Abstract
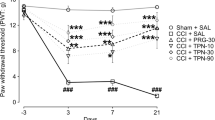
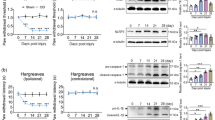
Neuropathic pain is initiated or caused due to the primary lesion or dysfunction in the nervous system and is proposed to be linked to a cascade of events including excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptosis. Oxidative/nitrosative stress aggravates the neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration through poly (ADP) ribose polymerase (PARP) overactivation. Hence, the present study investigated the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the phytoconstituent; morin in chronic constriction injury (CCI) induced neuropathy. Neuropathic pain was induced by chronic constriction of the left sciatic nerve in rats, and the effect of morin (15 and 30 mg/kg, p.o.) was evaluated by measuring behavioural and biochemical changes. Mechanical, chemical and thermal stimuli confirmed the CCI-induced neuropathic pain and treatment with morin significantly improved these behavioural deficits and improved the sciatic functional index by the 14th day after CCI induction. After 14 days of CCI induction, oxidative/nitrosative stress and inflammatory markers were elevated in rat lumbar spinal cord. Oxidative stress induced PARP overactivation resulted in depleted levels of ATP and elevated levels of poly (ADP) ribose (PAR). Treatment with morin reduced the levels of nitrites, restored glutathione levels and abrogated the oxidant induced DNA damage. It also mitigated the increased levels of TNF-α and IL-6. Protein expression studies confirmed the PARP inhibition and anti-inflammatory activity of morin. Findings of this study suggest that morin, by virtue of its antioxidant properties, limited PARP overactivation and neuroinflammation and protected against CCI induced functional, behavioural and biochemical deficits.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell JN, Meyer RA (2006) Mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Neuron 52:77–92
Bridges D, Thompson SWN, Rice ASC (2001) Mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth 87:12–26
Baron R, Binder A, Wasner G (2010) Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol 9:807–819
Dworkin RH, Backonja M, Rowbotham MC, Allen RR, Argoff CR, Bennett GJ, Bushnell MC, Farrar JT, Galer BS, Haythornthwaite JA (2003) Advances in neuropathic pain: diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations. Arch Neurol 60:1524–1534
Finnerup NB, SrH Sindrup, Jensen TS (2010) The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 150:573–581
Salvemini D, Little JW, Doyle T, Neumann WL (2011) Roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in pain. Free Radic Biol Med 51:951–966
Sommer C, Kress M (2004) Recent findings on how proinflammatory cytokines cause pain: peripheral mechanisms in inflammatory and neuropathic hyperalgesia. Neurosci Lett 361:184–187
Lee KM, Kang BS, Lee HL, Son SJ, Hwang SH, Kim DS, Park JS, Cho HJ (2004) Spinal NF-kB activation induces COX-2 upregulation and contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Eur J Neurosci 19:3375–3381
Choi DC, Lee JY, Lim EJ, Baik HH, Oh TH, Yune TY (2012) Inhibition of ROS-induced p38MAPK and ERK activation in microglia by acupuncture relieves neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol 236:268–282
Goecks CSB, Horst A, Moraes MS, Scheid T, Kolberg C, Bell-Klein A, Partata WA (2012) Assessment of oxidative parameters in rat spinal cord after chronic constriction of the sciatic nerve. Neurochem Res 37:1952–1958
Sandireddy R, Yerra VG, Komirishetti P, Areti A, Kumar A (2015) Fisetin imparts neuroprotection in experimental diabetic neuropathy by modulating Nrf2 and NF-kB pathways. Cell Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s10571-015-0272-9
Du L, Zhang X, Han YY, Burke NA, Kochanek PM, Watkins SC, Graham SH, Carcillo JA, Szaba C, Clark RSB (2003) Intra-mitochondrial poly (ADP-ribosylation) contributes to NAD+ depletion and cell death induced by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 278:18426–18433
Obrosova IG, Li F, Abatan OI, Forsell MA, Komjati K, Pacher P, Szaba C, Stevens MJ (2004) Role of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase activation in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 53:711–720
Obrosova IG, Xu W, Lyzogubov VV, Ilnytska O, Mashtalir N, Vareniuk I, Pavlov IA, Zhang J, Slusher B, Drel VR (2008) PARP inhibition or gene deficiency counteracts intraepidermal nerve fiber loss and neuropathic pain in advanced diabetic neuropathy. Free Radic Biol Med 44:972–981
Sharma SS, Kumar A, Kaundal RK (2008) Protective effects of 4-amino1, 8-napthalimide, a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Life Sci 82:570–576
Komirishetty P, Areti A, Yerra VG, Ruby PK, Sharma SS, Gogoi R, Sistla R, Kumar A (2016) PARP inhibition attenuates neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in chronic constriction injury induced peripheral neuropathy. Life Sci 150:50–60
Zhu X, Li Q, Chang R, Yang D, Song Z, Guo Q, Huang C (2014) Curcumin alleviates neuropathic pain by inhibiting p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase activity-regulated expression of BDNF and cox-2 in a rat model. PLoS ONE 9:e91303
Xu Y-Q, Jin S-J, Liu N, Li Y-X, Zheng J, Ma L, Du J, Zhou R, Zhao C-J, Niu Y (2014) Aloperine attenuated neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury via anti-oxidation activity and suppression of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451:568–573
Janzade A, Jameie SB, Choobchian S, Nasirinezhad F (2014) Neuroprotective effect of coenzyme Q10 in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rat. Thrita 3(1):e16607
Naik AK, Tandan SK, Dudhgaonkar SP, Jadhav SH, Kataria M, Prakash VR, Kumar D (2006) Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of peripheral neuropathy and modulation by N-acetyl-cysteine in rats. Eur J Pain 10:573
Kapoor R, Kakkar P (2012) Protective role of morin, a flavonoid, against high glucose induced oxidative stress mediated apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 7:e41663
Sreedharan V, Venkatachalam KK, Namasivayam N (2009) Effect of morin on tissue lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine induced experimental colon carcinogenesis. Invest New Drugs 27:21–30
Fang S-H, Hou Y-C, Chang W-C, Hsiu S-L, Chao P-DL, Chiang B-L (2003) Morin sulfates/glucuronides exert anti-inflammatory activity on activated macrophages and decreased the incidence of septic shock. Life Sci 74:743–756
AlSharari SD, Al-Rejaie SS, Abuohashish HM, Aleisa AM, Parmar MY, Ahmed MM (2014) Ameliorative potential of morin in streptozotocin-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Trop J Pharm Res 13:1429–1436
Ola MS, Aleisa AM, Al-Rejaie SS, Abuohashish HM, Parmar MY, Alhomida AS, Ahmed MM (2014) Flavonoid, morin inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and enhances neurotrophic support in the brain of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurol Sci 35:1003–1008
Noor H, Cao P, Raleigh DP (2012) Morin hydrate inhibits amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide and disaggregates amyloid fibers. Protein Sci 21:373–382
MadanKumar P, NaveenKumar P, Manikandan S, Devaraj H, NiranjaliDevaraj S (2014) Morin ameliorates chemically induced liver fibrosis in vivo and inhibits stellate cell proliferation in vitro by suppressing Wnta-catenin signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 277:210–220
Aleisa AM, Al-Rejaie SS, Abuohashish HM, Ahmed MM, Parmar MY (2013) Nephro-protective role of morin against experimentally induced diabetic nephropathy. Dig J Nanomater Biostructures 8:395–401
Park JY, Kang KA, Kim KC, Cha JW, Kim EH, Hyun JW (2013) Morin induces heme oxygenase-1 via ERK-Nrf2 signaling pathway. J Cancer Prev 18:249
Campos-Esparza MR, Sanchez-Gomez MV, Matute C (2009) Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotection by two natural antioxidant polyphenols. Cell Calcium 45:358–368
Kim JM, Lee EK, Park G, Kim MK, Yokozawa T, Yu BP, Chung HY (2010) Morin modulates the oxidative stress-induced NF-kB pathway through its anti-oxidant activity. Free Radic Res 44:454–461
Geraets L, Moonen HJJ, Brauers K, Wouters EFM, Bast A, Hageman GJ (2007) Dietary flavones and flavonoles are inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in pulmonary epithelial cells. J Nutr 137:2190–2195
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Varejao ASP, Meek MF, Ferreira AJA, Patrício JAB, Cabrita AMS (2001) Functional evaluation of peripheral nerve regeneration in the rat: walking track analysis. J Neurosci Methods 108:1–9
Huang C, Hu Z-P, Long H, Shi Y-S, Han J-S, Wan Y (2004) Attenuation of mechanical but not thermal hyperalgesia by electroacupuncture with the involvement of opioids in rat model of chronic inflammatory pain. Brain Res Bull 63:99–103
Decosterd I, Buchser E, Gilliard N, Saydoff J, Zurn AD, Aebischer P (1998) Intrathecal implants of bovine chromaffin cells alleviate mechanical allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 76:159–166
Bardin L, Malfetes N, Newman-Tancredi A, Depoortere R (2009) Chronic restraint stress induces mechanical and cold allodynia, and enhances inflammatory pain in rat: relevance to human stress-associated painful pathologies. Behav Brain Res 205:360–366
Jaggi AS, Singh N (2010) Differential effect of spironolactone in chronic constriction injury and vincristine-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 648:102–109
Naik AK, Tandan SK, Kumar D, Dudhgaonkar SP (2006) Nitric oxide and its modulators in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 530:59–69
Sharma SS, Kumar A, Arora M, Kaundal RK (2009) Neuroprotective potential of combination of resveratrol and 4-amino 1,8 naphthalimide in experimental diabetic neuropathy: focus on functional, sensorimotor and biochemical changes. Free Radic Res 43:400–408
Polgar E, Gray S, Riddell JS, Todd AJ (2004) Lack of evidence for significant neuronal loss in laminae I–III of the spinal dorsal horn of the rat in the chronic constriction injury model. Pain 111:144–150
Colleoni M, Sacerdote P (2010) Murine models of human neuropathic pain. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Mol Basis of Dis 1802:924–933
Saade NE, Jabbur SJ (2008) Nociceptive behavior in animal models for peripheral neuropathy: spinal and supraspinal mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 86:22–47
Wei X-H, Na X-D, Liao G-J, Chen Q-Y, Cui Y, Chen F-Y, Li Y-Y, Zang Y, Liu X-G (2013) The up-regulation of IL-6 in DRG and spinal dorsal horn contributes to neuropathic pain following L5 ventral root transection. Exp Neurol 241:159–168
Siniscalco D, Fuccio C, Giordano C, Ferraraccio F, Palazzo E, Luongo L, Rossi F, Roth KA, Maione S, de Novellis V (2007) Role of reactive oxygen species and spinal cord apoptotic genes in the development of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Res 55:158–166
Valsecchi AE, Franchi S, Panerai AE, Sacerdote P, Trovato AE, Colleoni M (2008) Genistein, a natural phytoestrogen from soy, relieves neuropathic pain following chronic constriction sciatic nerve injury in mice: anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity. J Neurochem 107:230–240
Li S-S, Zhang W-S, Ji D, Zhou Y-L, Li H, Yang J-L, Xiong Y-C, Zhang Y-Q, Xu H (2014) Involvement of spinal microglia and interleukin-18 in the anti-nociceptive effect of dexmedetomidine in rats subjected to CCI. Neurosci Lett 560:21–25
Jo D, Chapman CR, Light AR (2009) Glial mechanisms of neuropathic pain and emerging interventions. Korean J Pain 22:1–15
Sandireddy R, Yerra VG, Areti A, Komirishetty P, Kumar A (2014) Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy: futuristic strategies based on these targets. Int J Endocrinol 2014:674987
Chaitanya GV, Steven AJ, Babu PP (2010) PARP-1 cleavage fragments: signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell Commun Signal 8:31
Ta LE, Schmelzer JD, Bieber AJ, Loprinzi CL, Sieck GC, Brederson JD, Low PA, Windebank AJ (2013) A novel and selective poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor ameliorates chemotherapy-induced painful neuropathy. PLoS ONE 8:e54161
Sinha K, Sadhukhan P, Saha S, Pal PB, Sil PC (2015) Morin protects gastric mucosa from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, indomethacin induced inflammatory damage and apoptosis by modulating NF-kB pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Gen Subj 1850:769–783
Kumar A, Sharma SS (2010) NF-kB inhibitory action of resveratrol: a probable mechanism of neuroprotection in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:360–365
Negi G, Kumar A, Sharma SS (2011) Nrf2 and NF-kB modulation by sulforaphane counteracts multiple manifestations of diabetic neuropathy in rats and high glucose-induced changes. Curr Neurovascular Res 8:294–304
Attal N, Filliatreau G, Perrot S, Jazat F, Di Giamberardino L, Guilbaud G (1994) Behavioural pain-related disorders and contribution of the saphenous nerve in crush and chronic constriction injury of the rat sciatic nerve. Pain 59:301–312
Attal N, Jazat F, Kayser V, Guilbaud G (1990) Further evidence for a pain-related behaviours in a model of unilateral peripheral mononeuropathy. Pain 41:235–251
Na HS, Yoon YW, Chung JM (1996) Both motor and sensory abnormalities contribute to changes in foot posture in an experimental rat neuropathic model. Pain 67:173–178
Pathak NN, Balaganur V, Lingaraju MC, Kant V, Latief N, More AS, Kumar D, Kumar D, Tandan SK (2014) Atorvastatin attenuates neuropathic pain in rat neuropathy model by down-regulating oxidative damage at peripheral, spinal and supraspinal levels. Neurochem Int 68:1–9
Muthuraman A, Jaggi AS, Singh N, Singh D (2008) Ameliorative effects of amiloride and pralidoxime in chronic constriction injury and vincristine induced painful neuropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 587:104–111
Choi JI, Kim WM, Lee HG, Kim YO, Yoon MH (2012) Role of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the antiallodynic effects of intrathecal EGCG in a neuropathic pain rat model. Neurosci Lett 510:53–57
Guedes RP, Dal Bosco L, Teixeira CM, Araujo ASR, Llesuy S, Bello-Klein A, Ribeiro MFM, Partata WA (2006) Neuropathic pain modifies antioxidant activity in rat spinal cord. Neurochem Res 31:603–609
Horst A, Kolberg C, Moraes MS, Riffel APK, Finamor A, Bella Klein A, Pavanato MA, Partata WA (2014) Effect of N-acetylcysteine on the spinal-cord glutathione system and nitric-oxide metabolites in rats with neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 569:163–168
Jagtap P, Szaba C (2005) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase and the therapeutic effects of its inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:421–440
Areti A, Yerra VG, Naidu VGM, Kumar A (2014) Oxidative stress and nerve damage: role in chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy. Redox Biol 2:289–295
Zimmermann M (2001) Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:23–37
Di Cesare Mannelli L, Bartolini A, Ghelardini C (2009) Neuropathy-induced apoptosis: protective effect of physostigmine. J Neurosci Res 87:1871–1876
Bruckbauer A, Zemel MB (2014) Synergistic effects of polyphenols and methylxanthines with leucine on AMPK/Sirtuin-mediated metabolism in muscle cells and adipocytes. PLoS ONE 9:e89166
Areti A, Ganesh YV, Komirishetty P, Kumar A (2016) Potential therapeutic benefits of maintaining mitochondrial health in peripheral neuropathies. Curr Neuropharmacol 14:1–16
Xia Y, Liu H, Shen A, Liu Y, Sun L, Tao T, Ke Q, Cheng C (2010) A critical role of SRC-suppressed C kinase substrate in rat astrocytes after chronic constriction injury. Neuromol Med 12:205–216
Lee K-M, Jeon S-M, Cho H-J (2009) Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 induces interleukin-6 upregulation through NF-kappaB in a rat neuropathic pain model. Eur J Pain 13:794–806
Zhou Y, Huang X, Wu H, Xu Y, Tao T, Xu G, Cheng C, Cao S (2013) Decreased expression and role of GRK6 in spinal cord of rats after chronic constriction injury. Neurochem Res 38:2168–2179
Muthuraman A, Singh N (2012) Neuroprotective effect of saponin rich extract of Acorus calamus L. in rat model of chronic constriction injury (CCI) of sciatic nerve-induced neuropathic pain. J Ethnopharmacol 142:723–731
Barbosa RA, Nunes TL, Nunes TL, Paixao AO, Neto RB, Moura S, Albuquerque RL Jr, Candido EA, Padilha FF, Quintans LJ Jr, Gomes MZ, Cardoso JC (2016) Hydroalcoholic extract of red propolis promotes functional recovery and axon repair after sciatic nerve injury in rats. Pharm Biol 54(6):993–1004
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemical and Fertilizers and NIPER-Hyderabad for their support to carry out the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komirishetty, P., Areti, A., Sistla, R. et al. Morin Mitigates Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI)-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress Induced PARP Over-Activation and Neuroinflammation. Neurochem Res 41, 2029–2042 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1914-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1914-0