Abstract
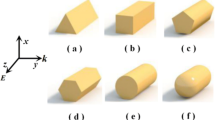
The localized surface plasmon resonance dependence on surrounding medium refractive index of Ag, Al, Au, and Cu nanoparticles is examined by electrodynamic approach. The refractive index sensitivity and sensing figure of merit (FOM) dependence of selected metal nanoparticles with similar geometry shows that although, sensing relevant parameters are shape (i.e., aspect ratio), and material dependent below the width 20 nm, but above this size these parameters are material independent under similar geometrical conditions. We have concluded that at optimum size, however, Al shows much higher refractive index sensitivity (RIS) in comparison to Au, Cu, and Ag, but FOM is higher for Ag in comparison to other metals. The observed sensing behavior is expected due to parameters like surface scattering, dynamic depolarization, radiation damping, and interband transitions, which may influence the nanorod plasmons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haes JA, Zou S, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2004) Nanoscale optical biosensor: short range distance dependence of the localized surface plasmon resonance of noble metal nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 108:6961–6968
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Dyune RP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453
Nusz GJ, Curry AC, Marinakos SM, Wax A, Chilkoti A (2009) Rational selection of gold nanorod geometry for lable-free plasmonic biosensors. ACS Nano 3(4):795–806
Sekhon JS, Verma SS (2011) Optimal dimensions of gold nanorod for plasmonic nanosensors. Plasmonics 6(1):163–169
McFarland AD, Van Duyne RP (2003) Single silver nanoparticles as real-time optical sensors with zeptomole sensitivity. Nano Lett 3(8):1057
Salzemann C, Lisiecki I, Brioude A, Urban J, Pileni MP (2004) Collections of copper nanocrystals characterized by different sizes and shapes: optical response of these nanoobjects. J Phys Chem B 108:13242–13248
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Noguez C (2007) Surface plasmon on metal nanoparticles: the influence of shape and physical environment. J Phys Chem C 111:3806–3819
Sekhon JS, Verma SS (2011) Refractive index sensitivity analysis of Ag, Au, and Cu nanoparticles. Plasmonics 6(2):311–317
Pena-Rodriguez O, Pal U, Rodriguez-Iglesias V, Rodriguez-Fernandez L, Oliver A (2011) Configuring Au and Ag nanorods for sensing applications. J Opt Soc Am B 28(4):714–720
Chan GH, Zhao J, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2008) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of triangular aluminum nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 112:13958–13963
Chan GH, Zhao J, Hicks EM, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2007) Plasmonic properties of copper nanoparticles fabricated by nanosphere lithography. Nano Lett 7:1947–1952
Slaughter LS, Chang W, Swanglap P, Tcherniak A, Khanal BP, Zubarev ER, Link S (2010) Single-particle spectroscopy of gold nanorods beyond the quasi-static limit: varying the width at constant aspect ratio. J Phys Chem C 114:4934–4938
Langhammer C, Schwind M, Kasemo B, Zoric I (2008) Localized surface plasmon resonance in aluminum nanodisks. Nano Lett 8(5):1461–1471
Mock JJ, Smith DR, Schultz S (2003) Local refractive index dependence of plasmon resonance spectra from individual nanoparticles. Nano Lett 3(4):485–491
Sherry LJ, Chang S, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP, Wiley BJ, Xia Y (2005) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver nanocubes. Nano Lett 5(10):2034–2038
Sherry LJ, Jin R, Mirkin CA, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2006) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver triangular nanoprisms. Nano Lett 6(9):2060–2065
Lee YH, Chen H, Xu Q, Wang J (2011) Refractive index sensitivities of noble metal nanocrystals: the effects of multipolar plasmon resonance and the metal type. J Phys Chem C 115(16):7997–8004
Wiley BJ, Chen Y, McLellan J, Xiong Y, Li Z, Ginger D, Xia Y (2007) Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanobars and nanorice. Nano Lett 7(4):1032–1036
Liu CM, Guo L, Xu HB, Wu ZY, Weber J (2003) Seed-mediated growth and properties of copper nanoparticles, nanoparticle 1D arrays and nanorods. Microelectron Eng 66:107–114
Wang P-I, Zhao Y-P, Lu T-M (2004) Novel growth mechanism of single crystalline Cu nanorods by electron beam irradiation. Nanotechnology 15:218–222
Yeshchenko OA, Dmitruk IM, Dmytruk AM, Alexeenko AA (2007) Influence of annealing conditions on size and optical properties of copper nanoparticles embedded in silica matrix. Mater Sci Eng B 137:247–254
Shrestha KM, Sorensen CM, Klabunde KJ (2010) Synthesis of CuO nanorods, reduction of CuO into Cu nanorods, and diffuse reflectance measurements of CuO and Cu nanomaterials in the near infrared region. J Phys Chem C 114:14368–14376
Rice KP, Walker EJ, Stoykovich MP, Saunders AE (2011) Solvent-dependent surface plasmon response and oxidation of copper nanocrystals. J Phys Chem C 115:1793–1799
Langhammer C, Kasemo B, Zoric I (2007) Absorption and scattering of light by Pt, Pd, Ag, and Au nanodisks: absolute cross sections and branching ratios. J Chem Phys 126:194702
Stockli T, Stadelmann P, Chatelain A (1997) Low-loss EELS of oxide-covered aluminum nanospheres. Microsc Microanal Microstruct 8:145–155
Heilweil EJ, Hochstrasser RM (1985) Nonlinear spectroscopy and picosecond transient grating study of colloidal gold. J Chem Phys 82:4762
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Lee KH, Chang KJ (1994) First-principles study of the optical properties and the dielectric response of Al. Phys Rev B 49:2362–2367
Ehrenreich H, Philipp HR, Segall B (1963) Optical properties of aluminum. Phys Rev 132:1918–1928
Kooij ES, Poelsema B (2006) Shape and size effects in the optical properties of metallic nanorods. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8:3349–3357
Coronado EA, Schatz GC (2003) Surface plasmon broadening for arbitrary shape nanoparticle: a geometrical probability approach. J Chem Phys 119(7):3926–3934
Cai W, Hofmeister H, Dubiel M (2001) Importance of lattice contraction in surface plasmon resonance shift for free and embedded silver particles. Eur Phys J D 13:245–253
Hu M, Novo C, Funston A, Wang H, Staleva H, Zou S, Mulvaney P, Xia Y, Hartland GV (2008) Dark-field microscopy studies of single metal nanoparticles: understanding the factors that influence the line width of the localized surface plasmon resonance. J Mater Chem 18:1949–1960
Lee K, El-Sayed MA (2006) Gold and silver nanoparticles in sensing and imaging: sensitivity of plasmon response to size, shape, and metal composition. J Phys Chem B 110:19220–19225
Blaber MG, Arnold MD, Ford MJ (2010) A review of the optical properties of alloys and intermetallics for plasmonics. J Phys Condens Matter 22:143201
Cottancin E, Celep G, Lerme J, Pellarin M, Huntzinger JR, Vialle JL, Broyer M (2006) Optical properties of noble metal clusters as a function of the size: comparison between experiments and a semi-quantal theory. Theor Chem Acc 116(4–5):514–523
Palik ED (1991) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic, New York
Chen H, Kou X, Yang Z, Ni W, Wang J (2008) Shape- and size-dependent refractive index sensitivity of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:5233–5237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekhon, J.S., Verma, S.S. Rational Selection of Nanorod Plasmons: Material, Size, and Shape Dependence Mechanism for Optical Sensors. Plasmonics 7, 453–459 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9328-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9328-6