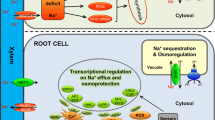
Abstract
The negative impact of soil salinity on agricultural yields is significant. For agricultural plants, sensitivity to salinity is commonly (but not exclusively) due to the abundance of Na+ in the soil as excess Na+ is toxic to plants. We consider reducing Na+ uptake to be the key, as well as the most efficient approach, to control Na+ accumulation in crop plants and hence to improve their salt resistance. Understanding the mechanism of Na+ uptake by the roots of higher plants is crucial for manipulating salt resistance. Hence, the aim of this review is to highlight and discuss recent advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of Na+ uptake by plant roots at both physiological and molecular levels. We conclude that continued efforts to investigate the mechanisms of root Na+ uptake in higher plants are necessary, especially that of low-affinity Na+ uptake, as it is the means by which sodium enters into plants growing in saline soils.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKT:
-
Arabidopsis K+ transporter
- CCC:
-
cation-Cl− cotransporter
- CNGC:
-
cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel
- HAK:
-
high-affinity K+ transporter
- HKT:
-
high-affinity K+ transporter
- KT:
-
K+ transporter
- KUP:
-
K+ uptake transporter
- LCT:
-
low-affinity cation transporter
- NSCC:
-
non-selective cation channel
- SOS:
-
salt overly sensitive
- VIC:
-
voltage-independent channel
References
Amtmann A, Sanders D (1999) Mechanism of Na+ uptake by plant cells. Adv Bot Res 29:75–112
Amtmann A, Laurie S, Leigh R, Sanders D (1997) Multiple inward channels provide flexibility in Na+/K+ discrimination at the plasma membrane of barley suspension culture cells. J Exp Bot 48:481–497
Amtmann A, Fischer M, Marsh EL, Stefanovic A, Sanders D, Schachtman DP (2001) The wheat cDNA LCT1 generates hypersensitivity to sodium in a salt-sensitive yeast strain. Plant Physiol 126:1061–1071
Anderson JA, Huprikar SS, Kochian LV, Lucas WJ, Gaber RF (1992) Functional expression of a probable Arabidopsis thaliana potassium channel in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3736–3740
Antosiewicz DM, Hennig J (2004) Overexpression of LCT1 in tobacco enhances the protective action of calcium against cadmium toxicity. Environ Pollut 129:237–245
Apse MP, Blumwald E (2007) Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett 581:2247–2254
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Apse MP, Sottosanto JB, Blumwald E (2003) Vacuolar cation/H+ exchange, ion homeostasis, and leaf development are altered in a T-DNA insertional mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. Plant J 36:229–239
Bao AK, Wang SM, Wu GQ, Xi JJ, Zhang JL, Wang CM (2008) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis H+-PPase enhanced the salt and drought tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Sci 176:232–240
Barkla BJ, Zingarelli L, Blumwald E, Smith JAC (1995) Tonoplast Na+/H+ antiport activity and its energization by the vacuolar H+-ATPase in the halophytic plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Plant Physiol 109:549–556
Berthomieu P, Conejero G, Nublat A, Brackenbury WJ, Lambert C, Savio C, Uozumi N, Oiki S, Yamada K, Cellier F, Gosti F, Simonneau T, Essah PA, Tester M, Very AA, Sentenac H, Casse F (2003) Functional analysis of AtHKT1 in Arabidopsis shows that Na+ recirculation by the phloem is crucial for salt tolerance. Embo J 22:2004–2014
Bertorello AM, Zhu JK (2009) SIK1/SOS2 networks: decoding sodium signals via calcium-responsive protein kinase pathways. Pflugers Arch-Eur J Physiol . doi:10.1007/s00424-00009-00646-00422
Binzel M, Hess FD, Bressan RA, Hasega PM (1988) Intracellular compartmentation of ion in salt adapted tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 86:607–614
Blumwald E (2003) Engineering salt tolerance in plants. In Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering Reviews, Vol 20, pp 261–275. INTERCEPT LTD SCIENTIFIC TECHNICAL & MEDICAL PUBLISHERS, Andover
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta-Biomembr 1465:140–151
Bolat I, Kaya C, Almaca A, Timucin S (2006) Calcium sulfate improves salinity tolerance in rootstocks of plum. J Plant Nutr 29:553–564
Box S, Schachtman DP (2000) The effect of low concentrations of sodium on potassium uptake and growth of wheat. Aust J Plant Physiol 27:175–182
Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1998) Plants use Calcium to resolve salt stress. Trends Plant Sci 3:411–412
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2008) Cellular mechanisms of potassium transport in plants. Physiol Plant 133:637–350
Buschmann PH, Vaidyanathan R, Gassmann W, Schroeder JI (2000) Enhancement of Na+ uptake currents, time-dependent inward-rectifying K+ channel currents, and K+ channel transcripts by K+ starvation in wheat root cells. Plant Physiol 122:1387–1397
Byrt CS, Platten JD, Spielmeyer W, James RA, Lagudah ES, Dennis ES, Tester M, Munns R (2007) HKT1;5-like cation transporters linked to Na+ exclusion loci in wheat, Nax2 and Kna1. Plant Physiol 143:1918–1928
Callahan MJ, Korn SJ (1994) Permeation of Na+ through a delayed rectifier K+ channel in chick dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Gen Physiol 104:747–771
Carden DE, Walker DJ, Flowers TJ, Miller AJ (2003) Single-cell measurements of the contributions of cytosolic Na+ and K+ to salt tolerance. Plant Physiol 131:676–683
Chan CWM, Schorrak LM, Smith RK Jr, Bent AF, Sussman MR (2003) A cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel, CNGC2, is crucial for plant development and adaptation to calcium stress. Plant Physiol 132:728–731
Cheeseman JM (1982) Pump leak sodium fluxes in low salt corn Zea mays roots. J Membr Biol 70:157–164
Cheeseman JM (1988) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol 87:547–550
Chen HX, Li PM, Gao HY (2007) Alleviation of photoinhibition by calcium supplement in salt-treated Rumex leaves. Physiol Plant 129:386–396
Clemens S, Antosiewicz DM, Ward JM, Schachtman DP, Schroeder JI (1998) The plant cDNA LCT1 mediates the uptake of calcium and cadmium in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12043–12048
Clough SJ, Fengler KA, Yu IC, Lippok B, Smith RK, Bent AF (2000) The Arabidopisis dnd1 “defense, no death” gene encodes a mutated cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9323–9328
Colmenero-Flores JM, Martinez G, Gamba G, Vazquez N, Iglesias DJ, Brumos J, Talon M (2007) Identification and functional characterization of cation-chloride cotransporters in plants. Plant J 50:278–292
Colmer TD, Fan TWM, Higashi RM, Lauchli A (1994) Interactions of Ca2+ and NaCl stress on the ion relations and intracellular pH of Sorghum bicolor root tips: An in vivo P-31-NMR study. J Exp Bot 45:1037–1044
Colmer TD, Flowers TJ, Munns R (2006) Use of wild relatives to improve salt tolerance in wheat. J Exp Bot 57:1059–1078
Cramer GR (2002) Sodium-calcium interactions under salinity stress. In: Läuchli A, Lüttge U (eds) Salinity: environment - plants–molecules. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, pp 205–227
Cramer GRL, Lauchli A, Polito VS (1985) Displacement of Ca2+ by Na+ from the plasmalemma of root cells. A primary response to salt stress. Plant Physiol 79:207–211
Cramer GR, Lynch J, Lauchli A, Epstein E (1987) Influx of Na+, K+, and Ca2+ into roots of salt-stressed cotton seedlings. Plant Physiol 83:510–516
Davenport RJ, Tester M (2000) A weakly voltage-dependent, nonselective cation channel mediates toxic sodium influx in wheat. Plant Physiol 122:823–834
Davenport R, Reid RJ, Smith FA (1996) Control of sodium influx by calcium and turgor in two charophytes differing in salinity tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 19:721–728
Davenport RJ, Munoz-Mayor A, Jha D, Essah PA, Rus A, Tester M (2007) The Na+ transporter AtHKT1;1 controls retrieval of Na+ from the xylem in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 30:497–507
Deal KR, Goyal S, Dvorak J (1999) Arm location of Lophopyrum elongatum genes affecting K+/Na+ selectivity under salt stress. Euphytica 108:193–198
Delpire E, Rauchman M, Beier D, Hebert S, Gullans S (1994) Molecular cloning and chromosome localization of a putative basolateral Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter from mouse inner medullary collecting duct (mIMCD-3) cells. J Biol Chem 269:25677–25683
Demidchik V, Tester M (2002) Sodium fluxes through nonselective cation channels in the plasma membrane of protoplasts from Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 379–387
Dubcovsky J, María GS, Epstein E, Luo MC, Dvorák J (1996) Mapping of the K+/Na+ discrimination locus Kna1 in wheat. 92, 448–454
Dvořák J, Gorham J (1992) Methodology of gene transfer by homoeologous recombination into Triticum turgidum: transfer of K+/Na+ discrimination from Triticum aestivum. Genome 35:639–646
Elumalai RP, Nagpal P, Reed JW (2002) A mutation in the arabidopsis KT2/KUP2 potassium transporter gene affects shoot cell expansion. Plant Cell 14:119–131
Epstein E (1998) How calcium enhances plant salt tolerance. Science 280:1906–1907
Essah PA (2002) Sodium transport and accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PhD thesis. Cambridge University, Cambridge, UK
Fairbairn DJ, Liu WH, Schachtman DP, Gomez-Gallego S, Day SR, Teasdale RD (2000) Characterisation of two distinct HKT1-like potassium transporters from Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Plant Mol Biol 43:515–525
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319
Flowers TJ, Lauchli A (1983) Sodium versus potassium: substitution and compartmentation. Encycl Plant Physiol 15:651–681
Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (1988) Ion relation of salt tolerance. In: Baker DA, Hall JL (eds) Solute transport in plant cells and tissues. Longman Scientific and Technical, Harlow, pp 392–413
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Flowers TJ, Troke PF, Yeo AR (1977) The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 28:89–121
Fu HH, Luan S (1998) AtKUP1: a dual-affinity K+ transporter from arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:63–73
Gamba G (2005) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol Rev 85:423–493
Garcia A, Rizzo CA, UdDin J, Bartos SL, Senadhira D, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (1997) Sodium and potassium transport to the xylem are inherited independently in rice, and the mechanism of sodium: potassium selectivity differs between rice and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 20:1167–1174
Garciadeblas B, Benito B, Rodrıguez-Navarro A (2002) Molecular cloning and functional expression in bacteria of the potassium transporters CnHAK1 and CnHAK2 of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa. Plant Mol Biol 50:623–633
Garciadeblas B, Senn ME, Banuelos MA, Rodriguez-Navarro A (2003) Sodium transport and HKT transporters: the rice model. Plant J 34:788–801
Gassmann W, Rubio F, Schroeder JI (1996) Alkali cation selectivity of the wheat root high-affinity potassium transporter HKT1. Plant J 10:869–882
Gaxiola RA, Li JS, Undurraga S, Dang LM, Allen GJ, Alper SL, Fink GR (2001) Drought- and salt-tolerant plants result from overexpression of the AVP1 H+-pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11444–11449
Genc Y, Mcdonald GK, Tester M (2007) Reassessment of tissue Na+ concentration as a criterion for salinity tolerance in bread wheat. Plant Cell Environ 30:1468–1498
Gierth M, Ma¨ser P, Schroeder JI (2005) The potassium transporter AtHAK5 functions in K+ deprivation-induced high-affinity K+ uptake and AKT1 K+ channel contribution to K+ uptake kinetics in arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 137:1105–1114
Gobert A, Park G, Amtmann A, Sanders D, Maathuis FJM (2006) Arabidopsis thaliana Cyclic Nucleotide Gated Channel 3 forms a non-selective ion transporter involved in germination and cation transport. J Exp Bot 57:791–800
Golldack D, Quigley F, Michalowski CB, Kamasani UR, Bohnert HJ (2003) Salinity stress-tolerant and -sensitive rice (Oryza sativa L.) regulate AKT1-type potassium channel transcripts differently. Plant Mol Biol 51:71–81
Gorham J (1990a) Salt tolerance in the Triticeae: ion discrimination in rye and Triticale. J Exp Bot 41:609–614
Gorham J (1990b) Salt tolerance in the Triticeae: K/Na discrimination in Aegilops species. J Exp Bot 41:615–621
Gorham J (1990c) Salt tolerance in the Triticeae: K/Na discrimination in synthetic hexaploid wheats. J Exp Bot 41:623–627
Gorham J (1994) Salt tolerance in the Triticeae:K/Na discrimination in some perennial wheatgrasses and their amphiploids with wheat. J Exp Bot 45:441–447
Gorham J, Bristol A, Young EM, Wyn Jones RG, Kashour G (1990) Salt tolerance in the Triticeae: K/Na discrimination in barley. J Exp Bot 41:1095–1101
Gorham J, Bristol A, Young EM, Wyn Jones RG (1991) The presence of the enhanced K/Na discrimination trait in diploid Triticum species. Theor Appl Genet 82:729–736
Gorham J, Bridges J, Dubcovsky J, Dvorak J, Hollington PA, Luo MC, Khan JA (1997) Genetic analysis and physiology of a trait for enhanced K+/Na+ discrimination in wheat. New Phytol 137:109–116
Grover A (1999) A novel approach for raising salt tolerant transgenic plants based on altering stress signalling through Ca2+/calmodulin- dependent protein phosphatase calcineurin. Curr Sci 76:136–137
Haas M (1994) The Na-K-Cl cotransporters. Am J Physiol 267:C869–C885
Haas M, Forbush B (1998) The Na-K-Cl cotransporters. J Bioenerg Biomembrane 30:161–172
Hajibagheri MA, Harvey DMR, Flowers TJ (1987) Quantitative ion distribution within root cells of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant maize varieties. New Phytol 105:367–379
Halfter U, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3735–3740
Haro R, Banuelos MA, Senn MAE, Barrero-Gil J, Rodriguez-Navarro A (2005) HKT1 mediates sodium uniport in roots. Pitfalls in the expression of HKT1 in yeast. Plant Physiol 139:1495–1506
He CX, Yan JQ, Shen GX, Fu LH, Holaday AS, Auld D, Blumwald E, Zhang H (2005) Expression of an arabidopsis vacuolar sodium/proton antiporter gene in cotton improves photosynthetic performance under salt conditions and increases fiber yield in the field. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1848–1854
He T, Cramer GR (1993) Salt tolerance of rapid-cycling brassica species in relation to potassium sodium ratio and selectivity at the whole plant and callus levels. J Plant Nutr 16:1263–1277
Hebert SC, Mount DB, Gamba G (2004) Molecular physiology of cation-coupled Cl cotransport: the SLC12 family. Pflugers Arch 447:580–593
Henriksson E, Henriksson KN (2005) Salt-stress signalling and the role of calcium in the regulation of the Arabidopsis ATHB7 gene. Plant Cell Environ 28:202–210
Hirschi KD (2004) The calcium conundrum. Both versatile nutrient and specific signal. Plant Physiol 136:2438–2442
Hirsch RE, Lewis BD, Spalding EP, Sussman MR (1998) A role for the AKT1 potassium channel in plant nutrition. Science 280:918–921
Horie T, Yoshida K, Nakayama H, Yamada K, Oiki S, Shinmyo A (2001) Two types of HKT transporters with different properties of Na+ and K+ transport in Oryza sativa. Plant J 27:129–138
Horie T, Horie R, Chan WY, Leung HY, Schroeder JI (2006) Calcium regulation of sodium hypersensitivities of sos3 and athkt1 mutants. Plant Cell Physiol 47:622–633
Horie T, Costa A, Kim TH, Han MJ, Horie R, Leung HY, Miyao A, Hirochika H, An G, Schroeder JI (2007) Rice OsHKT2;1 transporter mediates large Na+ influx component into K+-starved roots for growth. Embo J 26:3003–3014
Huang SB, Spielmeyer W, Lagudah ES, James RA, Platten JD, Dennis ES, Munns R (2006) A sodium transporter (HKT7) is a candidate for Nax1, a gene for salt tolerance in durum wheat. Plant Physiol 142:1718–1727
Huang S, Spielmeyer W, Lagudah ES, Munns R (2008) Comparative mapping of HKT genes in wheat, barley, and rice, key determinants of Na+ transport, and salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 59:927–937
Isenring P, Forbush B (1997) Ion and bumetanide binding by the Na-K-Cl cotransporter. importance of transmembrane domains. J Biol Chem 272:24556–24562
James RA, Davenport RJ, Munns R (2006) Physiological characterization of two genes for Na+ exclusion in durum wheat, Nax1 and Nax2. Plant Physiol 142:1537–1547
Jayasekaran K, Kim KN, Vivekanandan M, Shin JS, Ok SH (2006) Novel calcium-binding GTPase (AtCBG) involved in ABA-mediated salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 25:1255–1262
Kader MA, Seidel T, Golldack D, Lindberg S (2006) Expressions of OsHKT1, OsHKT2, and OsVHA are differentially regulated under NaCl stress in salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J Exp Bot
Katiyar-Agarwal S, Zhu J, Kim K, Agarwal M, Fu X, Huang A, Zhu JK (2006) The plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 interacts with RCD1 and functions in oxidative stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18816–18821
Kato Y, Hazama A, Yamagami M, Uozumi N (2003) Addition of a peptide tag at the C terminus of AtHKT1 inhibits its Na+ transport. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:2291–2293
Kim EJ, Kwak JM, Uozumi N, Schroeder JI (1998) AtKUP1: An Arabidopsis gene encoding high-affinity potassium transport activity. Plant Cell 10:51–62
Kim BG, Waadt R, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Dominguez-Solis JR, Schultke S, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:473–484
Kiss L, Immke D, LoTurco J, Korn S (1998) The interaction of Na+ and K+ in voltage-gated potassium channels: evidence for cation binding sites of different affinity. J Gen Physiol 111:195–206
Kiss L, LoTurco J, Korn S (1999) Contribution of the selectivity filter to inactivation in potassium channels. Biophys J 76:253–263
Kloareg B, Demarty M, Mabeau S (1987) Ion-exchange properties of isolated of isolated cell walls of brown algae: the interstitial solution. J Exp Bot 38:1652–1662
Knight H, Trewavas AJ, Knight MR (1997) Calcium signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana responding to drought and salinity. Plant J 12:1067–1078
Köhler C, Merkle T, Roby D, Neuhaus G (2001) Developmentally regulated expression of a cyclic nucleotidegated ion channel from Arabidopsis indicates its involvement in programmed cell death. Planta 213:327–332
Kronzucker HJ, Szczerba MW, Moazami-Goudarzi M, Britto DT (2006) The cytosolic Na+:K+ ratio does not explain salinity-induced growth impairment in barley: a dual-tracer study using 42 K+ and 24Na+. Plant Cell Environ 29:2228–2237
Kronzucker HJ, Szczerba MW, Schulze LM, Britto DT (2008) Non-reciprocal interactions between K+ and Na+ ions in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Exp Bot 59:2793–2801
Laurie S, Feeney KA, Maathuis FJM, Heard PJ, Brown SJ, Leigh RA (2002) A role for HKT1 in sodium uptake by wheat roots. Plant J 32:139–149
Lee SC, Lan WZ, Kim BG, Li LG, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Lu GH, Buchanan BB, Luan S (2007) A protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation network regulates a plant potassium channel. PNAS 104:15959–15964
Leng Q, Mercier RW, Hua BG, Fromm H, Berkowitz GA (2002) Electrophysiological analysis of cloned cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel. Plant Physiol 128:400–410
Li JY, Jiang GQ, Huang P, Ma J, Zhang FC (2007) Overexpression of the Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Suaeda salsa confers cold and salt tolerance to transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 90:41–48
Li J, He X, Xu L, Zhou J, Wu P, Shou H, Zhang F (2008) Molecular and functional comparisons of the vacuolar Na+/H+ exchangers originated from glycophytic and halophytic species. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9:132–140
Lindsay MP, Lagudah ES, Hare RA, Munns R (2004) A locus for sodium exclusion (Nax1), a trait for salt tolerance, mapped in durum wheat. Funct Plant Biol 31:1105–1114
Liu JP, Zhu JK (1997) An Arabidopsis mutant that requires increased calcium for potassium nutrition and salt tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14960–14964
Liu WH, Schachtman DP, Zhang W (2000) Partial Deletion of a Loop Region in the High Affinity K+ Transporter HKT1 Changes Ionic Permeability Leading to Increased Salt Tolerance. J Biol Chem 275:27924–27932
Liu WH, Fairbairn DJ, Reid RJ, Schachtman DP (2001) Characterization of two HKT1 homologues from Eucalyptus camaldulensis that display intrinsic osmosensing capability. Plant Physiol 127:283–294
Lopez-Barneo J, Hoshi T, Heinemann S, Aldrich R (1993) Effects of external cations and mutations in the pore region on C-type inactivation of shaker potassium channels. Recept Channels 1:61–71
Lynch J, Cramer GR, Lauchli A (1987) Salinity reduces membrane-associated calcium in corn root protoplasts. Plant Physiol 83:390–394
Lynch J, Polito VS, Läuchli A (1989) Salinity stress increases cytoplasmic Ca activity in maize root protoplasts. Plant Physiol (Bethesda) 90:1271–1274
Maathuis FJM, Amtmann A (1999) K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann Bot 84:123–133
Maathuis FJM, Sanders D (2001) Sodium uptake in Arabidopsis roots is regulated by cyclic nucleotides. Plant Physiol 127:1617–1625
Martinez-Atienza J, Jiang X, Garciablades B, Mendoza I, Zhu JK, Pardo JM, Quintero FJ (2007) Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 143:1001–1012
Maser P, Thomine S, Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Hirschi K, Sze H, Talke IN, Amtmann A, Maathuis FJM, Sanders D, Harper JF, Tchieu J, Gribskov M, Persans MW, Salt DE, Kim SA, Guerinot ML (2001) Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:1646–1667
Maser P, Eckelman B, Vaidyanathan R, Horie T, Fairbairn DJ, Kubo M, Yamagami M, Yamaguchi K, Nishimura M, Uozumi N, Robertson W, Sussman MR, Schroeder JI (2002) Altered shoot/root Na+ distribution and bifurcating salt sensitivity in Arabidopsis by genetic disruption of the Na+ transporter AtHKTI1. FEBS Lett 531:157–161
Melgar JC, Benlloch M, Fernandez-Escobar R (2006) Calcium increases sodium exclusion in olive plants. Sci Hortic 109:303–305
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Ann Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Munns R, Hare RA, James RA, Rebetzke GJ (2000) Genetic variation for improving the salt tolerance of durum wheat. Aust J Agric Res 51:69–74
Ogielska E, Aldrich R (1998) A mutation in S6 of Shaker potassium channels decreases the K+ affinity of an ion binding site revealing ionion interactions in the pore. J Gen Physiol 112:243–257
Ogielska E, Aldrich R (1999) Functional consequences of a decreased potassium affinity in a potassium channel pore ion interactions and C-type inactivation. J Gen Physiol 113:347–358
Oh DH, Gong QQ, Ulanov A, Zhang Q, Li YZ, Ma WY, Yun DJ, Bressan RA, Bohnert HJ (2007) Sodium stress in the halophyte Thellungiella halophila and transcriptional changes in a thsos1-RNA interference line. J Integr Plant Biol 49:1484–1496
Olías R, Eljakaoui Z, Li J, Morales PAD, Marín-manzano MC, Pardo JM, Belver A (2009) The plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 is essential for salt tolerance in tomato and affects the partitioning of Na+ between plant organs. Plant Cell Environ 32:904–916
Ozturk ZN, Talame V, Deyholos M, Michalowski CB, Galbraith DW, Gozukirmizi N, Tuberosa R, Bohnert HJ (2002) Monitoring large-scale changes in transcript abundance in drought- and salt-stressed barley. Plant Mol Biol 48:551–573
Panet R, Marcus M, Atlan H (1999) Overexpression of the Na+/K+/Cl− cotransporter gene induces cell proliferation and phenotypic transformation in mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 182:109–118
Pardo JM, Reddy MP, Yang S, Maggio A, Huh GH, Matsumoto T, Coca MA, Koiwa H, Yun DJ, Watad AA, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1998) Stress signalling through Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase calcineurin mediates saltadaptation in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9681–9686
Phean-O-pas S, Punteeranurak P, Buaboocha T (2005) Calcium signaling-mediated and differential induction of calmodulin gene expression by stress in Oryza sativa L. J Biochem Mol Biol 38:432–439
Pitman MG (1984) Transport across the root and shoot/root interactions. In: Staples RC, Toennissen GH (eds) Salinity tolerance in plants: strategies for crop improvement. Wiley, New York, pp 93–123
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8436–8441
Quintero FJ, Ohta M, Shi HZ, Zhu JK, Pardo JM (2002) Reconstitution in yeast of the Arabidopsis SOS signaling pathway for Na + homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9061–9066
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37:1141–1146
Rengasamy P (2006) World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J Exp Bot 57:1017–1023
Rodriguez-Navarro A (2000) Potassium transport in fungi and plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1469:1–30
Rodriguez-Navarro A, Rubio F (2006) High-affinity potassium and sodium transport systems in plants. J Exp Bot 57:1149–1160
Rubio F, Gassmann W, Schroeder JI (1995) Sodium-driven potassium uptake by the plant potassium transporter HKT1 and mutations conferring salt tolerance. Science 270:1660–1663
Rubio F, Flores P, Navarro JM, Martinez V (2003) Effects of Ca2+, K+ and cGMP on Na+ uptake in pepper plants. Plant Sci 165:1043–1049
Rus A, Yokoi S, Sharkhuu A, Reddy M, Lee BH, Matsumoto TK, Koiwa H, Zhu JK, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2001) AtHKT1 is a salt tolerance determinant that controls Na+ entry into plant roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14150–14155
Rus A, Lee BH, Munoz-Mayor A, Sharkhuu A, Miura K, Zhu JK, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2004) AtHKT1 facilitates Na+ homeostasis and K+ nutrition in planta. Plant Physiol 136:2500–2511
Rus AM, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2005) Unraveling salt tolerance in crops. Nat Genet 37:1029–1030
Rus A, Baxter I, Muthukumar B, Gustin J, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Salt DE (2006) Natural variants of AtHKT1 enhance Na+ accumulation in two wild Populations of Arabidopsis. Plos Genetics 2:1964–1973
Russel J (2000) Sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport. Physiol Rev 80:211–276
Sacala E, Biegun A, Demczuk A, Grzys E (2005) Effect of NaCl and supplemental calcium on growth parameters and nitrate reductase activity in maize. Acta Soc Bot Pol 74:119–123
Sanchez-Barrena MJ, Martinez-Ripoll M, Zhu JK, Albert A (2005) The structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana SOS3: Molecular mechanism of sensing calcium for salt stress response. J Mol Biol 345:1253–1264
Santa-María GE, Rubio F, Dubcovsky J, Rodríguez-Navarroa A (1997) The HAKl gene of barley is a member of a large gene family and encodes a high-affinity potassium transporter. Plant Cell 9:2281–2289
Schachtman DP (2000) Molecular insights into the structure and function of plant K+ transport mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:127–139
Schachtman DP, Schroeder JI (1994) Structure and transport mechanism of a high-affinity potassium uptake transporter from higher plants. Nature 370:655–658
Schachtman DP, Liu WH (1999) Molecular pieces to the puzzle of the interaction between potassium and sodium uptake in plants. Trends Plant Sci 4:281–287
Schachtman DP, Tyerman SD, Terry BR (1991) The K+/Na+ selectivity of a cation channel in the plasma membrane of root cells does not differ in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive wheat species. Plant Physiol 97:598–605
Schachtman DP, Kumar R, Schroeder JI, Marsh EL (1997) Molecular and functional characterization of a novel low-affinity cation transporter (LCT1) in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:11079–11084
Schmidt C, He T, Cramer GR (1993) Supplemental calcium does not improve growth of salt-stressed brassicas. Plant Soil 156:415–418
Senn ME, Rubio F, Banuelos MA, Rodrıguez-Navarro A (2001) Comparative functional features of plant potassium HvHAK1 and HvHAK2 transporters. J Biol Chem 30:44563–44569
Sentenac H, Bonneaud N, Minet M, Lacroute F, Salmon JM, Gaymard F, Grignon C (1992) Cloning and expression in yeast of a plant potassium ion transport system. Science 256:663–665
Shah SH, Gorham J, Forster BP, Wyn Jones RGW (1987) Salt tolerance in the Triticeae: the contribution of the D-genome to cation selectivity in hexaploid wheat. J Exp Bot 38:254–269
Shen MR, Chou CY, Hsu KF, Liu HS, Dunham PB, Holtzman EJ, Ellory JC (2001) The KCl cotransporter isoform KCC3 can play an important role in cell growth regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14714–14719
Shi HZ, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu JK (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Starkus J, Kuschel L, Rayner M, Heinemann S (1997) Ion conduction through C-type inactivated Shaker channels. J Gen Physiol 110:539–550
Starkus J, Kuschel L, Rayner M, Heinemann S (1998) Macroscopic Na+ currents in the "Nonconducting" Shaker potassium channel mutant W434F. J Gen Physiol 112:85–93
Starkus J, Heinemann S, Rayner M (2000) Voltage dependence of slow inactivation in Shaker potassium channels results from changes in relative K+ and Na+ permeabilities. J Gen Physiol 115:107–122
Stassart JM, Neirinckx L, Dejaegere R (1981) The interactions between monovalent cations and Ca during their absorption on isolated cell walls and absorption by intact barley roots. Ann Bot 47:647–652
Su H, Golldack D, Zhao CS, Bohnert HJ (2002) The expression of HAK-type K+ transporters is regulated in response to salinity stress in common ice plant. Plant Physiol 129:1482–1493
Su H, Balderas E, Vera-Estrella R, Golldack D, Quigley F, Zhao CS, Pantoja O, Bohnert JH (2003) Expression of the cation transporter McHKT1 in a halophyte. Plant Mol Biol 52:967–980
Subbarao GV, Ito O, Berry WL, Wheeler RM (2003) Sodium - a functional plant nutrient. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:391–416
Sunarpi HT, Motoda J, Kubo M, Yang H, Yoda K, Horie R, Chan WY, Leung HY, Hattori K, Konomi M, Osumi M, Yamagami M, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2005) Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporterinduced Naþ unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells. Plant J 44:928–938
Takahashi R, Nishio T, Ichizen N, Takano T (2007a) Cloning and functional analysis of the K+ transporter PhaHAK2 from salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant reed plants. Biotechnol Lett 29:501–506
Takahashi R, Nishio T, Ichizen N, Takano T (2007b) High affinity K+ transporter PhaHAK5 is expressed only in salt-sensitive reed plants and shows Na+ permeability under NaCl stress. Plant Cell Rep 26:1673–1679
Talke IN, Blaudez D, Maathuis FJM, Sanders D (2003) CNGCs: prime targets of plant cyclic nucleotide signalling? Trends Plant Sci 8:286–293
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Tobe K, Zhang LP, Omasa K (2003) Alleviatory effects of calcium on the toxicity of sodium, potassium and magnesium chlorides to seed germination in three non-halophytes. Seed Sci Res 13:47–54
Tuna AL, Kaya C, Ashraf M, Altunlu H, Yokas I, Yagmur B (2007) The effects of calcium sulphate on growth, membrane stability and nutrient uptake of tomato plants grown under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 59:173–178
Tyerman SD, Skerrett IM (1999) Root ion channels and salinity. Sci Hortic 78:175–235
Tyerman SD, Skerrett M, Garrill A, Findlay GP, Leigh RA (1997) Pathways for the permeation of Na+ and Cl− into protoplasts derived from the cortex of wheat roots. J Exp Bot 48:459–480
Uozumi N, Kim EJ, Rubio F, Yamaguchi T, Muto S, Tsuboi A, Bakker EP, Nakamura T, Schroeder JI (2000) The Arabidopsis HKT1 gene homolog mediates inward Na+ currents in Xenopus laevis oocytes and Na+ uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Physiol 122:1249–1259
Very AA, Sentenac H (2003) Molecular mechanisms and regulation of K+ transport in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:575–603
Wang ZQ, Zhu SQ, Yu RP (1993) Chinese Salinized Soil. Science Press, Beijing
Wang Z, Hesketh J, Fedida D (2000) A high-Na+ conduction state during recovery from inactivation in the K+ channel Kv1.5. Biophys Chem 79:2416–2433
Wang SM, Zheng WJ, Ren JZ, Zhang CL (2002) Selectivity of various types of salt-resistant plants for K+ over Na+. J Arid Environ 52:457–472
Wang SM, Wan CG, Wang YR, Chen H, Zhou ZY, Fu H, Sosebee RE (2004a) The characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. J Arid Environ 56:525–539
Wang SM, Zhao GQ, Gao YS, Tang ZC, Zhang CL (2004b) Puccinellia tenuiflora exhibits stronger selectivity for K+ over Na+ than wheat. J Plant Nutr 27:1841–1857
Wang SM, Zhang JL, Flowers TJ (2007) Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the Halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant Physiol 145:559–571
Wang CM, Zhang JL, Liu XS, Li Z, Wu GQ, Cai JY, Wang SM (2009) Puccinellia tenuiflora maintains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant Cell Environ 32:486–496
White PJ (1999) The molecular mechanism of sodium influx to root cells. Trends Plant Sci 4:245–246
Wu SJ, Ding L, Zhu JK (1996) SOS1, a genetic-locus essential for salt tolerance and potassium acquisition. Plant Cell 8:617–627
Xiong L, Zhu JK (2002) Salt tolerance. In: Somerville CR, Meyerowitz EM (eds) The arabidopsis book. The American Society of Plant Biologists, Rockville, MD, pp 1–22
Xu J, Lytle C, Zhu T, Payne J, Benz E, Forbush B (1994) Molecular cloning and functional expression of the bumetanide sensitive Na-K-Cl cotransporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2201–2205
Xu J, Li HD, Chen LQ, Wang Y, Liu LL, He L, Wu WH (2006) A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 125:1347–1360
Yamaguchi T, Blumwald E (2005) Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci 10:615–620
Yang Q, Chen ZZ, Zhou XF, Yin HB, Li X, Xin XF, Hong XH, Zhu JK, Gong ZZ (2009) Overexpression of SOS (Salt Overly Sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2:22–31
Yellen G (1998) The moving parts of voltage-gated ion channels. Q Rev Biophys 31:239–295
Yeo AR, Flowers TJ (1985) The absence of an effect of the Na/Ca ratio on sodium chloride uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.). New Phytol 99:81–90
Zhang JL (2008) Low-affinity Na+ uptake and accumulation in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Dissertation,. Lanzhou University
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt tolerant tomato plant accumulate salt in the foliage not in the fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768
Zhang H, Kim MS, Sun Y, Dowd SE, Shi H, Paré PW (2008) Soil bacteria confer plant salt tolerance by tissue-specific regulation of the sodium transporter HKT1. Mol Plant Microb Interact 21:737–744
Zhong HL, Läuchli A (1993a) Changes of cell wall composition and polymer size in primary roots of cotton seedlings under high salinity. J Exp Bot 44:773–778
Zhong HL, Läuchli A (1993b) Spatial and temporal aspects of growth in the primary root of cotton seedlings - effects of NaCl and CaCl2. J Exp Bot 44:763–771
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Zimmermann S, Sentenac H (1999) Plant ion channels: from molecular structures to physiological functions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:477–482
Acknowledgements
Research in our lab was funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, grant No. 2007CB108901), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 30671488, 30700562 and 30770347), the National High Tech Project of China (grant No. 2006AA10Z126), the program for New Century Excellent Talents, China (grant No. NCET-05-0882) and the Interdisciplinary Innovation Research Fund for Young Scholars, Lanzhou University (grant No. LZU200516).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JL., Flowers, T.J. & Wang, SM. Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant Soil 326, 45–60 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0076-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0076-0