Abstract
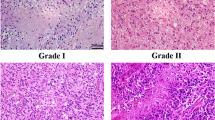
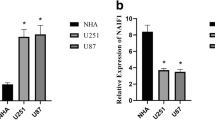
Gliomas are highly malignant tumors, the most common of which are astrocytomas. A growing number of studies suggest that dysregulation of miRNAs is a frequent event contributing to the pathogenesis of gliomas. In this study, we found that over-expression of miR-132 inhibited cell proliferation and migration and triggered apoptosis, while knockdown of miR-132 showed opposite effects. PEA-15 was identified as a direct target of miR-132. Reintroduction of PEA-15 without 3′UTR region reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-132 on cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. MiR-132 was inversely correlated with the PEA-15 expression. CREB (cAMP response element binding protein) and KLF (Krüppel-like factor 8) were conformed as transcription factors of miR-132, which bidirectionally regulate the expression of miR-132. Our study suggests that miR-132 is an important tumor suppressor of astrocytoma progression by targeting PEA-15, while CREB and KLF can modulate the expression of miR-132, thus providing new insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying astrocytoma progression in vitro.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2005) Epidemiology and etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 109:93–108. doi:10.1007/s00401-005-0991-y
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2005) Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:479–489
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359:492–507. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0708126
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D154–D158. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm952
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65:6029–6033. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-0137
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:7065–7070. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-1783
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, Iuliano R, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F, Roldo C, Garzon R, Sevignani C, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 353:1793–1801. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050995
Ciafre SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM, Farace MG (2005) Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:1351–1358. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.030
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2257–2261. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510565103
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838. doi:10.1038/nature03702
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:369–378. doi:10.1007/s10555-009-9188-5
Magill ST, Cambronne XA, Luikart BW, Lioy DT, Leighton BH, Westbrook GL, Mandel G, Goodman RH (2010) microRNA-132 regulates dendritic growth and arborization of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:20382–20387. doi:10.1073/pnas.1015691107
Mulik S, Xu J, Reddy PB, Rajasagi NK, Gimenez F, Sharma S, Lu PY, Rouse BT (2012) Role of miR-132 in angiogenesis after ocular infection with herpes simplex virus. Am J Pathol 181:525–534. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.04.014
Shaked I, Meerson A, Wolf Y, Avni R, Greenberg D, Gilboa-Geffen A, Soreq H (2009) MicroRNA-132 potentiates cholinergic anti-inflammatory signaling by targeting acetylcholinesterase. Immunity 31:965–973. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.09.019
Formosa A, Lena AM, Markert EK, Cortelli S, Miano R, Mauriello A, Croce N, Vandesompele J, Mestdagh P, Finazzi-Agro E, Levine AJ, Melino G, Bernardini S, Candi E (2013) DNA methylation silences miR-132 in prostate cancer. Oncogene 32:127–134. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.14
Li S, Meng H, Zhou F, Zhai L, Zhang L, Gu F, Fan Y, Lang R, Fu L, Gu L, Qi L (2013) MicroRNA-132 is frequently down-regulated in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of breast and acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Pathol Res and Pract 209: 179–183 doi:10.1016/j.prp.2012.12.002
Liu X, Yu H, Cai H, Wang Y (2014) The expression and clinical significance of miR-132 in gastric cancer patients. Diagn Pathol 9:57. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-9-57
Wei X, Tan C, Tang C, Ren G, Xiang T, Qiu Z, Liu R, Wu Z (2013) Epigenetic repression of miR-132 expression by the hepatitis B virus × protein in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Signal 25:1037–1043. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.019
Yang J, Gao T, Tang J, Cai H, Lin L, Fu S (2013) Loss of microRNA-132 predicts poor prognosis in patients with primary osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem 381:9–15. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1677-8
Zhang B, Lu L, Zhang X, Ye W, Wu J, Xi Q, Zhang X (2014) Hsa-miR-132 regulates apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer independent of acetylcholinesterase. J Mol Neurosci 53:335–344. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-0136-z
Zhang S, Hao J, Xie F, Hu X, Liu C, Tong J, Zhou J, Wu J, Shao C (2011) Downregulation of miR-132 by promoter methylation contributes to pancreatic cancer development. Carcinogenesis 32:1183–1189. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgr105
Skalsky RL, Cullen BR (2011) Reduced expression of brain-enriched microRNAs in glioblastomas permits targeted regulation of a cell death gene. PloS One 6:e24248. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024248
Wu C, Lin J, Hong M, Choudhury Y, Balani P, Leung D, Dang LH, Zhao Y, Zeng J, Wang S (2009) Combinatorial control of suicide gene expression by tissue-specific promoter and microRNA regulation for cancer therapy. Mol Ther 17:2058–2066. doi:10.1038/mt.2009.225
Wang H, Li XT, Wu C, Wu ZW, Li YY, Yang TQ, Chen GL, Xie XS, Huang YL, Du ZW, Zhou YX (2015) miR-132 can inhibit glioma cells invasion and migration by target MMP16 in vitro. Onco Targets Ther 8:3211–3218. doi:10.2147/ott.s79282
McManus MT (2003) MicroRNAs and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 13:253–258
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs––microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269. doi:10.1038/nrc1840
Zhou MK, Liu XJ, Zhao ZG, Cheng YM (2015) MicroRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting Lgr5 expression in colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 11:2947–2952. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.3052
Pritchard CC, Cheng HH, Tewari M (2012) MicroRNA profiling: approaches and considerations. Nat Rev Genet 13:358–369. doi:10.1038/nrg3198
Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y, Wang QS, Li SB, Xiao GC, Tong SL (2014) miR-132 inhibits colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis via directly targeting ZEB2. World J Gastroenterol 20:6515–6522. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6515
Lages E, Guttin A, El Atifi M, Ramus C, Ipas H, Dupre I, Rolland D, Salon C, Godfraind C, deFraipont F, Dhobb M, Pelletier L, Wion D, Gay E, Berger F, Issartel JP (2011) MicroRNA and target protein patterns reveal physiopathological features of glioma subtypes. PloS One 6:e20600. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020600
Araujo H, Danziger N, Cordier J, Glowinski J, Chneiweiss H (1993) Characterization of PEA-15, a major substrate for protein kinase C in astrocytes. J Biol Chem 268:5911–5920
Deng YC, Wang JC, Liu XP, Ji SP, Yao LB (2005) Cloning tumor-related genes and tumor suppressor genes in glioma with polymerase chain reaction-based subtractive hybridization. Ai zheng = Aizheng = Chin J Cancer 24:680–684
Eramo A, Pallini R, Lotti F, Sette G, Patti M, Bartucci M, Ricci-Vitiani L, Signore M, Stassi G, Larocca LM, Crino L, Peschle C, De Maria R (2005) Inhibition of DNA methylation sensitizes glioblastoma for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated destruction. Cancer Res 65:11469–11477. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-1724
Garofalo M, Romano G, Quintavalle C, Romano MF, Chiurazzi F, Zanca C, Condorelli G (2007) Selective inhibition of PED protein expression sensitizes B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int J Cancer (Journal International du Cancer) 120:1215–1222. doi:10.1002/ijc.22495
Zanca C, Garofalo M, Quintavalle C, Romano G, Acunzo M, Ragno P, Montuori N, Incoronato M, Tornillo L, Baumhoer D, Briguori C, Terracciano L, Condorelli G (2008) PED is overexpressed and mediates TRAIL resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Cell Mol Med 12:2416–2426. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00283.x
Siegelin MD, Habel A, Gaiser T (2008) Epigalocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) downregulates PEA15 and thereby augments TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in malignant glioma. Neurosci Lett 448:161–165. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.10.036
Incoronato M, Garofalo M, Urso L, Romano G, Quintavalle C, Zanca C, Iaboni M, Nuovo G, Croce CM, Condorelli G (2010) miR-212 increases tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the antiapoptotic protein PED. Cancer Res 70:3638–3646. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-3341
Vo N, Klein ME, Varlamova O, Keller DM, Yamamoto T, Goodman RH, Impey S (2005) A cAMP-response element binding protein-induced microRNA regulates neuronal morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16426–16431. doi:10.1073/pnas.0508448102
Steven A, Seliger B (2016) Control of CREB expression in tumors: from molecular mechanisms and signal transduction pathways to therapeutic target. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7721
Lahiri SK, Zhao J (2012) Kruppel-like factor 8 emerges as an important regulator of cancer. Am J Transl Res 4:357–363
Cox BD, Natarajan M, Stettner MR, Gladson CL (2006) New concepts regarding focal adhesion kinase promotion of cell migration and proliferation. J Cell Biochem 99:35–52. doi:10.1002/jcb.20956
Schnell O, Romagna A, Jaehnert I, Albrecht V, Eigenbrod S, Juerchott K, Kretzschmar H, Tonn JC, Schichor C (2012) Kruppel-like factor 8 (KLF8) is expressed in gliomas of different WHO grades and is essential for tumor cell proliferation. PloS One 7:e30429. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030429
Wan W, Zhu J, Sun X, Tang W (2012) Small interfering RNA targeting Kruppel-like factor 8 inhibits U251 glioblastoma cell growth by inducing apoptosis. Mol Med Rep 5:347–350. doi:10.3892/mmr.2011.669
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (2015 M572336).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, F., Wu, JL., Lu, GF. et al. MicroRNA-132 targets PEA-15 and suppresses the progression of astrocytoma in vitro. J Neurooncol 129, 211–220 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2173-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2173-2