Abstract
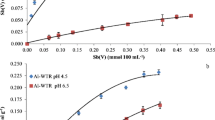
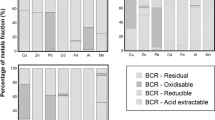
Here, we report on the ability of two different water treatment residues, a Fe-based (Fe-WTR) and an Al-based (Al-WTR) ones, to accumulate Cd(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solutions at different pH values (pH 4.5, 5.5, and 7.0). Fe-WTR showed a greater Zn(II) and Cd(II) sorption capacity than Al-WTR at all the pH values investigated, in particular at pH 7.0 (e.g., ∼0.200 and ∼0.100 mmol g−1 of Me(II) sorbed by Fe- and Al-WTR at pH 7.0, respectively). The greater capacity of the Fe-WTR to accumulate Me(II) seems to be linked to its higher content of iron and manganese ions and to its higher CEC value compared to Al-WTR. The role of the inorganic and organic fractions of WTRs in metal sorption was also assessed. A higher affinity of Cd(II) with respect to Zn(II) toward functional groups of the organic matter of both WTRs was observed, while Zn(II) showed a stronger association with the inorganic phases. The sorption of both metal ions appeared mainly governed by the formation of inner-sphere surface complexes with the inorganic and organic phases of WTRs, as suggested by the sequential extraction data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. New York: Springer Verlag.
Axe, L., & Trivedi, P. (2002). Intraparticle surface diffusion of metal contaminants and their attenuation in microporous amorphous Al, Fe, and Mn oxides. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 247(2), 259–265.
Babatunde, A. O., Zhao, Y. Q., Burke, A. M., Morris, M. A., & Hanrahan, J. P. (2009). Characterization of aluminium-based water treatment residual for potential phosphorus removal in engineered wetlands. Environmental Pollution, 157(10), 2830–2836.
Babel, S., & Kurniawan, T. A. (2003). Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 97(1–3), 219–243.
Baken, S., Degryse, F., Verheyen, L., Merckx, R., & Smolders, E. (2011). Metal complexation properties of freshwater dissolved organic matter are explained by its aromaticity and by anthropogenic ligands. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(7), 2584–2590.
Basta, N., & Gradwohl, R. (2000). Estimation of Cd, Pb, and Zn bioavailability in smelter-contaminated soils by a sequential extraction procedure. Journal of Soil Contamination, 9(2), 149–164.
Bradl, H. B. (2004). Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 277(1), 1–18.
Castaldi, P., Melis, P., Silvetti, M., Deiana, P., & Garau, G. (2009). Influence of pea and wheat growth on Pb, Cd, and Zn mobility and soil biological status in a polluted amended soil. Geoderma, 151(3–4), 241–248.
Castaldi, P., Lauro, G., Senette, C., & Deiana, S. (2010). Role of the Ca-pectates on the accumulation of heavy metals in the root apoplasm. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12), 1008–1014.
Castaldi, P., Mele, E., Silvetti, M., Garau, G., & Deiana, S. (2014). Water treatment residues as accumulators of oxoanions in soil. Sorption of arsenate and phosphate anions from an aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 264, 144–152.
Castaldi, P., Silvetti, M., Garau, G., Demurtas, D., & Deiana, S. (2015). Copper(II) and lead(II) removal from aqueous solution by water treatment residues. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 283, 140–147.
Chaney, R. L., Broadhurst, C. L., & Centofanti, T. (2010). Phytoremediation of soil trace elements. In P. Hooda (Ed.), Trace Elements in Soils (pp. 311–352). Oxford: Wiley.
Chen, Y. (1996). Organic matter reactions involving micronutrients in soils and their effect on plants. In A. Piccolo (Ed.), Humic substances in terrestrial ecosystems (pp. 507–529). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Chiang, Y. W., Ghyselbrecht, K., Santos, R. M., Martens, J. A., Swennen, R., Cappuyns, V., et al. (2012). Adsorption of multi-heavy metals onto water treatment residuals: sorption capacities and applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 200, 405–415.
Ciavatta, C., Govi, M., Antisari, L. V., & Sequi, P. (1990). Characterization of Humified Compounds by Extraction and Fractionation on Solid Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Journal of Chromatography, 509(1), 141–146.
Galunin, E., Ferreti, J., Zapelini, I., Vieira, I., Tarley, C. R. T., Abrao, T., et al. (2014). Cadmium mobility in sediments and soils from a coal mining area on Tibagi River watershed: environmental risk assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 265, 280–287.
Garau, G., Silvetti, M., Castaldi, P., Mele, E., Deiana, P., & Deiana, S. (2014). Stabilising metal(loid)s in soil with iron and aluminium-based products: microbial, biochemical and plant growth impact. Journal of Environmental Management, 139, 146–153.
Gibbons, M. K., & Gagnon, G. A. (2011). Understanding removal of phosphate or arsenate onto water treatment residual solids. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(2–3), 1916–1923.
Goldberg, S., & Johnston, C. T. (2001). Mechanisms of arsenic adsorption on amorphous oxides evaluated using macroscopic measurements, vibrational spectroscopy, and surface complexation modeling. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 234(1), 204–216.
Han, F. X., & Singer, A. (2007). Binding and distribution of trace elements among solid-phase components in arid zone soils. In B. J. Alloway & J. T. Trevors (Eds.), Biogeochemistry of trace elements in arid environments (pp. 131–167). Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer.
Hinz, C., & Selim, H. M. (1994). Transport of zinc and cadmium in soils—experimental-evidence and modeling approaches. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 58(5), 1316–1327.
Hizal, J., & Apak, R. (2006). Modeling of copper(II) and lead(II) adsorption on kaolinite-based clay minerals individually and in the presence of humic acid. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 295(1), 1–13.
Huang, P. M. (2008). Impacts of physicochemical-biological interactions on metal and metalloid transformations in soils: an overview. In A. Violante, P. M. Huang, & G. M. Gadd (Eds.), Biophysico-chemical processes of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments (pp. 3–52). Hobokken: Wiley.
Ippolito, J. A., Barbarick, K. A., & Elliott, H. A. (2011). Drinking water treatment residuals: a review of recent uses. Journal of Environmental Quality, 40(1), 1–12.
Izquierdo, M., Marzal, P., Gabaldon, C., Silvetti, M., & Castaldi, P. (2012). Study of the interaction mechanism in the biosorption of copper(II) ions onto Posidonia oceanica and peat. Clean-Soil Air Water, 40(4), 428–437.
Kurniawan, T. A., Chan, G. Y. S., Lo, W. H., & Babel, S. (2006). Comparisons of low-cost adsorbents for treating wastewaters laden with heavy metals. Science of the Total Environment, 366(2–3), 409–426.
Lambert, R., Grant, C., & Sauve, S. (2007). Cadmium and zinc in soil solution extracts following the application of phosphate fertilizers. Science of the Total Environment, 378(3), 293–305.
Li, T. Q., Xu, Z. H., Han, X., Yang, X. E., & Sparks, D. L. (2012). Characterization of dissolved organic matter in the rhizosphere of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii and its effect on the mobility of zinc. Chemosphere, 88(5), 570–576.
Li, Y. H., Wang, L., Yang, L. S., & Li, H. R. (2014). Dynamics of rhizosphere properties and antioxidative responses in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under cadmium stress. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 102, 55–61.
Makris, K. C., Sarkar, D., Parsons, J. G., Datta, R., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2009). X-ray absorption spectroscopy as a tool investigating arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) sorption by an aluminum-based drinking-water treatment residual. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1–3), 980–986.
Nachtegaal, M., & Sparks, D. L. (2004). Effect of iron oxide coatings on zinc sorption mechanisms at the clay-mineral/water interface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 276(1), 13–23.
Nagar, R., Sarkar, D., Makris, K. C., Datta, R., & Sylvia, V. L. (2009). Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of arsenic in a soil amended with drinking-water treatment residuals. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 57(4), 755–766.
Nagar, R., Sarkar, D., Makris, K. C., & Datta, R. (2010). Effect of solution chemistry on arsenic sorption by Fe- and Al-based drinking-water treatment residuals. Chemosphere, 78(8), 1028–1035.
Peacock, C. L., & Sherman, D. M. (2004). Copper(II) sorption onto goethite, hematite and lepidocrocite: a surface complexation model based on ab initio molecular geometries and EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(12), 2623–2637.
Shaheen, S. M., Tsadilas, C. D., & Rinklebe, J. (2013). A review of the distribution coefficients of trace elements in soils: influence of sorption system, element characteristics, and soil colloidal properties. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 201, 43–56.
Strawn, D. G., & Sparks, D. L. (1999). The use of XAFS to distinguish between inner- and outer-sphere lead adsorption complexes on montmorillonite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 216(2), 257–269.
Warwick, P., Hall, A., Pashley, V., Van der Lee, J., & Maes, A. (1999). Zinc and cadmium mobility in Podzol soils. Chemosphere, 38(10), 2357–2368.
Weng, L. P., Temminghoff, E. J. M., Lofts, S., Tipping, E., & Van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2002). Complexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(22), 4804–4810.
Zeng, F. R., Ali, S., Zhang, H. T., Ouyang, Y. B., Qiu, B. Y., Wu, F. B., et al. (2011). The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environmental Pollution, 159(1), 84–91.
Acknowledgments
The financial support of Regione Sardegna (L.R. 7/2007 Progetti di ricerca di base- Bando 2012) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silvetti, M., Castaldi, P., Garau, G. et al. Sorption of Cadmium(II) and Zinc(II) from Aqueous Solution by Water Treatment Residuals at Different pH Values. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 313 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2578-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2578-0