Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) compared with conventional radiography for identifying vertebral fractures.
Materials and methods
A total of 930 postmenopausal women underwent conventional radiography and DXA imaging of the spine. The images were evaluated by two expert skeletal radiologists using the semiquantitative (SQ) method for conventional radiography and the morphometric vertebral fracture assessment (VFA) for DXA.
Results
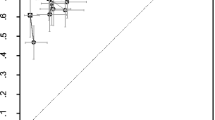
The SQ method for radiography (SQ-Rx) analysed 99.1% of vertebrae, identifying 442 vertebral fractures; VFA analysed 97.5% vertebrae, detecting 420 vertebral fractures. Agreement between SQ-Rx and VFA reached 98.76%, and the κ-score was 0.96 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.95–0.98]. Assessing the grading of vertebral fractures, agreement reached 97.5% and the κ-score was 0.841 (95% CI, 0.821–0.891). Considering SQ-Rx method as “gold standard”, VFA had a sensitivity of 97.85 % and a specificity of 99.81%. The negative (NPV) and positive (PPV) predictive value for VFA were 99.83 % and 98.15%, respectively. Fractures were identified in 251 (27 %) and 242 (26 %) of patients on SQ-Rx and VFA, respectively. On a per-patient basis, the agreement between the two methods was 97% and the κ-score was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.920–0.968). The diagnostic parameters for VFA were 97.23% sensitivity, 98.86% specificity, 97.60% PPV and 98.84% NPV.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that VFA with DXA may reach a high level of accuracy for diagnosing vertebral fractures, suggesting that VFA should be introduced in the screening of individuals with a risk of osteoporosis and in the follow-up of osteoporotic patients receiving treatment.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Scopo del presente lavoro è stato valutare l’accuratezza diagnostica della tecnica assorbimetrica a raggi X a doppia energia (DXA) a confronto con la radiologia convenzionale per la identificazione delle fratture vertebrali.
Materiali e metodi
Novecentotrenta donne in postmenopausa sono state sottoposte ad esame radiologico convenzionale e ad esame DXA del rachide. Le immagini sono state valutate da due radiologi esperti dello scheletro utilizzando rispettivamente il metodo semiquantitativo per l’esame radiologico (SQ-Rx) e la valutazione morfometrica vertebrale (VFA) per l’esame DXA.
Risultati
Il metodo SQ-Rx ha analizzato il 99,1% delle vertebre, identificando 442 fratture vertebrali; VFA ha analizzato il 97,5% delle vertebre identificando 420 fratture vertebrali; la concordanza tra i due metodi è risultata pari al 98,76% con k-score di 0,96; [95% intervallo di confidenza (CI) 0,95–0,98]. Valutando il grado delle fratture vertebrali, la concordanza tra SQRx e VFA è risultata 97,5% con k-score 0,84 (95% CI 0,821–0,891). Considerando il metodo SQ-Rx come riferimento, la VFA aveva una sensibilità del 97,85% ed una specificità 99,81%. Il valore predittivo negativo (VPN) ed il valore predittivo positivo (VPP) erano 99,83% e 98,15%, rispettivamente. Duecentocinquantuno (27%) e 242 (26%) dei pazienti sono stati giudicati fratturati con il metodo SQ-Rx e con il metodo VFA, rispettivamente. Nella valutazione per paziente la concordanza tra le due tecniche era 97% (k-score: 0,948; 95% CI 0,920–0,968). I parametri diagnostici della VFA sono risultati: sensibilità 97,2%; specificità 98,9%; VPP 97,60%; VPN: 98,84%.
Conclusioni
Questo studio dimostra che la VFA mediante la tecnica DXA può avere una elevata accuratezza per la diagnosi delle fratture vertebrali, suggerendone l’introduzione nello screening dei soggetti a rischio di osteoporosi e nel follow-up terapeutico di pazienti osteoporotici.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Cummings SR, Melton LJ (2002) Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet 359:1761–1767
Cauley JA, Palermo L, Vogt M et al (2008) Prevalent vertebral fractures in black women and white women. J Bone Miner Res 23:1458–1467
Delmas PD, van de Langerijt L, Watts NB et al (2005) Underdiagnosis of vertebral fractures is a worldwide problem: the IMPACT study. J Bone Miner Res 20:557–563
Kim N, Rowe BH, Raymond G et al (2004) Underreporting of vertebral fractures on routine chest radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:297–300
Lindsay R, Pack S, Li Z (2005) Longitudinal progression of fracture prevalence through a population of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 16:306–312
Roux C, Fechtenbaum J, Kolta S et al (2007) Mild prevalent and incident vertebral fractures are risk factors for new fractures. Osteoporos Int 18:1617–1624
Cauley JA, Hochberg MC, Lui LY et al (2007) Long-term risk of incident vertebral fractures. JAMA 298:2761–2767
Johnell O, Kanis JA, Oden A et al (2004) Mortality after osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 15:38–42
Romagnoli E, Carnevale V, Nofroni I et al (2004) Quality of life in ambulatory postmenopausal women: the impact of reduced bone mineral density and subclinical vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int 15:975–980
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8:1137–1148
Diacinti D, Guglielmi G, Tomei E et al (2001) Vertebral morphometry: evaluation of osteoporosis-caused fractures. Radiol Med 101:140–144
Lang T, Takada M, Gee R et al (1997) A preliminary evaluation of the lunar expert-XL for bone densitometry and vertebral morphometry. J Bone Miner Res 12:136–143
Crabtree N, Wright J, Walgrove A et al (2000) Vertebral morphometry: repeat scan precision using the Lunar Expert-XL and the Hologic 4500A. A study for the ‘WISDOM’ RCT of hormone replacement therapy. Osteoporos Int 11:537–543
Damilakis J, Adams JE, Guglielmi G et al (2010) Radiation exposure in X-raybased imaging techniques used in osteoporosis. Eur Radiol 20:2707–2714
Olenginski TP, Newman ED, Hummel JL et al (2006) Development and evaluation of a vertebral fracture assessment program using IVA and its integration with mobile DXA. J Clin Densitom 9:72–77
Schousboe JT, Vokes T, Broy SB et al (2008) Vertebral fracture assessment: the 2007 ISCD Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 11:92–108
Duboeuf F, Bauer DC, Chapurlat RD et al (2005) Assessment of vertebral fracture using densitometric morphometry. J Clin Densitom 8:362–368
Rea JA, Chen MB, Li J et al (2000) Morphometric X-ray absorptiometry and morphometric radiography of the spine: a comparison of prevalent vertebral deformity identification. J Bone Miner Res 15:564–574
Ferrar L, Jiang G, Eastell R et al (2003) Visual identification of vertebral fractures in osteoporosis using morphometric X-ray absorptiometry. J Bone Miner Res 18:933–938
Schousboe JT, Debold CR (2006) Reliability and accuracy of vertebral fracture assessment with densitometry compared to radiography in clinical practice. Osteoporos Int 17:281–289
Pavlov L, Gamble GD, Reid IR (2005) Comparison of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and conventional radiography for the detection of vertebral fractures. J Clin Densitom 8:379–385
Vokes TJ, Dixon LB, Favus MJ (2003) Clinical utility of dual-energy vertebral assessment (DVA). Osteoporos Int 14:871–878
Binkley N, Krueger D, Gangnon R et al (2005) Lateral vertebral assessment: a valuable technique to detect clinically significant vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int 16:1513–1518
Rea JA, Steiger P, Blake GM et al (1998) Optimizing data acquisition and analysis of morphometric x-ray absorptiometry. Osteoporos Int 8:177–183
Hurxthal LM (1968) Measurement of vertebral heights. AJR Am J Roentgenol 103:635–644
Hospers IC, van der Laan JG, Zeebregts CJ et al (2009) Vertebral fracture assessment in supine position: comparison by using conventional semiquantitative radiography and visual radiography. Radiology 251:822–828
Jager PL, Jonkman S, Koolhaas W et al (2011) Combined vertebral fracture assessment and bone mineral density measurement: a new standard in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in academic populations. Osteoporos Int 22:1059–1068
Kleerekoper M, Nelson DA (1992) Vertebral fracture or vertebral deformity. Calcif Tissue Int 50:5–6
Ziegler R, Scheidt-Nave C, Leidig-Bruckner G (1996) What is a vertebral fracture? Bone 18(3 Suppl):169S–177S
Ferrar L, Jiang G, Armbrecht G et al (2007) Is short vertebral height always an osteoporotic fracture? The Osteoporosis and Ultrasound Study (OPUS). Bone 41:5–12
Diacinti D, Pisani D, Del Fiacco R et al (2011) Vertebral morphometry by X-ray absorptiometry: Which reference data for vertebral heights? Bone 49:526–536
Giannini S, Nobile M, Dalle Carbonare L et al (2001) Vertebral morphometry by x-ray absorptiometry before and after liver transplant: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:1201–1207
Mazzaferro S, Diacinti D, Proietti E et al (2006) Morphometric x-ray absorptiometry in the assessment of vertebral fractures in renal transplant patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:466–471
Vosse D, Heijckmann C, Landewé R et al (2007) Comparing morphometric X-ray absorptiometry and radiography in defining vertebral wedge fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 46:1667–1671
Guglielmi G, Diacinti D, van Kuijk C et al (2008) Vertebral morphometry: current methods and recent advances. Eur Radiol 18:1484–1496
Fuerst T, Wu C, Genant HK et al (2009) Evaluation of vertebral fracture assessment by dual X-ray absorptiometry in a multicenter setting. Osteoporos Int 20:1199–1205
Diacinti D, Guglielmi G (2010) Vertebral morphometry. Radiol Clin North Am 48:561–575
Bartalena T, Giannelli G, Rinaldi MF et al (2009) prevalence of thoracolumbar vertebral fractures on multidetector CT underreporting by radiologists. Eur J Radiol 69:555–559
Difede G, Scalo G, Bucchieri S et al (2010) Underreported vertebral fractures in an Italian population: comparison of plain radiographs vs quantitative measurements. Radiol Med 115:1101–1110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diacinti, D., Guglielmi, G., Pisani, D. et al. Vertebral morphometry by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) for osteoporotic vertebral fractures assessment (VFA). Radiol med 117, 1374–1385 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0835-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0835-5