Abstract
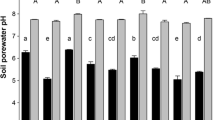
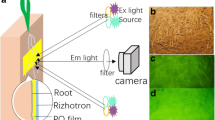
The present study presents new insights into pH dynamics in the rhizosphere of alpine pennycress (Noccaea caerulescens (J. Presl & C. Presl) F.K. Mey), maize (Zea mays L.) and ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.), when growing on three soils contaminated by trace metals with initial pH values varying from 5.6 to 7.4. The pH dynamics were recorded, using a recently developed 2D imaging technique based on planar pH optodes. This showed that alpine pennycress and ryegrass alkalinized their rhizosphere by up to 1.7 and 1.5 pH units, respectively, whereas maize acidified its rhizosphere by up to −0.7 pH units. The alkalinization by the roots of alpine pennycress and ryegrass was permanent and not restricted to specific root zones, whereas the acidification along the maize roots was restricted to the elongation zone and thus only temporary. Calculations showed that such pH changes should have noticeable effects on the solubility of the trace metal in the rhizosphere, and therefore on their uptake by the plants. As a result, it is suggested that models for trace metal uptake should include precise knowledge of rhizospheric pH conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber SA (1995) Soil nutrient bioavailability. A mechanistic approach. Wiley, New York, p 414
Blossfeld S, Gansert D (2007) A novel non-invasive optical method for quantitative visualization of pH dynamics in the rhizosphere of plants. Plant Cell Environ 30:176–186
Bravin M, Martí A, Clairotte M and Hinsinger P (2009a) Rhizosphere alkalisation—a major driver of copper bioavailability over a broad pH range in an acidic, copper-contaminated soil. Plant Soil 318:257–268
Bravin M, Tentscher P, Rose J, Hinsinger P (2009b) Rhizosphere pH gradient controls copper availability in a strongly acidic soil. Environmental Science & Technology (in press)
Bruemmer GW, Gerth J, Herms U (1986) Heavy metal species, mobility and availability in soils. Z PflanzenernaÉhr Bodenkd 149:382–398
Christensen TH (1984) Cadmium soil sorption at low concentrations: II. Reversibility, effect of changes in solute composition, and effect of soil aging. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 21:115–125
Colmer TD, Bloom AJ (1998) A comparison of NH4+ and NO3- net fluxes along roots of rice and maize. Plant Cell Environ 21:240–246
Costa R, Götz M, Mrotzek N, Lottmann J, Berg G, Smalla K (2006) Effects of site and plant species on rhizosphere community structure as revealed by molecular analysis of microbial guilds. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56:236–249
Fan L, Neumann PM (2004) The spatially variable inhibition by water deficit of maize root growth correlates with altered profiles of proton flux and cell wall pH. Plant Physiol 135:2291–2300
Fischer WR, Flessa H, Schaller G (1989) pH values and redox potentials in microsites of the rhizosphere. Z PflanzenernaÉhr Bodenkd 152:191–195
Gahoonia T, Claassen N, Jungk A (1992) Mobilization of phosphate in different soils by ryegrass supplied with ammonium or nitrate. Plant Soil 140:241–248
Gansert D, Blossfeld S (2008) The application of novel optical sensors (Optodes) in experimental plant ecology. In Progress in Botany. pp 333–358
Gansert D, Stangelmayr A, Krause C, Borisov AY, Wolfbeis OS, Arnold A, Müller A (2006) Hybrid optodes (HYBOP). In: Popp J, Strehle M (eds) Biophotonics: Visions for a better health care. Wiley VCH, Weinheim, pp 477–518
Gérard E (2000) Caractérisation du cadmium phytodisponible des sols par des méthodes isotopiques. In Ecole Nationale Supérieure d’Agronomie et des Industries Alimentaires. Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine, Vandoeuvre-Lès-Nancy, p 153
Gupta SK, Aten C (1993) Comparison and evaluation of extraction media and their suitability in a simple model to predict the biological relevance of heavy metal concentrations in contaminated soils. Int J Environ Anal Chem 51:25–46
Hinsinger P, Plassard C, Tang C, Jaillard B (2003) Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review. Plant Soil 248:43–59
Hinsinger P, Gobran GR, Gregory PJ, Wenzel WW (2005) Rhizosphere geometry and heterogeneity arising from root-mediated physical and chemical processes. New Phytol 168:293–303
Hinsinger P, Bengough A, Vetterlein D, Young I (2009) Rhizosphere: biophysics, biogeochemistry and ecological relevance. Plant and Soil
Huber C, Klimant I, Krause C, Wolfbeis OS (2001) Dual lifetime referencing as applied to a chloride optical sensor. Anal Chem 73:2097–2103
Jaillard B, Ruiz L, Arvieu J-C (1996) pH mapping in transparent gel using color indicator videodensitometry. Plant Soil 183:85–95
Kim TK, Silk WK (1999) A mathematical model for pH patterns in the rhizospheres of growth zones. Plant Cell Environ 22:1527–1538
Kirk GJD (2004) The biogeochemistry of submerged soils. In The Biogeochemistry of Submerged Soils. pp i–xi
Kirk GJD, Bajita JB (1995) Root-induced iron oxidation, pH changes and zinc solubilization in the rhizosphere of lowland rice. New Phytol 131:129–137
Kirk GJD, Kronzucker HJ (2005) The potential for nitrification and nitrate uptake in the rhizosphere of wetland plants: a modelling study. Ann Bot 96:639–646
Kirk GJD, Saleque MA (1995) Solubilization of phosphate by rice plants growing in reduced soil: prediction of the amount solubilized and the resultant increase in uptake. Eur J Soil Sci 46:247–255
Klimant I, Huber C, Liebsch G, Neurauter G, Stangelmayr A, Wolfbeis OS (2001) Dual lifetime referencing (DLR)—a new scheme for converting fluorescence intensity into a frequencydomain or time-domain information. In: Valeur B, Brochon JC (eds) New trends in fluorescence spectroscopy: Application to chemical and life sciences. Springer, Berlin, pp 257–275
Lebourg A, Sterckeman T, Ciesielski H, Proix N (1998) Trace metal speciation in three unbuffered salt solutions used to assess their bioavailability in soil. J Environ Quality 27:584–590
Loosemore N, Straczek A, Hinsinger P, Jaillard B (2004) Zinc mobilisation from a contaminated soil by three genotypes of tobacco as affected by soil and rhizosphere pH. Plant Soil 260:19–32
Luo YM, Christie P, Baker AJ (2000) Soil solution Zn and pH dynamics in non-rhizosphere soil and in the rhizosphere of Thlaspi caerulescens grown in a Zn/Cd-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 41:161–164
Luster J, Göttlein A, Sarret G, Nowack B (2009) Sampling, defining, characterising and modeling the rhizosphere—the soil science toolbox. Plant and Soil
Ma QY, Lindsay WL (1995) Estimation of Cd2+ and Ni2+ activities in soils by chelation. Geoderma 68:123–133
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic, London, p 889
Marschner H, Römheld V (1983) In vivo measurement of root induced pH changes at the soil-root interface: effect of plant species and nitrogen source. Z Pflanzenphysiol 111:241–251
McClure PR, Kochian LV, Spanswick RM, Shaff JE (1990) Evidence for Cotransport of Nitrate and Protons in Maize Roots: II. Measurement of NO(3) and H Fluxes with Ion-Selective Microelectrodes. Plant Physiol 93:290–294
McGrath SP, Shen ZG, Zhao FJ (1997) Heavy metal uptake and chemical changes in the rhizosphere of Thlaspi caerulescens and Thlaspi ochroleucum grown in contaminated soils. Plant Soil 188:153–159
Miller A, Cramer M (2004) Root nitrogen acquisition and assimilation. Plant Soil 274:1–36
Monsant AC, Tang C, Baker AJ (2008) The effect of nitrogen form on rhizosphere soil pH and zinc phytoextraction by Thlaspi caerulescens. Chemosphere 73:635–642
Page AL, Bingham FT, Chang AC (1981) Cadmium. In: Lepp NW (ed) Effect of heavy metal pollution on plants. Volume 1. Effects of trace metals on plant function. Applied Science, London, pp 77–109
Perriguey J (2006) Evaluation de l’equation de Nye-Tinker-Barber pour la modelisation du prelevement de Cadmium par le mais et le tabouret calaminaire. In ENSAIA. INPL, Nancy
Perriguey J, Sterckeman T, Morel J-L (2008) Effect of rhizosphere and plant-related factors on the cadmium uptake by maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Exper Bot 63:333–341
Peters WS (2004) Growth rate gradients and extracellular pH in roots: how to control an explosion. New Phytol 162:571–574
Pilet P-E, Versel J-M, Mayor G (1983) Growth distribution and surface pH patterns along maize roots. Planta 158:398–402
Pinel F, Leclerc-Cessac E, Staunton S (2003) Relative contributions of soil chemistry, plant physiology and rhizosphere induced changes in speciation on Ni accumulation in plant shoots. Plant Soil 255:619–629
Rausch C, Bucher M (2002) Molecular mechanisms of phosphate transport in plants. Planta 216:23–37
Reeves RD, Schwartz C, Morel JL, Edmondson J (2001) Distribution and metal-accumulating behavior of Thlaspi caerulescens and associated metallophytes in France. Int J Phytoremediat 3:145–172
Roose T, Kirk G (2009) The solution of convection–diffusion equations for solute transport to plant roots. Plant Soil 316:257–264
Salam AK, Helmke PA (1998) The pH dependence of free ionic activities and total dissolved concentrations of copper and cadmium in soil solution. Geoderma 83:281–291
Sauvé S, Hendershot W, Allen HE (2000) Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 34:1125–1131
Scheffer F, Schachtschabel P (2002) Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde. Heidelberg, Spektrum
Silk WK, Bambic DG, O’Dell RE, Green PG (2006) Seasonal and spatial patterns of metals at a restored copper mine site II. Copper in riparian soils and Bromus carinatus shoots. Environ Pollut 144:783–789
Sterckeman T, Baize D, Mench M, Sappin-Didier V, Proix N, Gomez A (2000) Comparison de trois methods d’extraction chimique d’estimation de la phytodisponibilité de Cd, Cu, Pb et Zn pour le blé. In A.I.P. AGREDE—QUASAR program p. 50. Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA)
Sterckeman T, Douay F, Proix N, Fourrier H, Perdrix E (2002) Assessment of the contamination of cultivated soils by eighteen trace elements around smelters in the North of France. Water Air Soil Pollut 135:173–194
Sterckeman T, Perriguey J, Caël M, Schwartz C, Morel JL (2004) Applying a mechanistic model to cadmium uptake by Zea mays and Thlaspi caerulescens: consequences for the assessment of the soil quantity and capacity factors. Plant Soil 262:289–302
Sterckeman T, Duquene L, Perriguey J, Morel JL (2005) Quantifying the effect of rhizosphere processes on the availability of soil cadmium and zinc. Plant Soil 276:335–345
Taylor AR, Bloom AJ (1998) Ammonium, nitrate, and proton fluxes along the maize root. Plant Cell Environ 21:1255–1263
Tinker PB, Nye PH (2000) Solute movement in the rhizosphere. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 444
Versel J-M, Mayor G (1985) Gradients in maize roots: local elongation and pH. Planta 164:96–100
Versel J-M, Pilet P-E (1986) Distribution of growth and proton efflux in gravireactive roots of maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 167:26–29
Walter A, Silk WK, Schurr U (2000) Effect of soil pH on growth and cation deposition in the root tip of zea mays L. J Plant Growth Regul 19:65–76
Wieland G, Neumann R, Backhaus H (2001) Variation of microbial communities in soil, rhizosphere, and rhizoplane in response to crop species, soil type, and crop development. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5849–5854
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the “Deutscher Akademischer Austausch Dienst” (DAAD) and the “Ministère de l’Education Nationale, de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche” within the framework of the PROCOPE programme in 2008.
The authors would like to express their thanks to Bernard Colin (INPL(ENSAIA)/INRA), W. Seidel, A. Lanzinger, M. Laug and W. Müller (University Düsseldorf) for their technical support and PreSens GmbH for the supply of planar optodes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Hinsinger.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blossfeld, S., Perriguey, J., Sterckeman, T. et al. Rhizosphere pH dynamics in trace-metal-contaminated soils, monitored with planar pH optodes. Plant Soil 330, 173–184 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0190-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0190-z