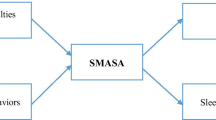
Abstract
Objective
The behaviors of children may be affected by sleep-disordered breathing (SDB). This study adopts a cross-sectional approach to investigate the relationship between the sleep apneas–hypopneas index during sleep and the behavioral and academic performance of schoolchildren in Taiwan.
Methods
A total of 138 children (85 boys and 53 girls), ages 6–11, were recruited from two elementary schools to participate in this study. Overnight polysomnographic examinations in hospital were performed to assess sleep quality, including total sleep time, arousal index, apneas–hypopneas index, desaturation index, and lowest oxygen saturation, as well as the percentage of total sleep time spent in rapid eye movement, stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, and stage 4. The children’s parents and teachers were required to complete a Chinese version of the Child Behavior Checklist and Teacher’s Report Form to assess child behavior and academic achievement.
Results
Compared with children without SDB (apneas–hypopneas index ≤1), those with severe SDB (apneas–hypopneas index >15) exhibited more irregular behavioral performance in somatic complaints (odds ratio (OR) = 9.43; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.04–85.71) and attention (OR = 9.95; 95% CI = 1.02–97.00). However, different severities of SDB groups did not show significant associations in academic performance.
Conclusion
Our study suggests that children with severe SDB may predispose to somatic complaints and attention problems so that sleep examination or medical intervention might be provided at an early age in these children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 22:667–689
Ali NJ, Pitson DJ, Stradling JR (1993) Snoring, sleep disturbance, and behaviour in 4–5 year olds. Arch Dis Child 68:360–366
Anuntaseree W, Rookkapan K, Kuasirikul S, Thongsuksai P (2001) Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea in Thai school-age children: prevalence and predisposing factors. Pediatr Pulmonol 32:222–227
Brunetti L, Rana S, Lospalluti ML, Pietrafesa A, Francavilla R, Fanelli M, Armenio L (2001) Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in a cohort of 1,207 children of southern Italy. Chest 120:1930–1935
Gislason T, Benediktsdóttir B (1995) Snoring, apneic episodes, and nocturnal hypoxemia among children 6 months to 6 years old. An epidemiologic study of lower limit of prevalence. Chest 107:963–966
Enlow DH, Poston WR (1990) Facial growth, 3rd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, USA
Lin RS, Sung FC, Huang SL, Gou YL, Ko YC, Gou HW, Shaw CK (2001) Role of urbanization and air pollution in adolescent asthma: a mass screening in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc 100:649–655
Rosen CL, Storfer-Isser A, Taylor HG, Kirchner HL, Emancipator JL, Redline S (2004) Increased behavioral morbidity in school-age children with sleep-disordered breathing. Pediatrics 114:1640–1648
Blunden S, Lushington K, Kennedy D, Martin J, Dawson D (2000) Behavior and neurocognitive performance in children aged 5–10 years who snore compared to controls. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 22:554–568
Chervin RD, Archbold KH, Dillon JE, Panahi P, Pituch KJ, Dahl RE, Guilleminault C (2002) Inattention, hyperactivity, and symptoms of sleep-disordered breathing. Pediatrics 109:449–456
Mulvaney SA, Goodwin JL, Morgan WJ, Rosen GR, Quan SF, Kaemingk KL (2006) Behavior problems associated with sleep disordered breathing in school-aged children-the Tucson children’s assessment of sleep apnea study. J Pediatr Psychol 31:322–330
Gozal D, Pope DE Jr (2001) Snoring during early childhood and academic performance at ages thirteen to fourteen years. Pediatrics 107:1394–1399
Montgomery-Downs HE, Jones VF, Molfese VJ, Gozal D (2003) Snoring in preschoolers: associations with sleepiness, ethnicity, and learning. Clin Pediatr 42:719–726
Urschitz MS, Guenther A, Eggebrecht E, Wolff J, Urschitz-Duprat PM, Schlaud M, Poets CF (2003) Snoring, intermittent hypoxia and academic performance in primary school children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:464–468
Hung CL, Marjoribanks K (2005) Parents, teachers and children’s school outcomes: a Taiwanese study. Edu Studies 31:3–13
Becker M, Drachman R, Kirscht P (1974) A new approach to explaining sick-role behaviour in low income populations. Am J Public Health 64:205–216
Harrison L, Mullen P, Green W (1992) A meta-analysis of studies of the Health Belief Model with adults. Health Educ Res 7:107–116
Kushida CA, Littner MR, Morgenthaler T, Alessi CA, Bailey D, Coleman J Jr, Friedman L, Hirshkowitz M, Kapen S, Kramer M, Lee-Chiong T, Loube DL, Owens J, Pancer JP, Wise M (2005) Practice parameters for the indications for polysomnography and related procedures: an update for 2005. Sleep 28:499–521
American Thoracic Society (1996) Standards and indications for cardiopulmonary sleep studies in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:866–878
Marcus CL, Omlin KJ, Basinki DJ, Bailey SL, Rachal AB, Von Pechmann WS, Keens TG, Ward SL (1992) Normal polysomnographic values for children and adolescents. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:1235–1239
Chau KW, Ng DK, Kwok CK, Chow PY, Ho JC (2003) Clinical risk factors for obstructive sleep apnoea in children. Singapore Med J 44:570–573
Li AM, Au CT, Sung RY, Ho C, Ng PC, Fok TF, Wing YK (2008) Ambulatory blood pressure in children with obstructive sleep apnoea: a community based study. Thorax 63:803–809
Leung PWL, Kwong SL, Tang CP, Ho TP, Hung SF, Lee CC, Hong SL, Chiu CM, Liu WS (2006) Test–retest reliability and criterion validity of the Chinese version of CBCL, TRF, and YSR. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 47:970–973
Yang HJ, Soong WT, Chiang CN, Chen WJ (2000) Competence and behavioral/emotional problems among Taiwanese adolescents as reported by parents and teachers. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psych 39:232–239
Achenbach TM (1999) Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 profile. University of Vermont Press, Burlington, VT, USA
Achenbach TM (2001) Achenbach system of empirically based assessment: Teacher’s Report Form. University of Vermont Press, Burlington, VT, USA
Chay OM, Goh A, Abisheganaden J, Tang J, Lim WH, Chan YH, Wee MK, Johan A, John AB, Cheng HK, Lin M, Chee T, Rajan U, Wang S, Machin D (2000) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in obese Singapore children. Pediatr Pulmonol 29:284–290
Verhulst SL, Schrauwen N, Haentjens D, Suys B, Rooman RP, Van Gaal L, De Backer WA, Desager KN (2007) Sleep-disordered breathing in overweight and obese children and adolescents: prevalence, characteristics and the role of fat distribution. Arch Dis Child 92:205–208
Naimark A, Cherniack RM (1960) Compliance of the respiratory system and its components in health and obesity. J Appl Physiol 15:377–382
O’donnell CP, Schaub CD, Haines AS, Berkowitz DE, Tankersley CG, Schwartz AR, Smith PL (1999) Leptin prevents respiratory depression in obesity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:1477–1484
Badr MS, Toiber F, Skatrud JB, Dempsey J (1995) Pharyngeal narrowing/occlusion during central sleep apnea. J Appl Physiol 78:1806–1815
Guimaraes CV, Kalra M, Donnelly LF, Shott SR, Fitz K, Singla S, Amin RS (2008) The frequency of lingual tonsil enlargement in obese children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:973–975
Kohler M (2009) Risk factors and treatment for obstructive sleep apnea amongst obese children and adults. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 9:4–9
Soultan Z, Wadowski S, Rao M, Kravath RE (1999) Effect of treating obstructive sleep apnea by tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy on obesity in children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 153:33–37
Khadra MA, McConnell K, VanDyke R, Somers V, Fenchel M, Quadri S, Jefferies J, Cohen AP, Rutter M, Amin R (2008) Determinants of regional cerebral oxygenation in children with sleep-disordered breathing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178:870–875
Tauman R, Ivanenko A, O’Brien LM, Gozal D (2004) Plasma C-reactive protein levels among children with sleep-disordered breathing. Pediatrics 113:564–569
Mezzanotte WS, Tangel DJ, White DP (1992) Waking genioglossal electromyogram in sleep apnea patients versus normal controls (a neuromuscular compensatory mechanism). J Clin Invest 89:1571–1579
Zhao Q, Sherrill DL, Goodwin JL, Quan SF (2008) Association between sleep disordered breathing and behavior in school-aged children: the Tucson children’s assessment of sleep apnea study. Open Epidemiol J 1:1–9
O’Brien LM, Mervis CB, Holbrook CR, Bruner JL, Smith NH, McNally N, Catherine McClimment M, Gozal D (2004) Neurobehavioral correlates of sleep-disordered breathing in children. J Sleep Res 13:165–172
Archbold KH (2006) Sleep disorders and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children: a missing differential diagnosis. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc 12:216–224
Aljadeff G, Gozal D, Bailey-Wahl SL, Burrell B, Keens TG, Ward SL (1996) Effects of overnight supplemental oxygen in obstructive sleep apnea in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:51–55
Beebe DW, Gozal D (2002) Obstructive sleep apnea and the prefrontal cortex: towards a comprehensive model linking nocturnal upper airway dysfunction to daytime cognitive and behavioural deficits. J Sleep Res 11:1–16
Pearson E, Rao N (2003) Socialization goals, parenting practices, and peer competence in Chinese and English preschoolers. Early Child Dev Care 173:131–146
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Taiwan National Science Council Grants 95-2413-H-040-003.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a conflict of interest involved in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ting, H., Wong, RH., Yang, HJ. et al. Sleep-disordered breathing, behavior, and academic performance in Taiwan schoolchildren. Sleep Breath 15, 91–98 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-010-0329-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-010-0329-4