Abstract
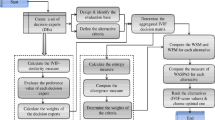
Flood control decisions are often involved with quantitative and qualitative criteria. In this paper, a decision model is presented for flood control operations based on the theory of variable fuzzy sets. Using dual comparison, two models computing relative membership grades with qualitative and quantitative criteria are established, respectively. A method integrating subjective preference and iterative weights is proposed for weight-assessment. First, an initial solution of criteria weights is obtained by using proposed fuzzy optimal iteration model. Then, according to their knowledge related to real time flood operations, operators may modify the initial weights if necessary. When the relative membership grades of alternatives belonging to all rankings are fixed by using multi-criterion variable fuzzy model proposed, the decision alternative is chosen according to the ranking characteristic value computed using a defuzzification equation. The case study of Fengman Reservoir flood operation (in China) is provided to illustrate the application of the proposed method. With the incorporation of operator’s knowledge related to flood operations, the proposed model is flexible and practical.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender MJ, Simonovic SP (2000) A fuzzy compromise approach to water resource systems planning under uncertainty. Fuzzy Sets Syst 115:35–44
Chen SY (1994) System fuzzy decision theory and the applications. Dalian University of Technology Press, Dalian, pp 65–78
Chen SY (1998) Engineering fuzzy set theory and the applications. National Defense Industrial Press, Beijing, pp 30–50
Chen SY (2000) Multiple criteria decision making for flood control operations: theory and model. J China Eng Sci (2):47–52
Chen SY, Hou ZC (2004) Multicriterion decision making for flood control operations: theory and applications. J Am Water Resour Assoc 40(1):67–76
Cheng C (1999) Fuzzy optimal model for the flood control system of upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Hydrol Sci J 44(4):573–582
Cheng C, Chau KW (2001) Fuzzy iteration methodology for reservoir flood control operation. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37(5):1381–1388
Cheng C, Chau KW (2002) Three-person multi-objective conflict decision in reservoir flood control. Eur J Oper Res 142:625–631
Cheng CT, Ou CP, Chau KW (2002) Combining a fuzzy optimal model with a genetic algorithm to solve multiobjective rainfall-runoff model calibration. J Hydrol 268:72–86
Despic O, Simonovic SP (2000) Aggregation operators for soft decision making in water resources. Fuzzy Sets Syst 115:11–33
Fontane DG, Gates TK, Moncada E (1997) Planning reservoir operations with imprecise objectives. J Water Resour Plan Manage 123(3):154–162
Houck MH (1982) Real-time reservoir operations by mathematical program. Water Resour Res 18(5):1345–1351
Huang W-C (1996) Decision support system for reservoir operation. Water-Resour Bull 32(6):1221–1232
Li D, Chen S (1997) Fuzzy cross iterated algorithm of multiobjective optimization problem and its convergence. Math Appl 10(3):107–109
Mehta R, Jain SK (2009) Optimal operation of a multi-purpose reservoir using neuro-fuzzy technique. Water Resour Manag 23:509–529
Nagesh Kumar D, Baliarsingh F, Srinivasa Raju K (2010) Optimal reservoir operation for flood control using folded dynamic programming. Water Resour Manag 24(6):1045–1064
Needham JT et al (2000) Linear programming for flood control in the Iowa and Des Moines Rivers. J Water Resour Plan Manage 126(3):118–127
Raju KS, Pillai CRS (1999) Multicriterion decision making in river basin planning and development. Eur J Oper Res 112:249–257
Russell SO, Campbell PF (1996) Reservoir operating rules with fuzzy programming. J Water Resour Plan Manage 122(3):165–170
Saad M et al (1996) Fuzzy learning decomposition for the scheduling of hydroelectric power systems. Water Resour Res 32(1):179–186
Shrestha BP, Duckstein L, Stakhiv EZ (1996) Fuzzy rule-based modeling of reservoir peration. J Water Resour Plan Manage 122(4):262–269
Wei CC, Hsu NS (2008) Multireservoir flood-control optimization with neural-based linear channel level routing under tidal effects. Water Resour Manag 22:1625–1647
Yakowitz S (1982) Dynamic programming application in water resources. Water Resour Res 18(40):673–696
Yeh WW-G (1985) Reservoir management and operations models: a state-of-the-art review. Water Resour Res 21(12):1797–1818
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.J., Zhao, R.H. & Hao, Y.W. Flood Control Operations Based on the Theory of Variable Fuzzy Sets. Water Resour Manage 25, 777–792 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9726-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9726-5