Abstract
Purpose
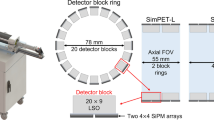
In this study, a small animal PET insert (SimPET-X, Brightonix Imaging Inc.) for simultaneous PET/MR imaging studies is presented. This insert covers an 11-cm-long axial field-of-view (FOV) and enables imaging of mouse total-bodies and rat heads.
Procedures
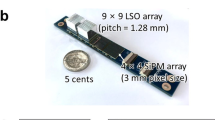
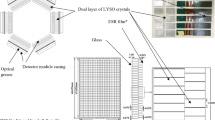
SimPET-X comprises 16 detector modules to yield a ring diameter of 63 mm and an axial FOV of 110 mm. The detector module supports four detector blocks, each comprising two 4 × 4 SiPM arrays coupled with a 20 × 9 array of LSO crystals (1.2 × 1.2 × 10 mm3). The physical characteristics of SimPET-X were measured in accordance with the NEMA NU4-2008 standard protocol. In addition, we assessed the compatibility of SimPET-X with a small animal-dedicated MRI (M7, Aspect Imaging) and conducted phantom and animal studies.
Results
The radial spatial resolutions at the center based on 3D OSEM without and with the warm background were 0.73 mm and 0.99 mm, respectively. The absolute peak sensitivity of the system was 10.44% with an energy window of 100–900 keV and 8.27% with an energy window of 250–750 keV. The peak NECR and scatter fraction for the mouse phantom were 348 kcps at 26.2 MBq and 22.1% with an energy window of 250–750 keV, respectively. The standard deviation of pixel value in the uniform region of an NEMA IQ phantom was 4.57%. The spillover ratios for air- and water-filled chambers were 9.0% and 11.0%, respectively. In the hot-rod phantom image reconstructed using 3D OSEM-PSF, all small rods were resolved owing to the high spatial resolution of the SimPET-X system. There was no notable interference between SimPET-X and M7 MRI. SimPET-X provided high-quality mouse images with superior spatial resolution, sensitivity, and counting rate performance.
Conclusion
SimPET-X yielded a remarkably improved sensitivity and NECR compared with SimPETTM.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pomper MG, Lee JS (2005) Small animal imaging in drug development. Curr Pharm Des 11:3247–3272
Yoo HJ, Lee JS, Lee JM (2015) Integrated whole body MR/PET: where are we? Korean J Radiol 16:32–49
Balyasnikova S, Löfgren J, de Nijs R, Zamogilnaya Y, Højgaard L, Fischer BM (2012) PET/MR in oncology: an introduction with focus on MR and future perspectives for hybrid imaging. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:458–474
Kubiessa K, Purz S, Gawlitza M, Kühn A, Fuchs J, Steinhoff KG, Boehm A, Sabri O, Kluge R, Kahn T, Stumpp P (2014) Initial clinical results of simultaneous 18 F-FDG PET/MRI in comparison to 18 F-FDG PET/CT in patients with head and neck cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41:639–648
Judenhofer MS, Wehrl HF, Newport DF, Catana C, Siegel SB, Becker M, Thielscher A, Kneilling M, Lichy MP, Eichner M, Klingel K, Reischl G, Widmaier S, Röcken M, Nutt RE, Machulla HJ, Uludag K, Cherry SR, Claussen CD, Pichler BJ (2008) Simultaneous PET-MRI: a new approach for functional and morphological imaging. Nat Med 14:459–465
Catana C, Procissi D, Wu Y, Judenhofer MS, Qi J, Pichler BJ, Jacobs RE, Cherry SR (2008) Simultaneous in vivo positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:3705–3710
Pichler BJ, Kolb A, Nägele T, Schlemmer H-P (2010) PET/MRI: paving the way for the next generation of clinical multimodality imaging applications. J Nucl Med 51:333–336
Karthik R, Radhakrishnan M, Rajalakshmi R, Raymann J (2020) Delineation of ischemic lesion from brain MRI using attention gated fully convolutional network. Biomed Eng Lett 11:3–13
Yoon HS, Ko GB, Kwon SI, Lee CM, Ito M, Chan Song I, Lee DS, Hong SJ, Lee JS (2012) Initial results of simultaneous PET/MRI experiments with an MRI-compatible silicon photomultiplier PET scanner. J Nucl Med 53:608–614
Yamamoto S, Watabe T, Watabe H et al (2011) Simultaneous imaging using Si-PM-based PET and MRI for development of an integrated PET/MRI system. Phys Med Biol 57:N1–N13
Ko GB, Yoon HS, Kim KY, Lee MS, Yang BY, Jeong JM, Lee DS, Song IC, Kim SK, Kim D, Lee JS (2016) Simultaneous multiparametric PET/MRI with silicon photomultiplier PET and ultra-high-field MRI for small-animal imaging. J Nucl Med 57:1309–1315
Levin CS, Maramraju SH, Khalighi MM, Deller TW, Delso G, Jansen F (2016) Design features and mutual compatibility studies of the time-of-flight PET capable GE SIGNA PET/MR system. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:1907–1914
Hong SJ, Kang HG, Ko GB, Song IC, Rhee J-T, Lee JS (2012) SiPM-PET with a short optical fiber bundle for simultaneous PET-MR imaging. Phys Med Biol 57:3869–3883
Schug D, Lerche C, Weissler B, Gebhardt P, Goldschmidt B, Wehner J, Dueppenbecker PM, Salomon A, Hallen P, Kiessling F, Schulz V (2016) Initial PET performance evaluation of a preclinical insert for PET/MRI with digital SiPM technology. Phys Med Biol 61:2851–2878
Stortz G, Thiessen JD, Bishop D, Khan MS, Kozlowski P, Retière F, Schellenberg G, Shams E, Zhang X, Thompson CJ, Goertzen AL, Sossi V (2018) Performance of a PET insert for high-resolution small-animal PET/MRI at 7 tesla. J Nucl Med 59:536–542
Hong SJ, Song IC, Ito M, Kwon SI, Lee GS, Sim KS, Park KS, Rhee JT, Lee JS (2008) An investigation Into the use of Geiger-mode solid-state photomultipliers for simultaneous PET and MRI acquisition. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 55:882–888
Son J-W, Kim KY, Park JY, Kim K, Lee YS, Ko GB, Lee JS (2020) SimPET: a preclinical PET insert for simultaneous PET/MR imaging. Mol Imaging Biol 22:1208–1217
Badawi RD, Shi H, Hu P, Chen S, Xu T, Price PM, Ding Y, Spencer BA, Nardo L, Liu W, Bao J, Jones T, Li H, Cherry SR (2019) First human imaging studies with the EXPLORER total-body PET scanner. J Nucl Med 60:299–303
Surti S, Pantel AR, Karp JS (2020) Total body PET: why, how, what for. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci 4:283–292
Berg E, Gill H, Marik J, Ogasawara A, Williams S, van Dongen G, Vugts D, Cherry SR, Tarantal AF (2020) Total-body PET and highly stable chelators together enable meaningful 89Zr-antibody PET studies up to 30 days after injection. J Nucl Med 61:453–460
Ko GB, Kim KY, Yoon HS et al (2016) Evaluation of a silicon photomultiplier PET insert for simultaneous PET and MR imaging. Med Phys 43:72
Kwon SI, Lee JS, Yoon HS, Ito M, Ko GB, Choi JY, Lee SH, Chan Song I, Jeong JM, Lee DS, Hong SJ (2011) Development of small-animal PET prototype using silicon photomultiplier (SiPM): initial results of phantom and animal imaging studies. J Nucl Med 52:572–579
Park H, Ko GB, Lee JS (2017) Hybrid charge division multiplexing method for silicon photomultiplier based PET detectors. Phys Med Biol 62:4390–4405
Ko GB, Lee JS (2017) Single transmission-line readout method for silicon photomultiplier based time-of-flight and depth-of-interaction PET. Phys Med Biol 62:2194–2207
Yoon HS, Lee JS (2014) Bipolar analog signal multiplexing for position-sensitive PET block detectors. Phys Med Biol 59:7835–7846
Son J-W, Won JY, Lee JS (2017) Evaluation of a FPGA-based real-time coincidence system for high count rate PET scanners. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Conf Rec:1–3
Hallen P, Schug D, Schulz V (2020) Comments on the NEMA NU 4-2008 standard on performance measurement of small animal positron emission tomographs. EJNMMI Phys 7:12
He X, Wedekind F, Kroll T et al (2019) Image-derived input functions for quantification of A(1) adenosine receptors availability in mice brains using PET and [(18)F]CPFPX. Front Physiol 10:1617
Kim SJ, Lee JS, Im KC, Kim SY, Park SA, Lee SJ, Oh SJ, Lee DS, Moon DH (2008) Kinetic modeling of 3'-deoxy-3'-18F-fluorothymidine for quantitative cell proliferation imaging in subcutaneous tumor models in mice. J Nucl Med 49:2057–2066
Lanz B, Poitry-Yamate C, Gruetter R (2014) Image-derived input function from the vena cava for 18F-FDG PET studies in rats and mice. J Nucl Med 55:1380–1388
Gsell W, Molinos C, Correcher C, Belderbos S, Wouters J, Junge S, Heidenreich M, Velde GV, Rezaei A, Nuyts J, Cawthorne C, Cleeren F, Nannan L, Deroose CM, Himmelreich U, Gonzalez AJ (2020) Characterization of a preclinical PET insert in a 7 Tesla MRI scanner: beyond NEMA testing. Phys Med Biol 65:245016
Courteau A, McGrath J, Walker PM, Pegg R, Martin G, Garipov R, Doughty P, Cochet A, Brunotte F, Vrigneaud JM (2021) Performance evaluation and compatibility studies of a compact preclinical scanner for simultaneous PET/MR imaging at 7 Tesla. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40:205–217
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from the Korean Ministry of SMEs and Startups (grant no. S2580037), the Korea Medical Device Development Fund (202011A06-1), and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2018R1D1A1B07045559).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Seoul National University Hospital.
Conflict of Interest
KY Kim, J-W Son, K Kim, Y Chung, GB Ko, and JS Lee are employees of Brightonix Imaging Inc.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 436 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K.Y., Son, JW., Kim, K. et al. Performance Evaluation of SimPET-X, a PET Insert for Simultaneous Mouse Total-Body PET/MR Imaging. Mol Imaging Biol 23, 703–713 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-021-01595-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-021-01595-z