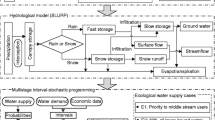
Abstract
The risk of water shortage caused by uncertainties, such as frequent drought, varied precipitation, multiple water resources, and different water demands, brings new challenges to the water transfer projects. Uncertainties exist for transferring water and local surface water; therefore, the relationship between them should be thoroughly studied to prevent water shortage. For more effective water management, an uncertainty-based water shortage risk assessment model (UWSRAM) is developed to study the combined effect of multiple water resources and analyze the shortage degree under uncertainty. The UWSRAM combines copula-based Monte Carlo stochastic simulation and the chance-constrained programming-stochastic multiobjective optimization model, using the Lunan water-receiving area in China as an example. Statistical copula functions are employed to estimate the joint probability of available transferring water and local surface water and sampling from the multivariate probability distribution, which are used as inputs for the optimization model. The approach reveals the distribution of water shortage and is able to emphasize the importance of improving and updating transferring water and local surface water management, and examine their combined influence on water shortage risk assessment. The possible available water and shortages can be calculated applying the UWSRAM, also with the corresponding allocation measures under different water availability levels and violating probabilities. The UWSRAM is valuable for mastering the overall multi-water resource and water shortage degree, adapting to the uncertainty surrounding water resources, establishing effective water resource planning policies for managers and achieving sustainable development.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allam A, Tawfik A, Yoshimura C, Fleifle A (2016) Multi-objective models of waste load allocation toward a sustainable reuse of drainage water in irrigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:11823–11834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6331-z
Borgomeo E, Hall JW, Fung F, Watts G, Colquhoun K, Lambert C (2014) Risk-based water resources planning: incorporating probabilistic nonstationary climate uncertainties. Water Resour Res 50:6850–6873. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014wr015558
Chang F-J, Wang Y-C, Tsai W-P (2016) Modelling intelligent water resources allocation for multi-users. Water Resour Manag 30:1395–1413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1229-6
Chen D, Chen Q, Leon AS, Li R (2016) A genetic algorithm parallel strategy for optimizing the operation of reservoir with multiple eco-environmental objectives. Water Resour Manag 30:2127–2142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1274-1
Chen L, Singh VP, Guo SL (2013) Measure of correlation between river flows using the copula-entropy method. J Hydrol Eng 18:1591–1606. https://doi.org/10.1061/(Asce)He.1943-5584.0000714
Chu J, Zhang C, Fu G, Li Y, Zhou H (2015) Improving multi-objective reservoir operation optimization with sensitivity-informed dimension reduction. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:3557–3570. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-3557-2015
Cui Q, Wang X, Li C, Cai Y, Liang P (2016) Improved Thomas–Fiering and wavelet neural network models for cumulative errors reduction in reservoir inflow forecast. J Hydro Environ Res 13:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2015.05.003
Dai C, Cai YP, Lu WT, Liu H, Guo HC (2016) Conjunctive water use optimization for watershed-lake water distribution system under uncertainty: a case study. Water Resour Manag 30:4429–4449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1430-7
Davidsen C, Pereira-Cardenal SJ, Liu S, Mo X, Rosbjerg D, Bauer-Gottwein P (2015) Using stochastic dynamic programming to support water resources management in the Ziya River Basin, China. J Water Resour Plan Manag 141:04014086. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0000482
de Andrade JGP, Barbosa PSF, Souza LCA, Makino DL (2011) Interbasin water transfers: the Brazilian experience and international case comparisons. Water Resour Manag 25:1915–1934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9781-6
Galán-Martín Á, Vaskan P, Antón A, Esteller LJ, Guillén-Gosálbez G (2017) Multi-objective optimization of rainfed and irrigated agricultural areas considering production and environmental criteria: a case study of wheat production in Spain. J Clean Prod 140:816–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.099
Hassanzadeh E, Elshorbagy A, Wheater H, Gober P (2016) A risk-based framework for water resource management under changing water availability, policy options, and irrigation expansion. Adv Water Resour 94:291–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.05.018
He L, Huang G, Lu H (2008) A simulation-based fuzzy chance-constrained programming model for optimal groundwater remediation under uncertainty. Adv Water Resour 31:1622–1635
Higgins A, Archer A, Hajkowicz S (2007) A stochastic non-linear programming model for a multi-period water resource allocation with multiple objectives. Water Resour Manag 22:1445–1460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-007-9236-2
Jafarzadegan K, Abed-Elmdoust A, Kerachian R (2013) A stochastic model for optimal operation of inter-basin water allocation systems: a case study. Stoch Env Res Risk A 28:1343–1358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0841-8
Kanakoudis V, Tsitsifli S, Papadopoulou A, Cencur Curk B, Karleusa B (2017) Water resources vulnerability assessment in the Adriatic Sea region: the case of Corfu Island. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:20173–20186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9732-8
Kanakoudis V, Tsitsifli S, Papadopoulou A, Curk BC, Karleusa B (2016) Estimating the water resources vulnerability index in the Adriatic Sea region. Procedia Engineering 162:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.11.091
Kollat JB, Reed PM (2007) A computational scaling analysis of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms in long-term groundwater monitoring applications. Adv Water Resour 30:408–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2006.05.009
Legendre P (2005) Species associations: the Kendall coefficient of concordance revisited. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 10:226–245. https://doi.org/10.1198/108571105x46642
Li M, Guo P, Singh VP, Yang G (2016) An uncertainty-based framework for agricultural water-land resources allocation and risk evaluation. Agric Water Manag 177:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.06.011
Li X-Y, Li F-F, Qiu J (2017a) A new evaluation for water transfer optimal schemes with the consideration of reliability, stability, and severity. Water Resour Manag 31:2823–2836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1665-y
Li Y, Cui Q, Li C, Wang X, Cai Y, Cui G, Yang Z (2017b) An improved multi-objective optimization model for supporting reservoir operation of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Sci Total Environ 575:970–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.165
Li Y, Gu W, Cui W, Chang Z, Xu Y (2015) Exploration of copula function use in crop meteorological drought risk analysis: a case study of winter wheat in Beijing, China. Nat Hazards 77:1289–1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1649-2
Lian J, He W, Ma C, Xu K (2015) Guarantee rate of freshwater in a river mouth intruded by saltwater with respect to the joint impact of runoff and tide. J Hydroinf 17:917–929. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2015.038
Lilliefors HW (1967) On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown. J Am Stat Assoc 62:399–402
Lu H, Du P, Chen Y, He L (2016) A credibility-based chance-constrained optimization model for integrated agricultural and water resources management: a case study in South Central China. J Hydrol 537:408–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.03.056
Manshadi HD, Niksokhan MH, Ardestani M (2015) A quantity-quality model for inter-basin water transfer system using game theoretic and virtual water approaches. Water Resour Manag 29:4573–4588
Mara TA, Tarantola S (2012) Variance-based sensitivity indices for models with dependent inputs. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 107:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2011.08.008
Nazemi A, Wheater HS, Chun KP, Elshorbagy A (2013) A stochastic reconstruction framework for analysis of water resource system vulnerability to climate-induced changes in river flow regime. Water Resour Res 49:291–305. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012wr012755
Nelsen RB (1999) An introduction to copulas, volume 139 of Lecture Notes in Statistics. Springer-Verlag, New York
Niu G, Li YP, Huang GH, Liu J, Fan YR (2016) Crop planning and water resource allocation for sustainable development of an irrigation region in China under multiple uncertainties. Agric Water Manag 166:53–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.12.011
Parsapour-Moghaddam P, Abed-Elmdoust A, Kerachian R (2015) A heuristic evolutionary game theoretic methodology for conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources. Water Resour Manag 29:3905–3918
Pereira LS, Allen RG, Smith M, Raes D (2015) Crop evapotranspiration estimation with FAO56: past and future. Agric Water Manag 147:4–20
Ren CF, Li RH, Zhang LD, Guo P (2016) Multiobjective stochastic fractional goal programming model for water resources optimal allocation among industries. J Water Resour Plan Manag 142:04016036. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0000681
Sun Z, Zhang J, Yan D, Wu L, Guo E (2015) The impact of irrigation water supply rate on agricultural drought disaster risk: a case about maize based on EPIC in Baicheng City, China. Nat Hazards 78:23–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1695-9
van Werkhoven K, Wagener T, Reed P, Tang Y (2009) Sensitivity-guided reduction of parametric dimensionality for multi-objective calibration of watershed models. Adv Water Resour 32:1154–1169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.03.002
Wang C (2016) A joint probability approach for coincidental flood frequency analysis at ungauged basin confluences. Nat Hazards 82:1727–1741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2265-5
Wang Y, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Peng H, Shi Y (2016a) Modelling water quality and quantity with the influence of inter-basin water diversion projects and cascade reservoirs in the Middle-lower Hanjiang River. J Hydrol 541:1348–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.08.039
Wang YY, Huang GH, Wang S, Li W, Guan PB (2016b) A risk-based interactive multi-stage stochastic programming approach for water resources planning under dual uncertainties. Adv Water Resour 94:217–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.05.011
WWDR (2016) World Water Development Report 2016: water and jobs. UNESCO, Paris (World Water Development Report)
Yang Y, Yang Y, Moiwo JP, Hu Y (2010) Estimation of irrigation requirement for sustainable water resources reallocation in North China. Agric Water Manag 97:1711–1721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.06.002
Yazdi J, Lee EH, Kim JH (2015) Stochastic multiobjective optimization model for urban drainage network rehabilitation. J Water Resour Plan Manag 141:04014091. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0000491
Ye A, Duan Q, Chu W, Xu J, Mao Y (2014) The impact of the South-North Water Transfer Project (CTP)’s central route on groundwater table in the Hai River basin, North China. Hydrol Process 28:5755–5768. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10081
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Singh VP (2015) Uncertainty evaluation of copula analysis of hydrological droughts in the East River basin. China Global and Planetary Change 129:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.03.001
Zhuang XW, Li YP, Huang GH, Zeng XT (2015) An inexact joint-probabilistic programming method for risk assessment in water resources allocation. Stoch Env Res Risk A 29:1287–1301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-1008-y
Funding
The research was supported by the National Science and Technology Support Program of China (2015BAB07B02), Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51621092), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51609166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Liu, Y. & Sun, B. Water shortage risk assessment considering large-scale regional transfers: a copula-based uncertainty case study in Lunan, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 23328–23341 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2408-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2408-1