Abstract
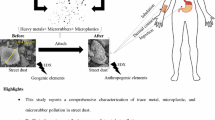
Environmental pollutants such as microplastics have become a major concern over the last few decades. We investigated the presence, characteristics, and potential health risks of microplastic dust ingestion. The plastic load of 88 to 605 microplastics per 30 g dry dust with a dominance of black and yellow granule microplastics ranging in size from 250 to 500 μm was determined in 10 street dust samples using a binocular microscope. Fluorescence microscopy was found to be ineffective for detecting and counting plastic debris. Scanning electron microscopy, however, was useful for accurate detection of microplastic particles of different sizes, colors, and shapes (e.g., fiber, spherule, hexagonal, irregular polyhedron). Trace amounts of Al, Na, Ca, Mg, and Si, detected using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, revealed additives of plastic polymers or adsorbed debris on microplastic surfaces. As a first step to estimate the adverse health effects of microplastics in street dust, the frequency of microplastic ingestion per day/year via ingestion of street dust was calculated. Considering exposure during outdoor activities and workspaces with high abundant microplastics as acute exposure, a mean of 3223 and 1063 microplastic particles per year is ingested by children and adults, respectively. Consequently, street dust is a potentially important source of microplastic contamination in the urban environment and control measures are required.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams P (2002) Soils: their implications to human health. Sci Total Environ 291:1–32
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Int 30(8):1009–1017
Akhbarizadeh R, Moore F, Keshavarzi B, Moeinpour A (2017) Microplastics and potentially toxic elements in coastal sediments of Iran’s main oil terminal (Khark Island). Environ Pollut 220:720–731
Andrady AL (2011) Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1596–1605
Arthur C, Baker J, Bamford J (2008) Proceedings of the International research workshop on the occurrence, effects and fate of microplastic marine debris, 9–11 September 2008, Tacoma, WA, USA, technical memorandum NOS-OR&R-30 2008 (National Oceanic and atmospheric
Barasarathi J, Agamuthu P, Emenike CU, Fauziah SH (2014) Microplastic abundance in selected mangrove forest in Malaysia. In proceeding of the ASEAN conference on Science and technology (1-5)
Barnes DK, Galgani F, Thompson RC, Barlaz M (2009) Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans Royal Soc Lond B Biol Sci 364(1526):1985–1998
Björkner B (1995) Plastic materials. Textbook of contact dermatitis Springer, 539–572
Bolgar M, Hubball J, Groeger J, Meronek S (2015) Handbook for the chemical analysis of plastic and polymer additives. CRC Press
Browne MA, Crump P, Niven SJ, Teuten E, Tonkin A, Galloway T, Thompson R (2011) Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: sources and sinks. Environ Sci Technol 45(21):9175–9179
Choate LM, Ranville JF, Bunge AL, Macalady DL (2006) Dermally adhered soil: 1. Amount and particle-size distribution. Integr Environ Asses Manage 2(4):375–384
Christie RM (1994) Pigments, dyes and fluorescent brightening agents for plastics: an overview. Polym Int 34:351–361
Cole M, Lindeque P, Fileman E, Halsband C, Goodhead R, Moger J, Galloway TS (2013) Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ Sci Technol 47(12):6646–6655
Cole M, Lindeque P, Halsband C, Galloway TS (2011) Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 62(12):2588–2597
Davis A, Drexler JW, Ruby MV, Nicholson A (1993) Micromineralogy of mine wastes in relation to lead bioavailability, Butte, Montana. Environ Sci Technol 27(7):1415–1425
Dehghani S, Moore F, Keshavarzi B, Beverley AH (2017) Health risk implications of potentially toxic metals in street dust and surface soil of Tehran, Iran. Ecotox Environ Saf 136:92–103
Dekiff JH, Remy D, Klasmeier J, Fries E (2014) Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney. Environ Pollut 186:248–256
Dris R, Gasperi J, Rocher V, Saad M, Renault N, Tassin B (2015) Microplastic contamination in an urban area: a case study in greater Paris. Environ Chem 12(5):592–599
Dris R, Gasperi J, Mirande C, Mandin C, Guerrouache M, Langlois V, Tassin B (2017) A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ Pollut 221:453–458
Dubaish F, Liebezeit G (2013) Suspended microplastics and black carbon particles in the jade system, southern North Sea. Water Air Soil Pollut 224
Eriksen M, Mason S, Wilson S, Box C, Zellers A, Edwards W, Amato S (2013) Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Marine Pollut Bull 77(1):177–182
Fries E, Dekiff JH, Willmeyer J, Nuelle MT, Ebert M, Remy D (2013) Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Env Sci Process Impact 15(10):1949–1956
Gallagher A, Rees A, Rowe R, Stevens J, Wright P (2016) Microplastics in the Solent estuarine complex, UK: an initial assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 102(2):243–249
Harris SG, Harper BL (2004) Exposure scenario for CTUIR traditional subsistence lifeways. Department of Science & Engineering, confederated tribes of the Umatilla Indian reservation, PO Box 638, Pendleton, OR 97801
Heiri O, Lotter AF, Lemcke G (2001) Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. J Paleolimnol 25(1):101–110
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC, Thiel M (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3060–3075
Ho KF, Lee SC, Chow JC, Watson JG (2003) Characterization of PM 10 and PM 2.5 source profiles for fugitive dust in Hong Kong. Atmos Environ 37(8):1023–1032
Holmes LA, Turner A, Thompson RC (2012) Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment. Environ Pollut 160:42–48
Holmes LA, Turner A, Thompson RC (2014) Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions. Mar Chem 167:25–32
Horton AA, Walton A, Spurgeon DJ, Lahive E, Svendsen C (2017) Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci Total Environ 586:127–141
Imhof HK, Ivleva NP, Schmid J, Niessner R, Laforsch C (2013) Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles. Curr Biol 23(19):R867–R868
Imhof HK, Schmid J, Niessner R, Ivleva NP, Laforsch C (2012) A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic environments. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 10(7):524–537
Järvholm B (2000) Natural organic fibers-health effects. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 73(9):S69–S74. doi:10.1007/PL00014629
Kissel JC, Shirai JH, Richter KY, Fenske RA (1998) Investigation of dermal contact with soil in controlled trials. J Soil Contam 7(6):737–752
Koch HM, Calafat AM (2009) Human body burdens of chemicals used in plastic manufacture. Philos Trans Royal Soc B Biol Sci 364:2063–2078
Leotsinidis M, Alexopoulos A, Kostopoulou-Farri E (2005) Toxic and essential trace elements in human milk from Greek lactating women: association with dietary habits and other factors. Chemosphere 61(2):238–247
Ljung K, Selinus O, Otabbong E, Berglund M (2006) Metal and arsenic distribution in soil particle sizes relevant to soil ingestion by children. Appl Geochem 21(9):1613–1624
Löder MG, Gerdts G (2015) Methodology used for the detection and identification of microplastics—a critical appraisal. In: Marine anthropogenic litter (201-227). Springer International publishing
Magnusson K, Eliasson K, Fråne A, Haikonen K, Hultén J, Olshammar M, Stadmark J, Voisin A (2016) Swedish sources and pathways for microplastics to the marine environment. A review of existing data IVL, C, 183
Managaki S, Takada H (2005) Fluorescent whitening agents in Tokyo Bay sediments: molecular evidence of lateral transport of land-derived particulate matter. Mar Chem 95:113–127
Mielke HW, Gonzales CR, Smith MK, Mielke PW (1999) The urban environment and children's health: soils as an integrator of lead, zinc, and cadmium in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Environ Res 81(2):117–129
Nuelle MT, Dekiff JH, Remy D, Fries E (2014) A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ Pollut 184:161–169
Patinha C, Duraes N, Sousa P, Dias AC, Reis AP, Noack Y, Ferreira da Silva E (2015) Assessment of the influence of traffic-related particles in urban dust using sequential selective extraction and oral bioaccessibility tests. Environ Geochem Health 37:707–724
Qiu Q, Peng J, Yu X, Chen F, Wang J, Dong F (2015) Occurrence of microplastics in the coastal marine environment: first observation on sediment of China. Mar Pollut Bull 98(1):274–280
Rillig MC (2012) Microplastic in terrestrial ecosystems and the soil? Environ Sci Technol 46:6453–6454
Robbins MA (2013) The collector’s book of fluorescent minerals. Springer Science & Business Media
Rocha-Santos T, Duarte AC (2015) A critical overview of the analytical approaches to the occurrence, the fate and the behavior of microplastics in the environment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 65:47–53
Rochman CM, Browne MA, Halpern BS, Hentschel BT, Hoh E, Karapanagioti HK, Rios-Mendoza LM, Takada H, Teh S, Thompson RC (2013) Classify plastic waste as hazardous. Nature 494(7436):169
Rojas-Bracho L, Suh HH, Oyola P, Koutrakis P (2002) Measurements of children’s exposures to particles and nitrogen dioxide in Santiago, Chile. Sci Total Environ 287(3):249–264
Siciliano SD, James K, Zhang G, Schafer AN, Peak JD (2009) Adhesion and enrichment of metals on human hands from contaminated soil at an Arctic urban brownfield. Environ Sci Technol 43(16):6385–6390
Song YK, Hong SH, Jang M, Han GM, Rani M, Lee J, Shim WJ (2015) A comparison of microscopic and spectroscopic identification methods for analysis of microplastics in environmental samples. Marine Pollut Bull 93(1):202–209
Tehran Municipality (2015) Annual Internal Report. http://www.tehran.ir
Thompson R C (2015) Microplastics in the marine environment: sources, consequences and solutions. In: Marine anthropogenic litter (185-200). Springer International publishing
Thompson RC (2016) Sources, Distribution, and Fate of Microscopic Plastics in Marine Environments
USEPA (2000) N. Child-specific exposure factors handbook. NCEA-W-0853. External Review Draft, 2002
Van Cauwenberghe L, Vanreusel A, Mees J, Janssen CR (2013) Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ Pollut 182:495–499
Vianello A, Boldrin A, Guerriero P, Moschino V, Rella R, Sturaro A, Da Ros L (2013) Microplastic particles in sediments of lagoon of Venice, Italy: first observations on occurrence, spatial patterns and identification. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 130:54–61
Yamamoto N, Takahashi Y, Yoshinaga J, Tanaka A, Shibata Y (2006) Size distributions of soil particles adhered to children’s hands. Arch Environ Con Tox 51(2):157–163
Yang YY, Rodrigez-Jorquera IA, McGuire M, Toor GS (2015) Contaminants in the urban environment: microplastics. UF/IFAS Extension
Zheng L, Tang Q, Fan J, Huang X, Jiang C, Cheng H (2015) Distribution and health risk assessment of mercury in urban street dust from coal energy dominant Huainan City, China. Environ Sci Technol 22:9316–9322
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful from Shiraz University research council support. The authors also greatly thank Mrs. M. Gholizadeh, the laboratory expert of the Department of Biology at Shiraz University, for the assistance in fluorescence microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Capsule: Street dust is a potential source of microplastic contamination in the urban environment and poses a potential health risk to inhabitants via inadvertent ingestion.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
(DOCX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dehghani, S., Moore, F. & Akhbarizadeh, R. Microplastic pollution in deposited urban dust, Tehran metropolis, Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 20360–20371 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9674-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9674-1