Abstract
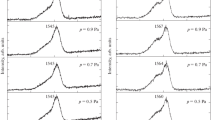
Amorphous carbon (a-C) films were deposited by d.c. magnetron sputtering with a graphite target in an argon plasma. We studied the dependence of the hardness and modulus of elasticity of the films on the deposition and annealing temperature in the range 20–650 °C by the indentation method, and we studied the structure of the films by electron diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. We have established that increasing the substrate temperature during condensation leads to a decrease in both the hardness and the modulus of elasticity of the a-C films. With annealing of the a-C films deposited at room temperature, these parameters vary insignificantly with temperature. The results obtained allow us to hypothesize that the structure of the films is formed predominantly by sp2-bonded carbon atoms. In the condensation temperature range of 50–450 °C, ordered formation of aromatic rings and graphite-like clusters occurs, and the degree of their ordering increases as the condensation temperature increases. At condensation temperatures T > 450 °C, the mechanism for growth of the C-film changes, and nuclei of graphite phase form directly on the substrate and grow. Annealing the C-films in the range 50–300 °C causes rapid transformation of distorted pentagonal and hexagonal aromatic rings to regular rings and ordering of the rings in the plane of the substrate without formation of graphite fragments. Further raising the annealing temperature has a weak effect on the structural changes in the film. The indicated changes in the film structure are the reason for the changes in hardness and modulus of elasticity in the studied temperature range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Anders, J. W. Ager III, G. M. Pharr, et al., “Heat treatment of cathodic arc deposited amorphous hard carbon films,” Thin Solid Films, 308-309, 186–190 (1997).
M. Chhowalla, A. C. Ferrary, J. Robertson, and G. A. J. Amaratunga, “Evolution of sp 2 bonding with deposition temperature in tetrahedral amorphous carbon studied by Raman spectroscopy,” Appl. Phys. Lett., 76, No. 11, 1419–1421 (2000).
M. A. Capano, N. T. McDevitt, R. K. Singh, and F. Qian, “Characterization of amorphous carbon thin films,” J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 14, No. 2, 431–435 (1996).
I. Alexandrou, H.-J. Scheibe, C. J. Kiely, et al., “Carbon films with a sp 2 network structure,” Phys. Rev. B, 60, No. 15, 10903–10907 (1999).
Y. Lifshitz, G. D. Lempert, S. Rotter, et al., “The influence of substrate temperature during ion beam deposition on the diamond-like or graphitic nature of carbon films,” Diamond Relat. Mater., 2, No. 2–4, 285–290 (1993).
H. Hofsass, H. Binder, T. Klumpp, and E. Recknagel, “Doping and growth of diamond-like carbon films by ion beam deposition,” Diamond Relat. Mater., 3, No. 1–2, 137–142 (1994).
J. J. Cuomo, D. L. Pappas, J. Bruley, et al., “Vapor deposition processes for amorphous carbon films with sp 3 fractions approaching diamond,” J. Appl. Phys., 70, No. 3, 1706–1711 (1991).
E. Mounier, F. Bertin, M. Adamik, et al., “Effect of the substrate temperature on the physical characteristics of amorphous carbon films deposited by d.c. magnetron sputtering,” Diamond Relat. Mater., 5, 1509–1515 (1996).
J. Fetter, M. Stüber, and S. Ulrich, “Growth effects in carbon coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 168, 169–178 (2003).
L. R. Shaginyan, A. A. Onoprienko, V. F. Britun, and V. P. Smirnov, “Influence of different physical factors on microstructure and properties of magnetron sputtered amorphous carbon films,” Thin Solid Films, 397, 288–295 (2001).
Y. Lifshitz, G. D. Lempert, S. Rotter, et al., “The effect of ion energy on the diamond-like/graphitic (sp 3/sp 2) nature of carbon films deposited by ion beams,” Diamond Relat. Mater., 3, No. 4–6, 542–546 (1994).
Ch. Wild and P. Koidl, “Thermal gas effusion from hydrogenated amorphous carbon films,” Appl. Phys. Lett., 51, No. 19, 1506–1508 (1987).
X. Jiang, W. Beyer, and K. Reichelt, “Gas evolution from hydrogenated amorphous carbon films, ” J. Appl. Phys., 68, No. 3, 1378–1380 (1990).
Y. Bounough, J. Spousta, M. Clin, et al., “Influence of the hydrogen evolution on the structural and electronic properties of a-C: H films,” Diamond Relat. Mater., 5, No. 3–5, 453–456 (1996).
R. Kalish, Y. Lifshit, K. Nugent, and S. Prawer, “Thermal stability and relaxation in diamond-like carbon. A Raman study of films with different sp 3 fractions (ta-C to a-C),” Appl. Phys. Lett., 74, No. 20, 2936–2938 (1999).
T. A. Friedman, J. P. Sullivan, J. A. Knapp, et al., “Thick stress-free amorphous-tetrahedral carbon films with hardness near that of diamond,” Appl. Phys. Lett., 71, No. 26, 3820–3822 (1997).
L. G. Jacobson, R. Priori, F. L. Freire, Jr., et all., “Comparative study of anneal induced modifications of amorphous carbon films deposited by dc magnetron sputtering at different argon plasma pressures, ” Diamond Relat. Mater., 9, 680–684 (2000).
A. A. Onoprienko, V. V. Artamonov, and I. B. Yanchuk, “Effect of deposition and anneal temperature on the resistivity of magnetron sputtered carbon films,” Surf. Coat. Tech., 172, 189–193 (2003).
A. C. Ferrary and J. Robertson, “Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon, ” Phys. Rev. B, 61, No. 20, 14095–14107 (2000).
S. Bhargava, H. D. Bist, A. V. Narlikar, et al., “Effect of substrate temperature and heat treatment on the microstructure of diamond-like carbon films,” J. Appl. Phys., 79, No. 4, 1917–1925 (1996).
M. Chhowalla, J. Robertson, C. W. Silva, et al., “Influence of ion energy and substrate temperature on the optical and electronic properties of tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) films,” J. Appl. Phys., 81, No. 1, 139–145 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Nos. 3–4(448), pp. 98–105, March–April, 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onoprienko, A.A., Yanchuk, I.B. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of amorphous carbon films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Powder Metall Met Ceram 45, 190–195 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-006-0062-5
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-006-0062-5