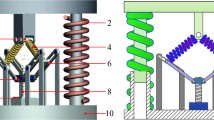
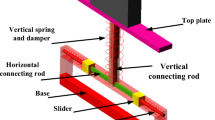
Abstract
Quasi-zero stiffness system has been widely used to isolate structural vibrations. However, its small dynamic stiffness may result in drastic low-frequency vibration. This is a curse of employing quasi-zero stiffness systems in engineering. In this paper, a nonlinear energy sink (NES) is used to overcome this difficulty. In order to reduce the additional weight of the NES, the mass of the NES is replaced by an inerter. By superposing the quasi-zero stiffness system and the inertial NES together, a combined vibration control technique is proposed. The equations of the motion of the primary structure and the combined control system are established. The steady-state response of the system is solved by the harmonic balance method and verified numerically. The suppression performance is evaluated based on the resonance suppression efficiency and the effective vibration isolation bandwidth. In addition, the parameters of the inertial NES are optimized. The results show that the combined control system has a better vibration control effect than the quasi-zero stiffness isolator. Specifically, the combined control system provides a smaller resonance amplitude and a wider vibration isolation band. In summary, the combined control scheme has both effects of the nonlinear isolation and the nonlinear absorption. Therefore, this paper proposes a vibration control technique that can achieve a wide band of vibration isolation and small vibration amplitude with a very little additional mass.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, L.Q., Li, X., Lu, Z.Q., Zhang, Y.W., Ding, H.: Dynamic effects of weights on vibration reduction by a nonlinear energy sink moving vertically. J. Sound Vib. 451, 99–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2019.03.005
AL-Shudeifat, M.A.: Nonlinear energy sinks with nontraditional kinds of nonlinear restoring forces. J. Vib. Acoust. 139, 1–5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4035479
Zang, J., Zhang, Y.-W., Ding, H., Yang, T.-Z., Chen, L.-Q.: The evaluation of a nonlinear energy sink absorber based on the transmissibility. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 125, 99–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.061
Ibrahim, R.A.: Recent advances in nonlinear passive vibration isolators. J. Sound Vib. 314, 371–452 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2008.01.014
Lu, Z.-Q., Chen, L.-Q.: Some recent progresses in nonlinear passive isolations of vibrations. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 49, 550–564 (2017). https://doi.org/10.6052/0459-1879-17-064
Lu, Z., Wang, Z., Zhou, Y., Lu, X.: Nonlinear dissipative devices in structural vibration control: a review. J. Sound Vib. 423, 18–49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.02.052
Wang, X., Yao, H., Zheng, G.: Enhancing the isolation performance by a nonlinear secondary spring in the Zener model. Nonlinear Dyn. 87, 2483–2495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3205-3
Yang, T., Cao, Q.: Delay-controlled primary and stochastic resonances of the SD oscillator with stiffness nonlinearities. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 103, 216–235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMSSP.2017.10.002
Yan, L., Xuan, S., Gong, X.: Shock isolation performance of a geometric anti-spring isolator. J. Sound Vib. 413, 120–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSV.2017.10.024
Lang, Z.Q., Jing, X.J., Billings, S.A., Tomlinson, G.R., Peng, Z.K.: Theoretical study of the effects of nonlinear viscous damping on vibration isolation of sdof systems. J. Sound Vib. 323, 352–365 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2009.01.001
Peng, Z.K., Lang, Z.Q., Jing, X.J., Billings, S.A., Tomlinson, G.R., Guo, L.Z.: The transmissibility of vibration isolators with a nonlinear antisymmetric damping characteristic. J. Vib. Acoust. 132 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4000476
Huang, X., Sun, J., Hua, H., Zhang, Z.: The isolation performance of vibration systems with general velocity-displacement-dependent nonlinear damping under base excitation: numerical and experimental study. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 777–796 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2722-4
Feng, X., Jing, X.: Human body inspired vibration isolation: beneficial nonlinear stiffness, nonlinear damping & nonlinear inertia. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 117, 786–812 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.08.040
Ahmed, S., Wang, H., Aslam, M.S., Ghous, I., Qaisar, I.: Robust adaptive control of robotic manipulator with input time-varying delay. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 17, 2193–2202 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-018-0767-5
Aslam, M.S., Qaisar, I., Saleem, M.A.: Quantized event-triggered feedback control under fuzzy system with time-varying delay and actuator fault. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 35, 100823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nahs.2019.100823
Tang, B., Brennan, M.J.: On the shock performance of a nonlinear vibration isolator with high-static-low-dynamic-stiffness. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 81, 207–214 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.02.019
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P., Lopes, V.: Force and displacement transmissibility of a nonlinear isolator with high-static-low-dynamic-stiffness. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 55, 22–29 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2011.11.012
Ahn, H.-J.: Performance limit of a passive vertical isolator using a negative stiffness mechanism. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 22, 2357 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0930-7
Lan, C.-C., Yang, S.-A., Wu, Y.-S.: Design and experiment of a compact quasi-zero-stiffness isolator capable of a wide range of loads. J. Sound Vib. 333, 4843–4858 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2014.05.009
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Kovacic, I., Waters, T.P.: On the force transmissibility of a vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 322, 707–717 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2008.11.034
Lu, Z., Brennan, M.J., Chen, L.-Q.: On the transmissibilities of nonlinear vibration isolation system. J. Sound Vib. 375, 28–37 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2016.04.032
Ding, H., Ji, J., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear vibration isolation for fluid-conveying pipes using quasi-zero stiffness characteristics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 121, 675–688 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.11.057
Fulcher, B.A., Shahan, D.W., Haberman, M.R., Conner Seepersad, C., Wilson, P.S.: Analytical and experimental investigation of buckled beams as negative stiffness elements for passive vibration and shock isolation systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 136, 031009 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4026888
Huang, X., Liu, X., Sun, J., Zhang, Z., Hua, H.: Vibration isolation characteristics of a nonlinear isolator using euler buckled beam as negative stiffness corrector: a theoretical and experimental study. J. Sound Vib. 333, 1132–1148 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSV.2013.10.026
Huang, X., Chen, Y., Hua, H., Liu, X., Zhang, Z.: Shock isolation performance of a nonlinear isolator using Euler buckled beam as negative stiffness corrector: theoretical and experimental study. J. Sound Vib. 345, 178–196 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2015.02.001
Sun, X., Jing, X., Xu, J., Cheng, L.: Vibration isolation via a scissor-like structured platform. J. Sound Vib. 333, 2404–2420 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSV.2013.12.025
Zhang, W., Zhao, J.: Analysis on nonlinear stiffness and vibration isolation performance of scissor-like structure with full types. Nonlinear Dyn. 86, 17–36 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2869-z
Wang, Y., Jing, X.: Nonlinear stiffness and dynamical response characteristics of an asymmetric X-shaped structure. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 125, 142–169 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.03.045
Bian, J., Jing, X.: Nonlinear passive damping of the X-shaped structure. Procedia Eng. 199, 1701–1706 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.09.372
Jing, X., Zhang, L., Feng, X., Sun, B., Li, Q.: A novel bio-inspired anti-vibration structure for operating hand-held jackhammers. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 118, 317–339 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.09.004
Zheng, Y., Zhang, X., Luo, Y., Zhang, Y., Xie, S.: Analytical study of a quasi-zero stiffness coupling using a torsion magnetic spring with negative stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 100, 135–151 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMSSP.2017.07.028
Zhou, J., Wang, K., Xu, D., Ouyang, H., Li, Y.: A six degrees-of-freedom vibration isolation platform supported by a hexapod of quasi-zero-stiffness struts. J. Vib. Acoust. 139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4035715
Ishida, S., Suzuki, K., Shimosaka, H.: Design and experimental analysis of origami-inspired vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness characteristic. J. Vib. Acoust. 139, 051004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4036465
Zheng, Y., Li, Q., Yan, B., Luo, Y., Zhang, X.: A Stewart isolator with high-static-low-dynamic stiffness struts based on negative stiffness magnetic springs. J. Sound Vib. 422, 390–408 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.02.046
Vakakis, A.F.: Inducing passive nonlinear energy sinks in vibrating systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 123, 324 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1368883
Gendelman, O.V., Sapsis, T., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A.: Enhanced passive targeted energy transfer in strongly nonlinear mechanical oscillators. J. Sound Vib. 330, 1–8 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2010.08.014
Gourc, E., Michon, G., Seguy, S., Berlioz, A.: Targeted energy transfer under harmonic forcing with a vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink: analytical and experimental developments. J. Vib. Acoust. 137 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4029285
Qiu, D., Li, T., Seguy, S., Paredes, M.: Efficient targeted energy transfer of bistable nonlinear energy sink: application to optimal design. Nonlinear Dyn. 92, 443–461 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4067-7
Zang, J., Yuan, T.C., Lu, Z.Q., Zhang, Y.W., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: A lever-type nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 437, 119–134 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.08.058
Zhang, Y.-W., Lu, Y.-N., Zhang, W., Teng, Y.-Y., Yang, H.-X., Yang, T.-Z., Chen, L.-Q.: Nonlinear energy sink with inerter. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 125, 52–64 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.08.026
Yang, T.-Z., Yang, X.-D., Li, Y., Fang, B.: Passive and adaptive vibration suppression of pipes conveying fluid with variable velocity. J. Vib. Control. 20, 1293–1300 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546313480547
Zang, J., Chen, L.Q.: Complex dynamics of a harmonically excited structure coupled with a nonlinear energy sink. Acta Mech. Sin. Xuebao 33, 801–822 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-017-0671-x
Zhang, Y.-W., Yuan, B., Fang, B., Chen, L.-Q.: Reducing thermal shock-induced vibration of an axially moving beam via a nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 87, 1159–1167 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3107-4
Lee, Y.S., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A., Michael McFarland, D.: Suppression of limit cycle oscillations in the van der Pol oscillator by means of passive non-linear energy sinks. Struct. Control Heal. Monit. 13, 41–75 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.143
Fang, Z.W., Zhang, Y.W., Li, X., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Integration of a nonlinear energy sink and a giant magnetostrictive energy harvester. J. Sound Vib. 391, 35–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2016.12.019
Li, X., Zhang, Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.: Integration of a nonlinear energy sink and a piezoelectric energy harvester. Appl. Math. Mech. (English Ed.) 38, 1019–1030 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-017-2220-6
Xiong, L., Tang, L., Liu, K., Mace, B.R.: Broadband piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting using a nonlinear energy sink. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 51, 185502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aab9e3
Viguié, R., Kerschen, G., Golinval, J.C., McFarland, D.M., Bergman, L.A., Vakakis, A.F., van de Wouw, N.: Using passive nonlinear targeted energy transfer to stabilize drill-string systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 23, 148–169 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2007.07.001
Zhang, Y.-W., Zhang, Z., Chen, L.-Q., Yang, T.-Z., Fang, B., Zang, J.: Impulse-induced vibration suppression of an axially moving beam with parallel nonlinear energy sinks. Nonlinear Dyn. 82, 61–71 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2138-6
Wierschem, N.E., Quinn, D.D., Hubbard, S.A., Al-Shudeifat, M.A., McFarland, D.M., Luo, J., Fahnestock, L.A., Spencer, B.F., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A.: Passive damping enhancement of a two-degree-of-freedom system through a strongly nonlinear two-degree-of-freedom attachment. J. Sound Vib. 331, 5393–5407 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2012.06.023
Wang, J., Wierschem, N.E., Spencer, B.F., Lu, X.: Track nonlinear energy sink for rapid response reduction in building structures. J. Eng. Mech. 141, 04014104 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000824
Lu, X., Liu, Z., Lu, Z.: Optimization design and experimental verification of track nonlinear energy sink for vibration control under seismic excitation. Struct. Control Heal. Monit. 24, e2033 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2033
Lo Feudo, S., Touzé, C., Boisson, J., Cumunel, G.: Nonlinear magnetic vibration absorber for passive control of a multi-storey structure. J. Sound Vib. 438, 33–53 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.09.007
Bergeot, B., Bellizzi, S., Cochelin, B.: Passive suppression of helicopter ground resonance using nonlinear energy sinks attached on the helicopter blades. J. Sound Vib. 392, 41–55 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2016.12.039
Mao, X.-Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.-Q.: Nonlinear torsional vibration absorber for flexible structures. J. Appl. Mech. 86, 021006 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4042045
Yang, K., Zhang, Y.-W., Ding, H., Yang, T.-Z., Li, Y., Chen, L.-Q.: Nonlinear energy sink for whole-spacecraft vibration reduction. J. Vib. Acoust. 139, 021011 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4035377
Gourc, E., Seguy, S., Michon, G., Berlioz, A.: Chatter control in turning process with a nonlinear energy sink. Adv. Mater. Res. 698, 89–98 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.698.89
Gourc, E., Seguy, S., Michon, G., Berlioz, A., Mann, B.P.: Quenching chatter instability in turning process with a vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 355, 392–406 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2015.06.025
Bab, S., Khadem, S.E., Shahgholi, M., Abbasi, A.: Vibration attenuation of a continuous rotor-blisk-journal bearing system employing smooth nonlinear energy sinks. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 84, 128–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.07.002
Zhang, Z., Lu, Z.Q., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: An inertial nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 450, 199–213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2019.03.014
Smith, M.C.: Synthesis of mechanical networks: the inerter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 47, 1648–1662 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2002.803532
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.11772181, 11422214, 11902203), the Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. 17SG38, 2019-01-07-00-09-E00018), the Key Research Projects of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (No. 18010500100), and the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC1807172).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhang, YW. & Ding, H. Vibration control combining nonlinear isolation and nonlinear absorption. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 2121–2139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05606-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05606-6