Abstract
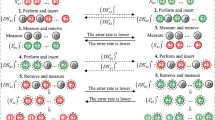
In this paper, we present a QKA protocol with the block transmission of EPR pairs. There are several advantages in this protocol. First, this protocol can guarantee both the fairness and security of the shared key. Second, this protocol has a high qubit efficiency since there is no need to consume any quantum state except the ones used for establishing the shared key and detecting eavesdropping. In addition, this protocol uses EPR pairs as the quantum information carriers and further utilizes single-particle measurements as the main operations. Therefore, it is more feasible than the protocols that need to perform Bell measurements. Especially, we also introduce a method for sharing EPR pairs between two participants over collective-dephasing channel and collective-rotation channel, respectively. This method is meaningful since sharing EPR pairs between two participants is an important work in many quantum cryptographic protocols, especially in the protocols over non-ideal channels. By utilizing this method, the QKA protocols, which are based on EPR pairs, can be immune to these kinds of collective noise.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, New Mexico, pp. 124–234 (1994)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of 28th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, New York, pp. 212–219 (1996)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–95 (2002)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Public-key distribution and coin tossing. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Bidirectional quantum key distribution protocol with practical faint laser pulses. Phys. Rev. A 70, 012311 (2004)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Wen, Q.Y.: Single-photon multiparty quantum cryptographic protocols with collective detection. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 47, 1389–1390 (2011)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Controlled order rearrangement encryption for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042315 (2003)
Tan, Y.G., Cai, Q.Y.: Practical decoy state quantum key distribution with finite resource. Eur. Phys. J. D 56, 449–455 (2010)
Song, S.Y., Wang, C.: Recent development in quantum communication. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57, 4694–4700 (1999)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052319 (2004)
Long, G.L., Deng, F.G., Wang, C., Li, X.H., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication and deterministic secure quantum communication. Front. Phys. China 2, 251 (2007)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 71, 044305 (2005)
Huang, W., Zuo, H.J., Li, Y.B.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of a multi-user quantum communication network using type entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 1354–1361 (2013)
Lin, S., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Quantum secure direct communication with \(\chi \)-type entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 78, 064304 (2008)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Li, C.Y., Liang, Y.J., Zhou, P., Zhou, H.Y.: Deterministic secure quantum communication without maximally entangled states. J. Koeran Phys. Soc. 49, 1354 (2006)
Yuan, H., Song, J., Zhou, J., Zhang, G., Wei, X.F.: High-capacity deterministic secure four-qubit W state protocol for quantum communication based on order rearrangement of particle pairs. Quantum Inf. Process. 50, 2403–2409 (2011)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Chen, H.: Deterministic secure quantum communication with collective detection using single photons. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 2787–2797 (2012)
Gu, B., Pei, S.X., Song, B., Zhong, K.: Deterministic secure quantum communication over a collective-noise channel. Sci. China Ser. G 52, 1913–1918 (2009)
Xiao, L., Long, G.L., Deng, F.G., Pan, J.W.: Efficient multiparty quantum secret sharing schemes. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052307 (2004)
Hao, L., Wang, C., Long, G.L.: Quantum secret sharing protocol with four state Grover algorithm and its proof-of-principle experimental demonstration. Opt. Commun. 284, 3639–3642 (2011)
Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: Multi-party quantum secret sharing based on two special entangled states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55, 460–464 (2012)
Massoud, H.D., Elham, F.: A novel and efficient multiparty quantum secret sharing scheme using entangled states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55, 1828–1831 (2012)
Adhikari, S., Chakrabarty, I., Agrawal, P.: Probabilistic secret sharing theory through noisy channel. Quantum Inf. Comput. 12, 253–270 (2012)
Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 42, 055305 (2009)
Jia, H.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Song, T.T., Gao, F.: Quantum protocol for millionaire problem. Opt. Commun. 284, 545–549 (2011)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Sun, Y.: Robust and efficient quantum private comparison of equality with collective detection over collective-noise channels. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56, 1670–1678 (2013)
Zeng, G.H., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 042312 (2002)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y.: Cryptanalysis of the arbitrated quantum signature protocols. Phys. Rev. A 84, 022344 (2011)
Su, Q., Huang, Z., Wen, Q.Y., Li, W.M.: Quantum blind signature based on two-state vector formalism. Opt. Commun. 283, 4408 (2010)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40, 1149 (2004)
Chong, S.K., Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: Improvement on “Quantum Key Agreement Protocol with Maximally Entangled States”. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 1793–1802 (2011)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Commun. 283, 1192–1195 (2010)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with bell states and bell measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 921–932 (2012)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Multiparty quantum key agreement protocol with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 1797–1805 (2012)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722 (1996)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Faithful qubit transmission against collective noise without ancillary qubits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 144101 (2007)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel. Phys. Rev. A 78, 022321 (2008)
Zanardi, P., Rasetti, M.: Noiseless quantum codes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 3306 (1997)
Huang, W., Guo, F.Z., Huang, Z., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Three-particle QKD protocol against a collective noise. Opt. Commun. 284, 536–540 (2011)
Skotiniotis, M., Duer, W., Kraus, B.: Efficient quantum communication under collective noise. Quantum Inf. Comput. 12, 290–323 (2013)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Jia, H.Y., Qin, S.J., Gao, F.: Fault tolerant quantum secure direct communication with quantum encryption against collective noise. Chin. Phys. B 21, 100308 (2012)
Li, X.H., Zhao, B.K., Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Fault tolerant quantum key distribution based on quantum dense coding with collective noise. Int. J. Quantum Inform. 7, 1479 (2009)
Shih, Y.: Entangled biphoton source-property and preparation. Rep. Prog. Phys. 66, 1009–1044 (2003)
Sweke, R., Sinayskiy, I., Petruccione, F.: Dissipative preparation of generalized Bell states. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 46, 104004 (2013)
Brida, G., Chekhova, M., Genovese, M., Krivitsky, L.: Generation of different Bell states within the spontaneous parametric down-conversion phase-matching bandwidth. Phys. Rev. A 76, 053807 (2007)
Agnew, M., Salvail, J.Z., Leach, J., Boyd, R.W.: Generation of orbital angular momentum bell states and their verification via accessible nonlinear witnesses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 030402 (2013)
Wang, T.J., Lu, Y., Long, G.L.: Generation and complete analysis of the hyperentangled Bell state for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 86, 042337 (2012)
Chen, Z.W., Zhao, B., Chen, Y.A., Schmiedmayer, J., Pan, J.W.: Fault-tolerant quantum repeater with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 76, 022329 (2007)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Long, G.L.: Hybrid entanglement purification for quantum repeaters. Phys. Rev. A 88, 022302 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by NSFC (Grant Nos. 61272057, 61170270, 61100203, 61003286, 61121061, 61103210), NCET (Grant No. NCET-10-0260), SRFDP (Grant No. 2009000 5110010), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 4112040, 4122054), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2011YB01) and BUPT Excellent Ph.D. Students Foundation (Grant No. CX201217, CX201334).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Wen, QY., Liu, B. et al. Quantum key agreement with EPR pairs and single-particle measurements. Quantum Inf Process 13, 649–663 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0680-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0680-z