Abstract
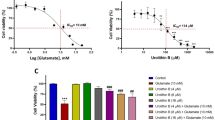
To investigate possible protective effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) on the rat cortex with glutamate injection and to understand the mechanisms linking the in vivo neuroprotection of PQQ. Adult Sprague–Dawley rats received glutamate injection into the rat cortex. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labeling assay was performed to observe influences of co-treatment with PQQ (simultaneous injection with PQQ and glutamate) on neural cell apoptosis in the rat cortex. The production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the rat cortex was detected by flow cytometry using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate labeling, and the activity of superoxide dismutase, glutathione and malondialdehyde was respectively determined. Real time quantitative RT-PCR and Western blot were applied to measure the mRNA and protein expressions of Nrf1, Nrf2, HO-1 and GCLC in the rat cortex. Western blot was used to detect the phosphorylation of Akt and GSK3β in the rat cortex. Co-treatment with PQQ protected neural cells in the rat cortex from glutamate-induced apoptosis. PQQ decreased the ROS production induced by glutamate injection. PQQ increased the mRNA and protein expressions of Nrf2, HO-1 and GCLC and the phosphorylation of Akt and GSK3β in the cortex of glutamate-injected rats. PQQ could produce neuroprotective effects on the rat cortex. The antioxidant properties of PQQ and PQQ-induced activation of Akt/GSK3β signal pathway might be responsible for the in vivo neuroprotection of PQQ.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hauge JG (1964) Glucose dehydrogenase of Bacterium anitratum: an enzyme with a novel prosthetic group. J Biol Chem 239:3630–3639
Salisbury SA, Forrest HS, Cruse WB, Kennard O (1979) A novel coenzyme from bacterial primary alcohol dehydrogenases. Nature 280:843–844
Cline HT, Tsien RW (1991) Glutamate-induced increases in intracellular Ca2+ in cultured frog tectal cells mediated by direct activation of NMDA receptor channels. Neuron 6:259–267
Stites TE, Mitchell AE, Rucker RB (2000) Physiological importance of quinoenzymes and the O-quinone family of cofactors. J Nutr 130:719–727
Rucker R, Chowanadisai W, Nakano M (2009) Potential physiological importance of pyrroloquinoline quinone. Altern Med Rev 14:268–277
Felton LM, Anthony C (2005) Biochemistry: role of PQQ as a mammalian enzyme cofactor? Nature 433: E10; discussion E11–E12
Kasahara T, Kato T (2003) Nutritional biochemistry: a new redox-cofactor vitamin for mammals. Nature 422:832
Rucker R, Storms D, Sheets A, Tchaparian E, Fascetti A (2005) Biochemistry: is pyrroloquinoline quinone a vitamin? Nature 433: E10–E11; discussion E11–E12
Misra HS, Khairnar NP, Barik A, Indira Priyadarsini K, Mohan H, Apte SK (2004) Pyrroloquinoline-quinone: a reactive oxygen species scavenger in bacteria. FEBS Lett 578:26–30
Misra HS, Rajpurohit YS, Khairnar NP (2012) Pyrroloquinoline-quinone and its versatile roles in biological processes. J Biosci 37:313–325
Hobara N, Watanabe A, Kobayashi M, Tsuji T, Gomita Y, Araki Y (1988) Quinone derivatives lower blood and liver acetaldehyde but not ethanol concentrations following ethanol loading to rats. Pharmacology 37:264–267
Ohwada K, Takeda H, Yamazaki M, Isogai H, Nakano M, Shimomura M, Fukui K, Urano S (2008) Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) prevents cognitive deficit caused by oxidative stress in rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr 42:29–34
Tao R, Karliner JS, Simonis U, Zheng J, Zhang J, Honbo N, Alano CC (2007) Pyrroloquinoline quinone preserves mitochondrial function and prevents oxidative injury in adult rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363:257–262
Zhu BQ, Zhou HZ, Teerlink JR, Karliner JS (2004) Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) decreases myocardial infarct size and improves cardiac function in rat models of ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 18:421–431
Reynolds IJ, Hastings TG (1995) Glutamate induces the production of reactive oxygen species in cultured forebrain neurons following NMDA receptor activation. J Neurosci 15:3318–3327
Ekinci FJ, Linsley MD, Shea TB (2000) Beta-amyloid-induced calcium influx induces apoptosis in culture by oxidative stress rather than tau phosphorylation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 76:389–395
Mendis E, Kim MM, Rajapakse N, Kim SK (2007) An in vitro cellular analysis of the radical scavenging efficacy of chitooligosaccharides. Life Sci 80:2118–2127
Duan Y, Gross RA, Sheu SS (2007) Ca2+-dependent generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species serves as a signal for poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation during glutamate excitotoxicity. J Physiol 585:741–758
Zhang Q, Shen M, Ding M, Shen D, Ding F (2011) The neuroprotective action of pyrroloquinoline quinone against glutamate-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neurons is mediated through the activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 252:62–72
Choi DW (1987) Ionic dependence of glutamate neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 7:369–379
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689
Aizenman E, Hartnett KA, Zhong C, Gallop PM, Rosenberg PA (1992) Interaction of the putative essential nutrient pyrroloquinoline quinone with the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor redox modulatory site. J Neurosci 12:2362–2369
Scanlon JM, Aizenman E, Reynolds IJ (1997) Effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone on glutamate-induced production of reactive oxygen species in neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 326:67–74
Kaspar JW, Niture SK, Jaiswal AK (2009) Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 47:1304–1309
Zhang Q, Ding M, Gao XR, Ding F (2012) Pyrroloquinoline quinone rescues hippocampal neurons from glutamate-induced cell death through activation of Nrf2 and up-regulation of antioxidant genes. Genet Mol Res 11:2652–2664
Kumar A, Singh RL, Babu GN (2010) Cell death mechanisms in the early stages of acute glutamate neurotoxicity. Neurosci Res 66:271–278
Liu S, Li H, Ou Yang J, Peng H, Wu K, Liu Y, Yang J (2005) Enhanced rat sciatic nerve regeneration through silicon tubes filled with pyrroloquinoline quinone. Microsurgery 25:329–337
Hara H, Hiramatsu H, Adachi T (2007) Pyrroloquinoline quinone is a potent neuroprotective nutrient against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 32:489–495
Zhang Y, Feustel PJ, Kimelberg HK (2006) Neuroprotection by pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) in reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the adult rat. Brain Res 1094:200–206
Hirakawa A, Shimizu K, Fukumitsu H, Furukawa S (2009) Pyrroloquinoline quinone attenuates iNOS gene expression in the injured spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 378:308–312
Murase K, Hattori A, Kohno M, Hayashi K (1993) Stimulation of nerve growth factor synthesis/secretion in mouse astroglial cells by coenzymes. Biochem Mol Biol Int 30:615–621
Zhang L, Liu J, Cheng C, Yuan Y, Yu B, Shen A, Yan M (2012) The neuroprotective effect of pyrroloquinoline quinone on traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 29(5):851–864
Chen X, Liu J, Gu X, Ding F (2008) Salidroside attenuates glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death in primary cultured hippocampal neurons of rats. Brain Res 1238:189–198
Li N, Liu B, Dluzen DE, Jin Y (2007) Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg2 against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 111:458–463
Liu CL, Siesjo BK, Hu BR (2004) Pathogenesis of hippocampal neuronal death after hypoxia-ischemia changes during brain development. Neuroscience 127:113–123
Nicotera P, Leist M, Manzo L (1999) Neuronal cell death: a demise with different shapes. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:46–51
Portera-Cailliau C, Price DL, Martin LJ (1997) Excitotoxic neuronal death in the immature brain is an apoptosis-necrosis morphological continuum. J Comp Neurol 378:70–87
Gunasekar PG, Kanthasamy AG, Borowitz JL, Isom GE (1995) NMDA receptor activation produces concurrent generation of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species: implication for cell death. J Neurochem 65:2016–2021
Lafon-Cazal M, Pietri S, Culcasi M, Bockaert J (1993) NMDA-dependent superoxide production and neurotoxicity. Nature 364:535–537
Savolainen KM, Loikkanen J, Eerikainen S, Naarala J (1998) Glutamate-stimulated ROS production in neuronal cultures: interactions with lead and the cholinergic system. Neurotoxicology 19:669–674
Keller JN, Kindy MS, Holtsberg FW, St Clair DK, Yen HC, Germeyer A, Steiner SM, Bruce-Keller AJ, Hutchins JB, Mattson MP (1998) Mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase prevents neural apoptosis and reduces ischemic brain injury: suppression of peroxynitrite production, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurosci 18:687–697
Yang YC, Lii CK, Lin AH, Yeh YW, Yao HT, Li CC, Liu KL, Chen HW (2011) Induction of glutathione synthesis and heme oxygenase 1 by the flavonoids butein and phloretin is mediated through the ERK/Nrf2 pathway and protects against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 51:2073–2081
Valdivia A, Perez-Alvarez S, Aroca-Aguilar JD, Ikuta I, Jordan J (2009) Superoxide dismutases: a physiopharmacological update. J Physiol Biochem 65:195–208
Zhang Y, Rosenberg PA (2002) The essential nutrient pyrroloquinoline quinone may act as a neuroprotectant by suppressing peroxynitrite formation. Eur J Neurosci 16:1015–1024
Bauerly KA, Storms DH, Harris CB, Hajizadeh S, Sun MY, Cheung CP, Satre MA, Fascetti AJ, Tchaparian E, Rucker RB (2006) Pyrroloquinoline quinone nutritional status alters lysine metabolism and modulates mitochondrial DNA content in the mouse and rat. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:1741–1748
Stites T, Storms D, Bauerly K, Mah J, Harris C, Fascetti A, Rogers Q, Tchaparian E, Satre M, Rucker RB (2006) Pyrroloquinoline quinone modulates mitochondrial quantity and function in mice. J Nutr 136:390–396
Zhu BQ, Simonis U, Cecchini G, Zhou HZ, Li L, Teerlink JR, Karliner JS (2006) Comparison of pyrroloquinoline quinone and/or metoprolol on myocardial infarct size and mitochondrial damage in a rat model of ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 11:119–128
Chowanadisai W, Bauerly KA, Tchaparian E, Wong A, Cortopassi GA, Rucker RB (2009) Pyrroloquinoline quinone stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis through cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation and increased PGC-1alpha expression. J Biol Chem 285:142–152
Shih AY, Li P, Murphy TH (2005) A small-molecule-inducible Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response provides effective prophylaxis against cerebral ischemia in vivo. J Neurosci 25:10321–10335
Ishii T, Itoh K, Takahashi S, Sato H, Yanagawa T, Katoh Y, Bannai S, Yamamoto M (2000) Transcription factor Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible genes in macrophages. J Biol Chem 275:16023–16029
Motohashi H, O’Connor T, Katsuoka F, Engel JD, Yamamoto M (2002) Integration and diversity of the regulatory network composed of Maf and CNC families of transcription factors. Gene 294:1–12
Blank V (2008) Small Maf proteins in mammalian gene control: mere dimerization partners or dynamic transcriptional regulators? J Mol Biol 376:913–925
Jung KA, Kwak MK (2010) The Nrf2 system as a potential target for the development of indirect antioxidants. Molecules 15:7266–7291
Dhakshinamoorthy S, Long DJ 2nd, Jaiswal AK (2000) Antioxidant regulation of genes encoding enzymes that detoxify xenobiotics and carcinogens. Curr Top Cell Regul 36:201–216
Lee JM, Johnson JA (2004) An important role of Nrf2-ARE pathway in the cellular defense mechanism. J Biochem Mol Biol 37:139–143
Niture SK, Kaspar JW, Shen J, Jaiswal AK (2010) Nrf2 signaling and cell survival. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244:37–42
Ohtsuji M, Katsuoka F, Kobayashi A, Aburatani H, Hayes JD, Yamamoto M (2008) Nrf1 and Nrf2 play distinct roles in activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes. J Biol Chem 283:33554–33562
Satoh T, Baba M, Nakatsuka D, Ishikawa Y, Aburatani H, Furuta K, Ishikawa T, Hatanaka H, Suzuki M, Watanabe Y (2003) Role of heme oxygenase-1 protein in the neuroprotective effects of cyclopentenone prostaglandin derivatives under oxidative stress. Eur J Neurosci 17:2249–2255
Poss KD, Tonegawa S (1997) Reduced stress defense in heme oxygenase 1-deficient cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10925–10930
Griffith OW, Mulcahy RT (1999) The enzymes of glutathione synthesis: gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 73: 209–267, xii
Franklin CC, Backos DS, Mohar I, White CC, Forman HJ, Kavanagh TJ (2009) Structure, function, and post-translational regulation of the catalytic and modifier subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase. Mol Aspects Med 30:86–98
Suh JH, Shenvi SV, Dixon BM, Liu H, Jaiswal AK, Liu RM, Hagen TM (2004) Decline in transcriptional activity of Nrf2 causes age-related loss of glutathione synthesis, which is reversible with lipoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:3381–3386
Brazil DP, Hemmings BA (2001) Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci 26:657–664
Pap M, Cooper GM (1998) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt cell survival pathway. J Biol Chem 273:19929–19932
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA (1995) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378:785–789
Salazar M, Rojo AI, Velasco D, de Sagarra RM, Cuadrado A (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibits the xenobiotic and antioxidant cell response by direct phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of the transcription factor Nrf2. J Biol Chem 281:14841–14851
Rojo AI, Rada P, Egea J, Rosa AO, Lopez MG, Cuadrado A (2008) Functional interference between glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and the transcription factor Nrf2 in protection against kainate-induced hippocampal cell death. Mol Cell Neurosci 39:125–132
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81171180 and 81201017) and Natural Science Funding from the Education Department of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. 12KJB310011). We thank Professor Jie Liu for assistance in manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qi Zhang and Mei Ding contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Ding, M., Cao, Z. et al. Pyrroloquinoline Quinine Protects Rat Brain Cortex Against Acute Glutamate-Induced Neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 38, 1661–1671 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1068-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1068-2