Abstract
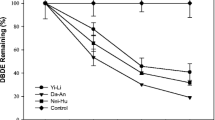
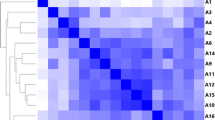
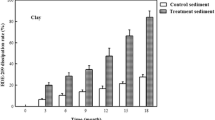
This study evaluated decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) anaerobic debromination and bacterial community changes in mangrove sediment. BDE-209 debromination rates were enhanced with zerovalent iron compared to without zerovalent iron in the sediment. BDE-209 debromination rates in microcosms constructed with sediments collected in autumn were higher than in microcosms constructed with sediments collected in spring and were higher at the Bali sampling site than the Guandu sampling site. The intermediate products resulting from the reductive debromination of BDE-209 in sediment were nona-BDE (BDE-206, BDE-207), octa-BDEs (BDE-196, BDE-197), hepta-BDEs (BDE-183, BDE-184, BDE-191), hexa-BDEs (BDE-137, BDE-138, BDE-154, BDE-157), penta-BDEs (BDE-85, BDE-99, BDE-100, BDE-126), tetra-BDEs (BDE-47, BDE-49, BDE-66, BDE-77), tri-BDEs (BDE-17, BDE-28), and di-BDEs (BDE-15). Fifty bacterial genera associated with BDE-209 debromination were identified. Overall, 12 of the 50 bacterial genera were reported to be involved in dehalogenation of aromatic compounds. These bacteria have high potential to be BDE-209 debromination bacteria. Different combinations of bacterial community composition exhibit different abilities for BDE-209 anaerobic debromination.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mailem DM, Eliyas M, Khanafer M, Radwan SS (2015) Biofilms constructed for the removal of hydrocarbon pollutants from hypersaline liquids. Extremophiles 19:189–196. doi:10.1007/s00792-014-0698-x
Andrade LL, Leite DCA, Ferreir EM, Ferreir LQ, Paula GR, Maguire MJ, Hubert CRJ, Peixoto RS, Domingues RMCP, Rosado AS (2012) Microbial diversity and anaerobic hydrocarbon degradation potential in an oil-contaminated mangrove sediment. BMC Microbiol 12:186–195. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-12-186
Battin TJ, Kaplan LA, Findlay S, Hopkinson CS, Marti E, Packman AI, Newbold JD, Sabater F (2008) Biophysical controls on organic carbon fluxes in fluvial networks. Nat Geosci 1:95–100. doi:10.1038/ngeo101
Castillo-Carvajal LC, Sanz-Martín JL, Barragán-Huerta BE (2014) Biodegradation of organic pollutants in saline wastewater by halophilic microorganisms: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:9578–9588. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3036-z
Chang BV, Chang IT, Yuan SY (2008) Anaerobic degradation of phenanthrene and pyrene in mangrove sediment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:145–149. doi:10.1007/s00128-007-9333-1
Chang BV, Lu ZJ, Yuan SY (2009) Anaerobic degradation of nonylphenol in subtropical mangrove sediments. J Hazard Mater 165:162–167. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.085
Chen CY, Tien CJ, Sun YM, Hsieh CY, Lee CC (2013) Influence of water quality parameters on occurrence of polybrominated diphenyl ether in sediment and sediment to biota accumulation. Chemosphere 90:2420–2427. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.073
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn879
De Wit CA (2002) An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment. Chemosphere 46:583–624. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00225-9
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Gerecke AC, Hartmann PC, Heeb NV, Kohler HPE, Giger W, Schmid P, Zennegg M, Kohler M (2005) Anaerobic degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether. Environ Sci Technol 39:1078–1083. doi:10.1021/es048634j
Hausler S, Weber M, Siebert C, Holtappels M, Noriega-Ortega BE, De Beer D, Ionescu D (2014) Sulfate reduction and sulfide oxidation in extremely steep salinity gradients formed by freshwater springs emerging into the Dead Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 90:956–969. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12449
He Q, Sanford RA (2002) Induction characteristics of reductive dehalogenation in the ortho-halophenol-respiring bacterium, Anaeromyxobacter dehalogenans. Biodegradation 13:307–316. doi:10.1023/A:1022342421909
Huang HW, Chang BV, Lee CC (2014) Reductive debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether by anaerobic microbes from river sediment. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 87:60–65. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.10.011
Jesenska A, Sedlacek I, Damborsky J (2000) Dehalogenation of haloalkanes by Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and other mycobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:219–222. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.1.219-222.2000
Keum YS, Li QX (2005) Reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39:2280–2286. doi:10.1021/es048846g
Kim YM, Murugesan K, Chang YY, Kim EJ, Chang YS (2011) Degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by a sequential treatment with nanoscale zero valent iron and aerobic biodegradation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87:216–224. doi:10.1002/jctb.2699
Li CH, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2010) Anaerobic biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with amendment of iron(III) in mangrove sediment slurry. Biores Technol 101:8083–8092. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.005
Li H, Zhang Q, Wang XL, Ma XY, Lin KF, Liu YD, JD G, SG L, Shi L, Lu Q, Shen TT (2012) Biodegradation of benzene homologues in contaminated sediment of the East China Sea. Bioresour Technol 124:129–136. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.033
Li Y, Li X, Liu Y, Wang ET, Ren C, Liu W, Xu H, Wu H, Jiang N, Li Y, Zhang X, Xie Z (2016) Genetic diversity and community structure of rhizobia nodulating Sesbania cannabina in saline-alkaline soils. Syst Appl Microbiol 39:195–202. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2016.02.004
Liu C, Wang SK, Lu YB (2000) Chemical characterization of river sediment in Taiwan. Toxicol Environ Chem 76:205–218. doi:10.1080/02772240009358929
Lohner ST, Spormann AM (2013) Identification of a reductive tetrachloroethene dehalogenase in Shewanella sediminis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 368:20120326–20120335. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0326
Lu M, Zhang ZZ, Wu XJ, Xu YX, Su XL, Zhang M, Wang JX (2013) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by a metal resistant strain, Bacillus cereus JP12. Bioresour Technol 149:8–15. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.040
Oba Y, Futagami T, Amachi S (2014) Enrichment of a microbial consortium capable of reductive deiodination of 2,4,6-triiodophenol. J Biosci Bioeng 117:310–317. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.08.011
Pandey J, Heipieper HJ, Chauhan A, Arora PK, Prakash D, Takeo M, Jain RK (2011) Reductive dehalogenation mediated initiation of aerobic degradation of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol (2C4NP) by Burkholderia sp. strain SJ98. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:597–607. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3254-y
Redwood MD, Deplanche K, Baxter-Plant VS, Macaskie LE (2008) Biomass-supported palladium catalysts on Desulfovibrio desulfuricans and Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biotechnol Bioeng 99:1045–1054. doi:10.1002/bit.21689
Schreiber T, Gassmann K, Gotz C, Hubenthal U, Moors M, Krause G, Merk HF, Nguyen NH, Scanlan TS, Abel J, Rose CR, Fritsche E (2010) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers induce developmental neurotoxicity in a human in vitro model: evidence for endocrine disruption. Environ Health Perspect 118:572–578. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901435
Shi G, Yin H, Ye J, Peng H, Li J, Luo C (2013) Aerobic biotransformation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chemosphere 93:1487–1493. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.044
Shih YH, Tai YT (2010) Reaction of decabrominated diphenyl ether by zerovalent iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 78:1200–1206. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.12.061
Shih YH, Chou HL, Peng YH (2012) Microbial degradation of 4-monobrominated diphenyl ether with anaerobic sludge. J Hazard Mater 213–214:341–346. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.009
Smidt H, deVos WM (2004) Anaerobic microbial dehalogenation. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:43–73. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.58.030603.123600
Stiborova H, Vrkoslavova J, Pulkrabova J, Poustka J, Hajslova J, Demnerova K (2015) Dynamics of brominated flame retardants removal in contaminated wastewater sewage sludge under anaerobic conditions. Sci Total Environ 533:439–445. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.131
Sun WM, Li JW, Jiang L, Sun ZL, MY F, Peng XT (2015) Profiling microbial community structures across six large oilfields in China and the potential role of dominant microorganisms in bioremediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8751–8764. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6748-1
Tang S, Bai J, Yin H, Ye J, Peng H, Liu Z, Dang Z (2014) Tea saponin enhanced biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether by Brevibacillus brevis. Chemosphere 114:255–261. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.009
Tseng LH, Li MH, Tsai SS, Lee CW, Pan MH, Yao WJ, Hsu PC (2008) Developmental exposure to decabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-209): effects on thyroid hormone and hepatic enzyme activity in male mouse offspring. Chemosphere 70:640–647. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.078
Vavourakis CD, Ghai R, Rodriguez-Valera F, Sorokin DY, Tringe SG, Hugenholtz P, Muyzer G (2016) Metagenomic insights into the uncultured diversity and physiology of microbes in four hypersaline soda lake brines. Front Microbiol 7:211. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00211
Xu J, Wang P, Guo W, Dong J, Wang L, Dai S (2006) Seasonal and spatial distribution of nonylphenol in Lanzhou Reach of Yellow River in China. Chemosphere 65:1445–1451. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.042
Yang CW, Huang HW, Chao WL, Chang BV (2015a) Bacterial communities associated with aerobic degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from river sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3810–3819. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3626-9
Yang Y, Wang Z, He T, Dai Y, Xie S (2015b) Sediment bacterial communities associated with anaerobic biodegradation of bisphenol-A. Microb Ecol 70:97–104. doi:10.1007/s00248-014-0551-x
Yousuf B, Kumar R, Mishra A, Jha B (2014) Differential distribution and abundance of diazotrophic bacterial communities across different soil niches using a gene-targeted clone library approach. FEMS Microbiol Lett 360:117–125. doi:10.1111/1574-6968.12593
Yu KSH, Wong AHY, Yau KWY, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2005) Natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation on biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in mangrove sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 51:1071–1077. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.06.006
Zhang W, Zhang M, An S, Lin K, Li H, Cui C, Fu R, Zhu J (2012) The combined effect of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) and copper (Cu) on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 34:358–369. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2012.05.009
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, Republic of China (grant no. MOST 104-2313-B-031-001-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Diane Purchase
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, CW., Lee, CC., Ku, H. et al. Bacterial communities associated with anaerobic debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether from mangrove sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 5391–5403 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8259-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8259-8