Abstract
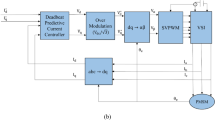
Because permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) system driven by permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) based on wind turbine emulator (WTE) is a nonlinear and time-varying system with high complication, an accurate dynamic model of the PMSG system directly driven by WTE is difficult to establish for the linear controller design. In order to conquer this difficulty and improve the robustness of dynamic system, the PMSG system controlled by the online-tuned parameters of the novel modified recurrent wavelet neural network (NN)-controlled system is proposed to control output voltages and powers of controllable rectifier and inverter in this study. First, a closed-loop PMSM-driven system based on WTE is designed for driving the PMSG system to generate output power. Second, the rotor speeds of the PMSG, the voltages, and currents of the two power converters are detected simultaneously to yield maximum power output. In addition, two sets of the online-tuned parameters of the modified recurrent wavelet NN controllers in the controllable rectifier and inverter are developed for the voltage-regulating controllers in order to improve output performance. Finally, some experimental results are verified to show the effectiveness of the proposed novel modified recurrent wavelet NN controller for the power output of the PMSG system driven by WTE.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan, K., Islam, S.: Optimum control strategies in energy conversion of pmsg wind turbine system without mechanical sensors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 19, 392–400 (2004)
Kolhe, M., Joshi, J.C., Kothari, D.P.: Performance analysis of a directly coupled photovoltaic water-pumping system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 19, 613–618 (2004)
Andersen, G.K., Klumpner, C., Kjaer, S.B., Blaabjerg, F.: A new green power inverter for fuel cells. In: Proceedings of IEEE 33rd Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference, pp. 727–733 (2002)
Lubosny, Z.: Wind Turbine Operation in Electric Power Systems. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Ackermann, T.: Wind Power in Power Systems. Wiley, New York (2005)
Karrari, M., Rosehart, W., Malik, O.P.: Comprehensive control strategy for a variable speed cage machine wind generation unit. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 20, 415–423 (2005)
Boldea, I.: Synchronous Generators. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton (2005)
Chinchilla, M., Arnaltes, S., Burgos, I.C.: Control of permanent magnet generators applied to variable-speed wind-energy systems connected to the grid. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 21, 130–135 (2006)
Sajedi, S., Kahlifeh, F., Karimi, T., Khalifeh, Z.: Maximum power point tracking of variable speed wind energy conversion system. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 6, 6843–6851 (2011)
Gharedaghi, F., Jamali, H., Deysi, M., Khalili, A.: Maximum power point tracking of variable speed wind generation system connected to permanent magnet synchronous generator. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 4, 1044–1049 (2011)
Bueno, E.J., Cobreces, S., Rodriguez, F.J., Hernandez, A., Felipe, E.: Design of a back-to-back npc converter interface for wind turbines with squirrel-cage induction generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 23, 932–945 (2008)
Arbi, J., Ghorbal, M.J.B., Slama-Belkhodja, I., Charaabi, L.: Direct virtual torque control for doubly fed induction generator grid connection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56, 4163–4173 (2009)
Chen, C.H., Hong, C.M., Ou, T.C.: WRBF network based control strategy for PMSG on smart grid. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent System Applications to Power Systems, pp. 1–6 (2011)
Delyon, D., Juditsky, A., Benveniste, A.: Accuracy analysis for wavelet approximations. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 6, 332–348 (1995)
Chen, C.F., Hsiao, C.H.: Wavelet approach to optimizing dynamic systems. IEE Proc. Control Theory Appl. 146, 213–219 (1999)
Zhang, Q., Benveniste, A.: Wavelet networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 3, 889–898 (1992)
Zhang, J., Walter, G.G., Miao, Y., Lee, W.N.W.: Wavelet neural networks for function learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43, 1485–1496 (1995)
Zhang, Z., Zhao, C.: A fast learning algorithm for wavelet network and its application in control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, pp. 1403–1407 (2007)
Wei, H.L., Billings, S.A.: A unified wavelet-based modelling framework for nonlinear system identification: the wanarx model structure. Int. J. Control 77, 351–366 (2004)
Wei, H.L., Billings, S.A., Balikhin, M.A.: Wavelet based nonparametric narx models for nonlinear input–output system identification. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 37, 1089–1096 (2006)
Ravan, M., Amineh, R.K., Karrari, M., Rosehart, W.B., Malik, O.P.: Synchronous machine model identification using continuous wavelet narx network. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 223, 467–477 (2009)
Xu, J., Ho, D.W.C.: Adaptive wavelet networks for nonlinear system identification. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference, pp. 3472–3473 (1999)
Sureshbabu, N., Farrell, J.A.: Wavelet-based system identification for nonlinear control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 44, 412–417 (1999)
Billings, S.A., Wei, H.L.: A new class of wavelet networks for nonlinear system identification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 16, 862–874 (2005)
Abiyev, R.H., Kaynak, O.: Fuzzy wavelet neural networks for identification and control of dynamic plants—a novel structure and a comparative study. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55, 3133–3140 (2008)
Giaouris, D., Finch, J.W., Ferreira, O.C., Kennel, R.M., El-Murr, G.M.: Wavelet denoising for electric drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55, 543–550 (2008)
Gonzalez, D., Bialasiewicz, J.T., Balcells, J., Gago, J.: Wavelet-based performance evaluation of power converters operating with modulated switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55, 3167–3176 (2008)
Chung, C.A., Lee, T.T., Tien, C.C., Hsu, C.F.: Adaptive wavelet neural network control for dc motors via second-order sliding-mode approach. In: Proceedings International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, pp. 1174–1179 (2011)
Gokmen, G.: Wavelet based instantaneous reactive power calculation method and a power system application sample. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 4, 745–752 (2011)
Ling, S.H., Iu, H.H.C., Leung, F.H.F., Chan, K.Y.: Improved hybrid particle swarm optimized wavelet neural network for modeling the development of fluid dispensing for electronic packaging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55, 3447–3460 (2008)
Wen, G.X., Liu, Y.J., Tong, S.C., Li, X.L.: Adaptive neural output feedback control of nonlinear discrete-time systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 65, 65–75 (2011)
Zou, A.M., Kumar, K.D.: Neural network-based adaptive output feedback formation control for multi-agent systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1283–1296 (2012)
Sun, G., Wang, D., Li, T., Peng, Z., Wang, H.: Single neural network approximation based adaptive control for a class of uncertain strict-feedback nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 72, 175–184 (2013)
Wang, H., Chen, B., Lin, C.: Adaptive neural tracking control for a class of perturbed pure-feedback. Nonlinear Dyn. 72, 207–220 (2013)
Bouzari, H., Moradi, H., Bouzari, E.: Adaptive neuro-wavelet system for the robust control of switching power supplies. In: IEEE International Multitopic Conference, pp. 1–6 (2008)
Funahashi, K., Nakamura, Y.: Approximation of dynamical systems by continuous time recurrent neural network. Neural Netw. 6, 801–806 (1993)
Jin, L., Nikiforuk, P.N., Gupta, M.: Approximation of discrete-time state-space trajectories using dynamic recurrent networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 40, 1266–1270 (1995)
Ku, C.C., Lee, K.Y.: Diagonal recurrent neural networks for dynamical system control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 6, 144–156 (1995)
Lu, C.H., Tsai, C.C.: Adaptive predictive control with recurrent neural network for industrial processes: an application to temperature control of a variable-frequency oil-cooling machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55, 1366–1375 (2008)
Yu, J., Yu, H., Chen, B., Gao, J., Qin, Y.: Direct adaptive neural control of chaos in the permanent magnet synchronous motor. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1879–1887 (2012)
Wang, H., Chen, B., Lin, C.: Direct adaptive neural control for strict-feedback stochastic nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 2703–2718 (2012)
Yoo, S.J., Park, J.B., Choi, Y.H.: Stable predictive control of chaotic systems using self-recurrent wavelet neural network. Int. J. Autom. Control Syst. 3, 43–55 (2005)
Yoo, S.J., Choi, Y.H., Park, J.B.: Generalized predictive control based on self-recurrent wavelet neural network for stable path tracking of mobile robots: adaptive learning rates approach. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 53, 1381–1394 (2006)
Lu, C.H.: Design and application of stable predictive controller using recurrent wavelet neural networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56, 3733–3742 (2009)
Chen, C.H., Hsu, C.F.: Recurrent wavelet neural backstepping controller design with a smooth compensator. Neural Comput. Appl. 19, 1089–1100 (2010)
Han, S.I., Lee, J.M.: Adaptive dynamic surface control with sliding mode control and rwnn for robust positioning of a linear motion stage. Mechatronics 22, 222–238 (2012)
Singh, M., Santoso, S.: Dynamic models for wind turbines and wind power plants. Subcontract, Report. NREL/SR-5500-52780 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
1. The modified recurrent wavelet NN controlled output power of the PMSG system.
2. A WTE is designed to generate the maximum power for the PMSG system.
3. Two sets online training modified recurrent wavelet NNs are developed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CH. Dynamic control for permanent magnet synchronous generator system using novel modified recurrent wavelet neural network. Nonlinear Dyn 77, 1261–1284 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1376-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1376-3