. Environ. Health. Perspect 112: 687–694; 2004.
Szatrowski T. P.; Nathan C. F. Production of large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer Res 51: 794–798; 1991.
Tavasoli Z.; Abdolmaleki P.; Mowla S. J.; Ghanati F.; Sabet Sarvestani A. Investigation of the effects of static magnetic field on apoptosis in bone marrow stem cells of rat. Environmentalist 29: 220–224; 2009.
Tenuzzo B.; Vergallo C.; Dini L. Effect of 6 mT static magnetic field on the bcl-2, bax, p53 and hsp70 expression in freshly isolated and in vitro aged human lymphocytes. Tissue and Cell 41: 169–179; 2009.
Teodori L.; Gohde W.; Valente M. G.; Tagliaferri F.; Coletti D.; Perniconi B.; Bergamaschi A.; Cerella C.; Ghibelli L. Static magnetic fields affect calcium fluxes and inhibit stress-induced apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Cytometry 49: 143–149; 2002a.
Teodori L.; Grabarek J.; Smolewski P.; Ghibelli L.; Bergamaschi A.; De Nicola M.; Darzynkiewicz Z. Exposure of cells to static magnetic fields accelerates loss of integrity of plasma membrane during apoptosis. Cytometry 49: 113–118; 2002b.
Williams C. D.; Marcov M. S.; Hardman W. E.; Cameron I. L. Therapeutic electromagnetic field effects on angiogenesis and tumor growth. Anticancer Res 21: 3887–3892; 2001.
Yano A.; Hidaka E.; Fujiwara K.; Iimoto M. Induction of primary root curvature in radish seedlings in a static magnetic field. Bioelectromagnetics 22: 194–199; 2001.
Yoshizawa H.; Tsuchiya T.; Mizoe H.; Ozeki H.; Kanao S.; Yomori H.; Sakane C.; Hasebe S.; Motomura T.; Yamakawa T.; Mizuno F.; Hirose H.; Otaka Y. No effect of extremely low-frequency magnetic field observed on cell growth or initial response of cell proliferation in human cancer cell lines. Bioelectromagnetics 23: 355–368; 2002.
Zuk P.; Zhu M.; Mizuno H. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 7: 211–228; 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: T. Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javani Jouni, F., Abdolmaleki, P. & Movahedin, M. Investigation on the effect of static magnetic field up to 15 mT on the viability and proliferation rate of rat bone marrow stem cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 49, 212–219 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-013-9580-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-013-9580-x