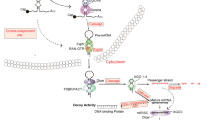
Abstract
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is still a major reason for therapeutic failure in cancers. The mechanisms underlying MDR are multifactorial and are not fully understood. miRNAs are evolutionarily conserved non-coding RNAs that function as key post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression. Emerging evidence indicates a vital role of miRNAs in the resistance to cancer treatments and suggests their potential for cancer therapy, as they can modulate multiple mechanisms link to the development of MDR. This review summarizes the recent findings on the role of miRNAs in MDR, and highlights the molecular targets and mechanisms of miRNA regulated pathways in MDR. Finally, the challenges and prospects of miRNA-targeted therapies for reversing drug resistance are reviewed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szakács G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA et al (2006) Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:219–234
Gomes BC, Rueff J, Rodrigues AS (2016) MicroRNAs and cancer drug resistance. Methods Mol Biol 1395:137–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3347-1_9
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J et al (2003) The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 425:415–419
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Fojo T (2007) Multiple paths to a drug resistance phenotype: mutations, translocations, deletions and amplification of coding genes or promoter regions, epigenetic changes and microRNAs. Drug Resist Updat 10:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drup.2007.02.002
van Jaarsveld MT, Helleman J, Berns EM et al (2010) MicroRNAs in ovarian cancer biology and therapy resistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:1282–1290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2010.01.014
Zheng T, Wang J, Chen X et al (2010) Role of microRNA in anticancer drug resistance. Int J Cancer 126:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24782
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE (2002) Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer 2:48–58
Lage H (2003) ABC-transporters: implications on drug resistance from microorganisms to human cancers. Int J Antimicrob Agents 22:188–199
Dean M, Rzhetsky A, Allikmets R (2001) The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. Genome Res 11(7):1156–1166
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X et al (2008) Role of MicroRNA miR-27a and miR-451 in the regulation of MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression in human cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 76:582–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.06.007
Yang L, Li N, Wang H et al (2012) Altered microRNA expression in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells and upregulation of miR-130a associated with MDR1/P-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance. Oncol Rep 28:592–600. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2012.1823
Wang F, Li T, Zhang B et al (2013) MicroRNA-19a/b regulates multidrug resistance in human gastric cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 434(3):688–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.04.010
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J et al (2008) Involvement of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2152–2159. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0021
Chen J, Tian W, Cai H et al (2012) Down-regulation of microRNA-200c is associated with drug resistance in human breast cancer. Med Oncol 29(4):2527–2534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0117-4
Lu C, Shan Z, Li C et al (2017) MiR-129 regulates cisplatin-resistance in human gastric cancer cells by targeting P-gp. Biomed Pharmacother 86:450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.139
Yang X, Ren W, Shao Y et al (2017) MiR-466b-1-3p regulates P-glycoprotein expression in rat cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Neurosci Lett 645:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.044
Zhou H, Lin C, Zhang Y et al (2017) miR-506 enhances the sensitivity of human colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by suppressing MDR1/P-gp expression. Cell Prolif 50(3):e12341. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12341
Bao L, Hazari S, Mehra S et al (2012) Increased expression of P-glycoprotein and doxorubicin chemoresistance of metastatic breast cancer is regulated by miR-298. Am J Pathol 180(6):2490–2503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.02.024
Xu K, Liang X, Shen K et al (2012) miR-297 modulates multidrug resistance in human colorectal carcinoma by down-regulating MRP-2. Biochem J 446:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20120386
Jiao X, Zhao L, Ma M et al (2013) MiR-181a enhances drug sensitivity in mitoxantone-resistant breast cancer cells by targeting breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Breast Cancer Res Treat 139:717–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2607-x
Ma MT, He M, Wang Y et al (2013) MiR-487a resensitizes mitoxantrone (MX)-resistant breast cancer cells (MCF-7/MX) to MX by targeting breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Cancer Lett 339:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.07.016
Yang G, Jiang O, Ling D et al (2015) MicroRNA-522 reverses drug resistance of doxorubicin-induced HT29 colon cancer cell by targeting ABCB5. Mol Med Rep 12:3930–3936. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3890
Shi L, Wang Z, Sun G et al (2014) miR-145 inhibits migration and invasion of glioma stem cells by targeting ABCG2. Neuromol Med 16(2):517–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8305-y
Pei K, Zhu JJ, Wang CE et al (2016) MicroRNA-185-5p modulates chemosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin via targeting ABCC1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:4697–4704
Shang Y, Zhang Z, Liu Z et al (2014) miR-508-5p regulates multidrug resistance of gastric cancer by targeting ABCB1 and ZNRD1. Oncogene 33:3267–3276
To KK, Leung WW, Ng SS (2015) Exploiting a novel miR-519c-HuR-ABCG2 regulatory pathway to overcome chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Exp Cell Res 338(2):222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.09.011
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B et al (2007) Differential regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively parallel sequencing: miR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis and G1-arrest. Cell Cycle 6(13):1586–1593
Chen JJ, Liu SX, Chen MZ et al (2015) Has–miR-125a and 125b are induced by treatment with cisplatin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibit apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner by targeting p53 mRNA. Mol Med Rep 12(3):3569–3574. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3863
Zhang Y, Geng L, Talmon G et al (2015) MicroRNA-520 g confers drug resistance by regulating p21 expression in colorectal cancer. J Biol Chem 290(10):6215–6225. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.620252
Bommer GT, Gerin I, Feng Y et al (2007) p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor genes. Curr Biol 17:1298–1307
Akao Y, Noguchi S, Iio A et al (2011) Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression causes drug-resistance to 5-FU in human colon cancer DLD-1 cells. Cancer Lett 300(2):197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.006
Fan YN, Meley D, Pizer B et al (2014) Mir-34a mimics are potential therapeutic agents for p53-mutated and chemo-resistant brain tumour cells. PLoS ONE 9(9):e108514. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108514
Kastl L, Brown I, Schofield A (2012) miRNA-34a is associated with docetaxel resistance in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131(2):445–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1424-3
Li Q, Liang X, Wang Y et al (2016) miR-139-5p inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating BCL2. Sci Rep 6:27157. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27157
Zhuang M, Shi Q, Zhang X et al (2015) Involvement of miR-143 in cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cells via targeting IGF1R and BCL2. Tumour Biol 36(4):2737–2745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2898-5
Wang T, Ge G, Ding Y et al (2014) MiR-503 regulates cisplatin resistance of human gastric cancer cell lines by targeting IGF1R and BCL2. Chin Med J (Engl) 127(12):2357–2362
Yang M, Shan X, Zhou X et al (2014) miR-1271 regulates cisplatin resistance of human gastric cancer cell lines by targeting IGF1R, IRS1, mTOR, and BCL2. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 14:884–891
Yang D, Zhan M, Chen T et al (2017) miR-125b-5p enhances chemotherapy sensitivity to cisplatin by down-regulating Bcl2 in gallbladder cancer. Sci Rep 7:43109. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43109
Wang H, Zhu LJ, Yang YC et al (2014) MiR-224 promotes the chemoresistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin via regulating G1/S transition and apoptosis by targeting p21WAF1/CIP1. Br J Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.157
Xu S, Huang H, Chen Y et al (2016) DNA damage responsive miR-33b-3p promoted lung cancer cells survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting p21WAF1/CIP1. Cell Cycle 15(21):2920–2930
Xu B, Niu X, Zhang X et al (2011) miR-143 decreases prostate cancer cells proliferation and migration and enhances their sensitivity to docetaxel through suppression of KRAS. Mol Cell Biochem 350(1–2):207–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0700-6
van Jaarsveld M, van Kuijk P, Boersma A et al (2015) miR-634 restores drug sensitivity in resistant ovarian cancer cells by targeting the Ras-MAPK pathway. Mol Cancer 14:196. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0464-4
Cao W, Yang W, Fan R et al (2014) miR-34a regulates cisplatin-induce gastric cancer cell death by modulating PI3K/AKT/survivin pathway. Tumour Biol 35(2):1287–1295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1171-7
Rao E, Jiang C, Ji M et al (2012) The miRNA-17∼92 cluster mediates chemoresistance and enhances tumor growth in mantle cell lymphoma via PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Leukemia 26(5):1064–1072. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.305
Zhao G, Cai C, Yang T et al (2013) MicroRNA-221 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance through PI3K/Akt pathway in human osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE 8(1):e53906. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053906
Zhao M, Luo R, Liu Y et al (2016) miR-3188 regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation and chemosensitivity through a FOXO1-modulated positive feedback loop with mTOR-p-PI3K/AKT-c-JUN. Nat Commun 7:11309. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11309
Jeong J, Kang H, Kim T et al (2017) MicroRNA-136 inhibits cancer stem cell activity and enhances the anti-tumor effect of paclitaxel against chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells by targeting Notch3. Cancer Lett 386:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.11.017
Giovannetti E, Erozenci A, Smit J et al (2012) Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in anticancer drug resistance and implications for clinical practice. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 81(2):103–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2011.03.010
He X, Xiao X, Dong L et al (2015) MiR-218 regulates cisplatin chemosensitivity in breast cancer by targeting BRCA1. Tumour Biol 36(3):2065–2075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2814-z
Tan X, Peng J, Fu Y et al (2014) miR-638 mediated regulation of BRCA1 affects DNA repair and sensitivity to UV and cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 16(5):435. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-014-0435-5
Moskwa P, Buffa FM, Pan Y et al (2011) miR-182-mediated downregulation of BRCA1 impacts DNA repair and sensitivity to PARP inhibitors. Mol Cell 41:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.12.005
Sun C, Li N, Yang Z et al (2013) miR-9 regulation of BRCA1 and ovarian cancer sensitivity to cisplatin and PARP inhibition. J Natl Cancer Inst 105:1750–1758. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djt302
Xiao M, Cai J, Cai L et al (2017) Let-7e sensitizes epithelial ovarian cancer to cisplatin through repressing DNA double strand break repair. J Ovarian Res 10(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-017-0321-8
Choi YE, Meghani K, Brault ME et al (2016) Platinum and PARP inhibitor resistance due to overexpression of microRNA-622 in BRCA1-mutant ovarian cancer. Cell Rep 14:429–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.046
Meghani K, Fuchs W, Detappe A et al (2018) Multifaceted impact of microRNA 493-5p on genome-stabilizing pathways induces platinum and PARP inhibitor resistance in BRCA2-mutated carcinomas. Cell Rep 23:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.038
Reardon JT, Vaisman A, Chaney SG et al (1999) Efficient nucleotide excision repair of cisplatin, oxaliplatin, and Bis-aceto-ammine-dichloro-cyclohexylamine-platinum(IV) (JM216) platinum intrastrand DNA diadducts. Cancer Res 59:3968–3971
Liu RL, Dong Y, Deng YZ et al (2015) Tumor suppressor miR-145 reverses drug resistance by directly targeting DNA damage-related gene RAD18 in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol 36:5011–5019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3152-5
Valeri N, Gasparini P, Braconi C et al (2010) MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:21098–21103. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1015541107
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Wernicke D et al (2011) Mutator activity induced by microRNA-155 (miR-155) links inflammation and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4908–4913. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1101795108
Ye L, Jiang T, Shao H et al (2017) miR-1290 is a biomarker in DNA-mismatch-repair-deficient colon cancer and promotes resistance to 5-Fluorouracil by directly targeting hMSH2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 7:453–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.05.006
Vinod B, Maliekal T, Anto R (2013) Phytochemicals as chemosensitizers: from molecular mechanism to clinical significance. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(11):1307–1348. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4573
Li YJ, Lei YH, Yao N et al (2017) Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer. Chin J Cancer 36:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-017-0219-2
O’Donovan T, O’Sullivan G, McKenna S (2011) Induction of autophagy by drug-resistant esophageal cancer cells promotes their survival and recovery following treatment with chemotherapeutics. Autophagy 7:509–524
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X et al (2009) Regulation of autophagy by a beclin 1-targeted microRNA, miR-30a, in cancer cells. Autophagy 5:816–823
Zheng B, Zhu H, Gu D et al (2015) MiRNA-30a-mediated autophagy inhibition sensitizes renal cell carcinoma cells to sorafenib. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 459(2):234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.084
Xu R, Liu S, Chen H et al (2016) MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy. Oncol Rep 35(3):1757–1763. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4497
Zhang R, Xu J, Zhao J et al (2017) Mir-30d suppresses cell proliferation of colon cancer cells by inhibiting cell autophagy and promoting cell apoptosis. Tumour Biol 39(6):1010428317703984. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317703984
Lai L, Chen J, Wang N et al (2017) MiRNA-30e mediated cardioprotection of ACE2 in rats with Doxorubicin-induced heart failure through inhibiting cardiomyocytes autophagy. Life Sci 169:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.09.006
Wang C, Zhang Z, Yang W et al (2017) MiR-210 facilitates ECM degradation by suppressing autophagy via silencing of ATG7 in human degenerated NP cells. Biomed Pharmacother 93:470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.048
Comincini S, Allavena G, Palumbo S et al (2013) microRNA-17 regulates the expression of ATG7 and modulates the autophagy process, improving the sensitivity to temozolomide and low-dose ionizing radiation treatments in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 14(7):574–586. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.24597
An Y, Zhang Z, Shang Y et al (2015) miR-23b-3p regulates the chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells by targeting ATG12 and HMGB2. Cell Death Dis 6:e1766. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.123
Chen R, Li X, He B et al (2017) MicroRNA-410 regulates autophagy-related gene ATG16L1 expression and enhances chemosensitivity via autophagy inhibition in osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep 15(3):1326–1334. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6149
Seca H, Lima R, Lopes-Rodrigues V et al (2013) Targeting miR-21 induces autophagy and chemosensitivity of leukemia cells. Curr Drug Targets 14:1135–1143
Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay D, Chakrabarti G (2015) MiR-16 targets Bcl-2 in paclitaxel-resistant lung cancer cells and overexpression of miR-16 along with miR-17 causes unprecedented sensitivity by simultaneously modulating autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Signal 27(2):189–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.11.023
Zhang H, Tang J, Li C et al (2015) MiR-22 regulates 5-FU sensitivity by inhibiting autophagy and promoting apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett 356(2 Pt B):781–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.029
He C, Dong X, Zhai B et al (2015) MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt pathway. Oncotarget 6(30):28867–28881. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4814
Shi Y, Zhao Y, Shao N et al (2017) Overexpression of microRNA-96-5p inhibits autophagy and apoptosis and enhances the proliferation, migration and invasiveness of human breast cancer cells. Oncol Lett 13(6):4402–4412. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6025
Bao L, Lv L, Feng J et al (2016) miR-487b-5p regulates temozolomide resistance of lung cancer cells through LAMP2-medicated autophagy. DNA Cell Biol 35(8):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2016.3259
Tsuchiya Y, Nakajima M, Takagi S et al (2006) MicroRNA regulates the expression of human cytochrome P450 1B1. Cancer Res 66:9090–9098
Rieger J, Reutter S, Hofmann U et al (2015) Inflammation-associated microRNA-130b down-regulates cytochrome P450 activities and directly targets CYP2C9. Drug Metab Dispos 43(6):884–888. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.114.062844
Nakano M, Fukushima Y, Yokota S et al (2015) CYP2A7 pseudogene transcript affects CYP2A6 expression in human liver by acting as a decoy for miR-126. Drug Metab Dispos 43(5):703–712. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.063255
Pan Y, Gao W, Yu A (2009) MicroRNAs regulate CYP3A4 expression via direct and indirect targeting. Drug Metab Dispos 37(10):2112–2117. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.109.027680
Vachirayonstien T, Yan B (2016) MicroRNA-30c-1-3p is a silencer of the pregnane X receptor by targeting the 3′-untranslated region and alters the expression of its target gene cytochrome P450 3A4. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859(9):1238–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.03.016
Wang L, Li C, Li R et al (2016) MicroRNA-764-3p regulates 17β-estradiol synthesis of mouse ovarian granulosa cells by targeting steroidogenic factor-1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 52(3):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9977-9
Sharma D, Turkistani A, Chang W et al (2017) Negative regulation of human pregnane x receptor by microRNA-18a-5p: evidence for suppression of microRNA-18a-5p expression by rifampin and rilpivirine. Mol Pharmacol 92(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.116.107003
Kawahara K, Nakayama H, Nagata M et al (2014) A low Dicer expression is associated with resistance to 5-FU-based chemoradiotherapy and a shorter overall survival in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 43:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12140
Cai L, Wang Z, Liu D (2016) Interference with endogenous EZH2 reverses the chemotherapy drug resistance in cervical cancer cells partly by up-regulating Dicer expression. Tumour Biol 37:6359–6369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4416-9
Chen JC, Su YH, Chiu CF et al (2014) Suppression of Dicer increases sensitivity to gefitinib in human lung cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol 21(Suppl 4):S555–S563. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3673-y
Bu Y, Lu C, Bian C et al (2009) Knockdown of Dicer in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells results in G1 arrest and increased sensitivity to cisplatin. Oncol Rep 21:13–17
Munoz JL, Rodriguez-Cruz V, Ramkissoon SH et al (2015) Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma occurs by miRNA-9-targeted PTCH1, independent of sonic hedgehog level. Oncotarget 6:1190–1201. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2778
Sha LY, Zhang Y, Wang W et al (2016) MiR-18a upregulation decreases Dicer expression and confers paclitaxel resistance in triple negative breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:2201–2208
Geretto M, Pulliero A, Rosano C et al (2017) Resistance to cancer chemotherapeutic drugs is determined by pivotal microRNA regulators. Am J Cancer Res 7:1350–1371
Sun HL, Cui R, Zhou J et al (2016) ERK activation globally downregulates miRNAs through phosphorylating exportin-5. Cancer Cell 30:723–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.001
Chen QW, Zhu XY, Li YY et al (2014) Epigenetic regulation and cancer (review). Oncol Rep 31:523–532. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2013.2913
Ye XM, Zhu HY, Bai WD et al (2014) Epigenetic silencing of miR-375 induces trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer by targeting IGF1R. BMC Cancer 14:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-134
Liu MX, Siu MK, Liu SS et al (2014) Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-199b-5p is associated with acquired chemoresistance via activation of JAG1-Notch1 signaling in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 5:944–958. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1458
Schliesser MG, Claus R, Hielscher T et al (2016) Prognostic relevance of miRNA-155 methylation in anaplastic glioma. Oncotarget 7:82028–82045. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13452
Zhou D, Wan Y, Xie D et al (2015) DNMT1 mediates chemosensitivity by reducing methylation of miRNA-20a promoter in glioma cells. Exp Mol Med 47:e182. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2015.57
Hong L, Han Y, Zhang Y et al (2013) MicroRNA-21: a therapeutic target for reversing drug resistance in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17(9):1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2013.819853
Xie Z, Cao L, Zhang J (2013) miR-21 modulates paclitaxel sensitivity and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Lett 6:795–800
Jin B, Liu Y, Wang H (2015) Antagonism of miRNA-21 sensitizes human gastric cancer cells to paclitaxel. Cell Biochem Biophys 72(1):275–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0450-2
Kopczynska E (2015) Role of microRNAs in the resistance of prostate cancer to docetaxel and paclitaxel. Contemp Oncol (Pozn) 19:423–427. https://doi.org/10.5114/wo.2015.56648
De Mattos-Arruda L, Bottai G, Nuciforo P et al (2015) MicroRNA-21 links epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inflammatory signals to confer resistance to neoadjuvant trastuzumab and chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 6(35):37269–37280. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5495
Nielsen BS, Balslev E, Poulsen TS et al (2014) miR-21 expression in cancer cells may not predict resistance to adjuvant trastuzumab in primary breast cancer. Front Oncol 4:207. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00207
Corcoran C, Rani S, O’Driscoll L (2014) miR-34a is an intracellular and exosomal predictive biomarker for response to docetaxel with clinical relevance to prostate cancer progression. Prostate 74:1320–1334
Dwivedi S, Mustafi S, Mangala L et al (2016) Therapeutic evaluation of microRNA-15a and microRNA-16 in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 7(12):15093–15104. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7618
Xu Y, Huang J, Ma L et al (2016) MicroRNA-122 confers sorafenib resistance to hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting IGF-1R to regulate RAS/RAF/ERK signaling pathways. Cancer Lett 371(2):171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.034
Yu D, Lv M, Chen W et al (2015) Role of miR-155 in drug resistance of breast cancer. Tumour Biol 36(3):1395–1401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3263-z
Shibayama Y, Kondo T, Ohya H et al (2015) Upregulation of microRNA-126-5p is associated with drug resistance to cytarabine and poor prognosis in AML patients. Oncol Rep 33(5):2176–2182. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3839
Zhang W, Zhou J, Zhu X et al (2017) MiR-126 reverses drug resistance to TRAIL through inhibiting the expression of c-FLIP in cervical cancer. Gene 627:420–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.055
Liu S, Tetzlaff M, Cui R et al (2012) miR-200c inhibits melanoma progression and drug resistance through down-regulation of BMI-1. Am J Pathol 181(5):1823–1835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.07.009
Zhao J, Chu Z, Hu Y et al (2015) Targeting the miR-221-222/PUMA/BAK/BAX pathway abrogates dexamethasone resistance in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res 75(20):4384–4397. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0457
Beg M, Brenner A, Sachdev J et al (2017) Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 35(2):180–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0407-y
Li Z, Rana T (2014) Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs: current status and future challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(8):622–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4359
Kao S, Fulham M, Wong K et al (2015) A significant metabolic and radiological response after a novel targeted microRNA-based treatment approach in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 191(12):1467–1469. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201503-0461LE
Reid G, Kao S, Pavlakis N et al (2016) Clinical development of TargomiRs, a miRNA mimic-based treatment for patients with recurrent thoracic cancer. Epigenomics 8(8):1079–1085. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2016-0035
Rupaimoole R, Slack F (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):203–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) microRNA involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis 33(6):1126–1133. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgs140
van Rooij E, Olson EN (2012) MicroRNA therapeutics for cardiovascular disease: opportunities and obstacles. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:860–872. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3864
Jackson AL, Linsley PS (2010) Recognizing and avoiding siRNA off-target effects for target identification and therapeutic application. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3010
Grueter CE, van Rooij E, Johnson BA et al (2012) A cardiac microRNA governs systemic energy homeostasis by regulation of MED13. Cell 149:671–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.029
Raemdonck K, Vandenbroucke RE, Demeester J et al (2008) Maintaining the silence: reflections on long-term RNAi. Drug Discov Today 13:917–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2008.06.008
Kim DH, Rossi JJ (2007) Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet 8:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2006
Pecot CV, Calin GA, Coleman RL et al (2011) RNA interference in the clinic: challenges and future directions. Nat Rev Cancer 11:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2966
Acknowledgements
We thank the grants below for support: National Natural Science Foundation of China (31502056), the Youth Talent Development Plan of Shanghai Municipal Agricultural System (20170116), and the Young Scientist Plan of Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences (ZP173).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest is in this paper.
Ethical approval
The review is not related to either human or animals use.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, R., Lin, Y. & Zhu, L. Molecular pathways involved in microRNA-mediated regulation of multidrug resistance. Mol Biol Rep 45, 2913–2923 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4358-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4358-6