Abstract
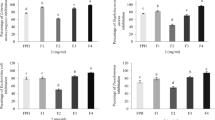
The enzymatic hydrolysis using Prolyve BS coupled to membrane process (Ultrafiltration (UF) and nanofiltration (NF)) is a means of biotransformation of tuna protein waste to Tuna protein hydrolysate (TPH) with higher added values. This method could be an effective solution for the production of bioactive compounds used in various biotechnological applications and minimizing the pollution problems generated by the seafood processing industries. The amino acid composition, functional and antioxidant properties of produced TPH were evaluated. The results show that the glutamic acid, aspartic acid, glycine, alaline, valine and leucine were the major amino acids detected in the TPH profile. After membrane fractionation process, those major amino acids were concentrated in the NF retentate (NFR). The NFR and NF permeate (NFP) have a higher protein solubility (>95 %) when compared to TPH (80 %). Higher oil and water binding capacity were observed in TPH and higher emulsifying and foam stability was found in UF retentate. The NFP showed the highest DPPH radical scavenging activity (65 %). The NFR contained antioxidant amino acid (30.3 %) showed the highest superoxide radical and reducing power activities. The TPH showed the highest iron chelating activity (75 %) compared to other peptide fractions. The effect of the membrane fractionation on the molecular weight distribution of the peptide and their bioactivities was underlined. We concluded that the TPH is a valuable source of bioactive peptides and their peptide fractions may serve as useful ingredients for application in food industry and formulation of nutritional products.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler-Nissen J (1979) Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. J Agri Food Chem 27:1256–1262
Adler-Nissen J (1986) A review of food hydrolysis specific areas. In: Adler-Nissen J (ed) Enzymic hydrolysis of food proteins. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, Copenhagen, pp. 57–59
Ahn CB, Kim JG, Je JY (2014) Purification and antioxidant properties of octapeptide from salmon byproduct protein hydrolysate by gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem 147:78–83
AOAC (2005) Official Methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. In (16 ed.). Washington: Washington DC.
Bersuder P, Hole M, Smith G (1998) Antioxidants from a heated histidine-glucose model system. I: investigation of the antioxidant role of histidine and isolation of antioxidants by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Amer Oil Chem Soci 75:181–187
Bhaskar N, Mahendrakar NS (2008) Protein hydrolysate from visceral waste proteins of catla (Catla catla): optimization of hydrolysis conditions for a commercial neutral protease. Bioresour Technol 99:4105–4111
Bougatef A, Nedjar-Arroume N, Manni L, Ravallec R, Barkia A, Guillochon D, Nasri M (2010) Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products proteins. Food Chem 118:559–565
Chi CF, Wang B, Deng YY, Wang YM, Deng SG, Ma JY (2014) Isolation and characterization of three antioxidant pentapeptides from protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle. Food Res Int 55:222–228
Chi CF, Hu FY, Wang B, Li ZR, Luo HY (2015) Influence of amino acid compositions and peptide profiles on antioxidant capacities of two protein hydrolysates from skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) dark muscle. Mar Drugs 13(5):2580–2601
Chobert JM, Bertrand-Harb C, Nicolas MG (1988) Solubility and emulsifying properties of caseins and whey proteins modified enzymically by trypsin. J Agri Food Chem 36:883–892
Chung SK, Osawa T, Kawakishi S (1997) Hydroxyl radical scavenging effects of spices and scavengers from brown mustard (Brassica nigra). Biosc Biotechnol Biochem 61:118–123
Diaz MN, Frei B, Vita JA, Keaney JF (1997) Antioxidants and atherosclerotic heart disease. New Eng J Med 337:408–416
Dickinson E, Lorient D (1994) Emulsions. In: Dickinson E, Lorient D (eds) Food macromolecules and colloids. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 201–274
Dong S, Zeng M, Wang D, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Yang H (2008) Antioxidant and biochemical properties of protein hydrolysates prepared from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Food Chem 107:1485–1493
Drioli E, Stankiewicz AI, Macedonio F (2011) Membrane engineering in process intensification- an overview. J Membrane Sci 380:1–8
Erkan N, Ozden O (2007) The changes of fatty acid and amino acid compositions in sea bream (Sparus aurata) during irradiation process. Radia Physic Chem 76:1636–1641
FAO (2008) fisheries departement: La situation mondiale des pêches et de l’aquaculture
FAO/WHO (1999) Energy and protein requirements. Report of Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation Technical Report. FAO/WHO and United Nations University. (pp. 113–121). Geneva
Gbogouri GA, Linder M, Fanni J, Parmentier M (2004) Influence of hydrolysis degree on the functional properties of Salmon byproducts hydrolysates. J Food Scie 69:615–622
Girgih AT, Udenigwe CC, Hasan FM, Gill TA, Aluko RE (2013) Antioxidant properties of Salmon (Salmo salar) protein hydrolysate and peptide fractions isolated by reverse-phase HPLC. Food Res Int 52:315–322
Halldorsdottir SM, Sveinsdottir H, Freysdottir J, Kristinsson HG (2014) Oxidative processes during enzymatic hydrolysis of cod protein and their influence on antioxidant and immunomodulating ability. Food Chem 142:201–209
He R, Girgih AT, Malomo SA, Ju X, Aluko RE (2013) Antioxidant activities of enzymatic rapeseed protein hydrolysates and the membrane ultrafiltration fractions. J Funct Food 5:219–227
Hsu KC (2010) Purification of antioxidative peptides prepared from enzymatic hydrolysates of tuna dark muscle by-product. Food Chem 122:42–48
Hsu K-C, Lu G-H, Jao C-L (2009) Antioxidative properties of peptides prepared from tuna cooking juice hydrolysates with orientase (Bacillus Subtilis). Food Res Inter 42(5–6):647–652
Huong TMN, Khalifa SBS, Zo R, Clair D-M, Jacques M, Luyen TT, et al. (2011) Enzymatic hydrolysis of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) by-products using Protamex protease. Food Tech Biotechnol 49(1):48–55
Iwasaki M, Harada R (1985) Proximate and amino acid composition of the roe and muscle of selected marine species. J Food Sci 50:1585–1587
Je J-Y, Qian Z-J, Byun H-G, Kim S-K (2007) Purification and characterization of an antioxidant peptide obtained from tuna backbone protein by enzymatic hydrolysis. Process Biochem 42(5):840–846
Je JY, Qian ZJ, Lee SH, Byun HG, Kim SK (2008) Purification and antioxidant properties of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) dark muscle peptide on free radical-mediated oxidative systems. J Med Food 11:629–637
Klompong V, Benjakul S, Kantachote D, Shahidi F (2007) Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem 102:1317–1327
Kristinsson HG, Rasco BA (2000) Fish protein hydrolysates: production, biochemical, and functional properties. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 40:43–81
Ktari N, Jridi M, Bkhairia I, Sayari N, Ben Salah R, Nasri M (2012) Functionalities and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysates from muscle of zebra blenny (Salaria basilisca) obtained with different crude protease extracts. Food Res Int 49:747–756
Kwon DY, Vigneswaran S, Fane AG, Aim RB (2000) Experimental determination of critical flux in cross-flow microfiltration. Sep Pur Tech 19:169–181
Lawal OS (2004) Functionality of African locust bean (Parkia biglobossa) protein isolate: effects of pH, ionic strength and various protein concentrations. Food Chem 86:345–355
Lempek TS, Martins VSG, Prentice C (2007) Rheology of Surimi-based products from fatty fish underutilized by the industry. J Aqu Food Prod Technol 16:27–44
Li ZY, Youravong W, H-Kittikun A (2009) Protein hydrolysis by protease isolated from tuna spleen by membrane filtration: a comparative study with commercial proteases. LWT Food Sci Technol 43:166–172
Li Z, Wang B, Chi C, Gong Y, Luo H, Ding G (2013) Influence of average molecular weight on antioxidant and functional properties of cartilage collagen hydrolysates from Sphyrna lewini, Dasyatis akjei and Raja porosa. Food Res Int 51:283–293
Lin MJY, Humbert ES, Sosulski FW (1974) Certain functional properties of sunflower meal products. J Food Sci 39:368–370
Liu F, Ooi VEC, Chang ST (1997) Free radical scavenging activities of mushroom polysaccharide extracts. Life Sci 60:763–771
McConnell AA, Eastwood MA, Mitchell WD (1974) Physical characteristics of vegetable foodstuffs that could influence bowel function. J Sci Food Agric 25:1457–1464
Memarpoor-Yazdi M, Mahaki H, Zare-Zardini H (2013) Antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysates and purified peptides from Zizyphus jujuba fruits. J Funct Foods 5:62–70
Mitsuda H, Yasumoto K, Iwami K (1996) Antioxidative action of indole compounds during the autoxidation of linoleic acid. Eiyo to Shokuryo 19:210–214
Motamedzadegan A, Davarniam B, Asadi G, Abedian A, Ovissipour M (2010) Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of yellowfin tuna Thunnus albacares viscera using Neutrase. Int Aqu Res 2:173–181
Mutilangi WAM, Panyam D, Kilara A (1996) Functional properties of hydrolysates from proteolysis of heat-denatured whey protein isolate. J Food Sci 61:270–275
Nazeer RA, Sampath Kumar NS, Jai Ganesh R (2012) In vitro and in vivo studies on the antioxidant activity of fish peptide isolated from the croaker (Otolithes ruber) muscle protein hydrolysate. Peptides 35:261–268
Osawa T, Namiki M (1985) Natural antioxidants isolated from eucalyptus leaf waxes. J Agric Food Chem 33:777–780
Pearce KN, Kinsella JE (1978) Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J Agric Food Chem 26:716–723
Peng X, Xiong YL, Kong B (2009) Antioxidant activity of peptide fractions from whey protein hydrolysates as measured by electron spin resonance. Food Chem 113:196–201
Pownall TL, Udenigwe CC, Aluko RE (2010) Amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of pea seed ( Pisum sativum L.) enzymatic protein hydrolysate fractions. J Agric Food Chem 58:4712–4718
Qian ZJ, Jung WK, Byun HG, Kim SK (2008) Protective effect of an antioxidative peptide purified from gastrointestinal digests of oyster, Crassostrea gigas against free radical induced DNA damage. Bioresour Technol 99:3365–3371
Rahali V, Chobert JM, Haertle T, Gueguen J (2000) Emulsification of chemical and enzymatic hydrolysates of beta-lactoglobulin: characterization of the peptides adsorbed at the interface. Nahrung 44:89–95
Rajapakse N, Mendis E, Jung WK, Je JY, Kim SK (2005) Purification of a radical scavenging peptide from fermented mussel sauce and its antioxidant properties. Food Res Int 38:175–182
Ranathunga S, Rajapakse N, Kim SK (2006) Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptide derived from muscle of conger eel (Conger myriaster). Eur Food Res Technol 222:310–315
Saidi S, Deratani A, Ben Amar R, Belleville MP (2013) Fractionation of a tuna dark muscle hydrolysate by a two-step membrane process. Sep Pur Tech 108:28–36
Samaranayaka AGP, Li-Chan ECY (2011) Food-derived peptidic antioxidants: a review of their production, assessment, and potential applications. J Funct Foods 3:229–254
Sampath Kumar NS, Nazeer RA, Jaiganesh R (2012) Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from the skin protein hydrolysate of two marine fishes, horse mackerel (Magalaspis cordyla) and croaker (Otolithes ruber). Amino Acids 42:1641–1649
Sarmadi BH, Ismail A (2010) Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: a review. Peptides 31:1949–1956
Sayari N, Sila A, Haddar A, Balti R, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Bougatef A (2016) Valorisation of smooth hound (Mustelus mustelus) waste biomass through recovery of functional, antioxidative and antihypertensive bioactive peptides. Envir Sci Poll Res 23:366–376
Shahidi F, Han XQ, Synowiecki J (1995) Production and characteristics of protein hydrolysates from capelin (Mallotus villosus). Food Chem 53:285–293
Sriket P, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Kijroongrojana K (2007) Comparative studies on chemical composition and thermal properties of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) meats. Food Chem 103:1199–1207
Thiansilakul Y, Benjakul S, Shahidi F (2007) Compositions, functional properties and antioxidative activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi). Food Chem 103:1385–1394
Tsumura K, Saito T, Tsuge K, Ashida H, Kugimiya W, Inouye K (2005) Functional properties of soy protein hydrolysates obtained by selective proteolysis. LWT Food Sci Technol 38:255–261
Udenigwe CC, Aluko RE (2011) Chemometric analysis of the amino acid requirements of antioxidant food protein hydrolysates. Int J Mole Sci 12:3148–3161
Van der Ven C, Gruppen H, de Bont DBA, Voragen AGJ (2002) Correlations between biochemical characteristics and foam-forming and -stabilizing ability of whey and casein hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem 50:2938–2946
Wang B, Li L, Chi CF, Ma JH, Luo HY, Xu Y (2013) Purification and characterisation of a novel antioxidant peptide derived from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 138:1713–1719
Wu HC, Chen HM, Shiau CY (2003) Free amino acids and peptides as related to antioxidant properties in protein hydrolysates of mackerel (Scomber austriasicus). Food Res Int 36:949–957
Yang JI, Ho HY, Chu YJ, Chow CJ (2008) Characteristic and antioxidant activity of retorted gelatin hydrolysates from cobia (Rachycentron canadum) skin. Food Chem 110:128–136
Yildirim A, Mavi A, Kara AA (2001) Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rumex crispus L. Extracts. J Agric Food Chem 49:4083–4089
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saidi, S., Ben Amar, R. Valorisation of tuna processing waste biomass for recovery of functional and antioxidant peptides using enzymatic hydrolysis and membrane fractionation process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 21070–21085 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7334-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7334-5