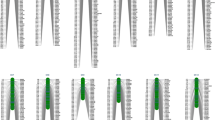
Abstract
Preharvest sprouting (PHS) and high alpha-amylase activity (AA) negatively affect quality of rye grain. The objective of this study was to reveal genetic relationship between PHS and AA by developing a consensus map of QTLs controlling each trait. A method of composite interval mapping (CIM) was used to search for QTLs within the 541 × Ot1-3 and DS2 × RXL10 F2 mapping populations representing wide variation range of both traits. Sixteen QTLs for AA were detected on chromosomes 1R (3), 2R (2), 3R (2), 4R (3), 5R (3), 6R (2) and 7R (1). Their distribution was not random showing a tendency of QTL location in distal regions of chromosomes. Nine QTLs for AA located on chromosome arms 1RS, 2RL, 3RS, 4RL, 5RS, 5RL, 6RS, 6RL and 7RS coincided with QTLs for PHS. Seven QTLs for AA independent from PHS were detected on chromosome arms 1RL (2), 2RS, 3RL, 4RS, 4RL and 5RL. Four QTLs for PHS not associated with those for AA were identified on chromosomes 1RL, 2RL, 5RL and 7RL. Partial overlapping of the genetic systems controlling AA and PHS suggests that alpha-amylase found in sound grain of rye could be produced through at least three independent mechanisms i.e. PHS at its initial stage, late maturity alpha-amylase (LMA) and/or retained pericarp alpha-amylase (RPAA). Six QTLs co-located on both maps were found on chromosome arms 1RS, 2RS, 5RS, 5RL, 6RS and 6RL. Valuable features of line Ot1-3 i.e. resistance to preharvest sprouting and low alpha-amylase production in ripening grain can be attributed to seven major QTLs from chromosomes 1RL, 2RL, 5RL (2), 6RL and 7R (2). This set of QTLs, identified in line Ot1-3, might be useful in breeding sprouting resistant cultivars of rye.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui KH, Peng SB, Xing YZ et al (2002) Molecular dissection of seedling-vigor and associated physiological traits in rice. Theor Appl Genet 105:745–753. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0908-2
Devos KM, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CD et al (1993) Chromosomal rearrangements in the rye genome relative to that of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 85:673–680. doi:10.1007/BF00225004
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SSL, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell Suppl 2002:815–845
Flintham J, Adam R, Bassoi M et al (2002) Mapping genes for resistance to sprouting damage in wheat. Euphytica 126:39–45. doi:10.1023/A:1019632008244
Gale MD, Flintham JE, Devos KM (2002) Cereal comparative genetics and pre-harvest sprouting. Euphytica 126:21–25. doi:10.1023/A:1019675723265
Gao W, Clancy JA, Han F et al (2004) Fine mapping of a malting-quality QTL complex near the chromosome 4HS telomere in barley. Theor Appl Genet 109:750–760. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1688-7
Gelin JR, Elias EM, Kianian SF (2006) Evaluation of two durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var durum) crosses for preharvest sprouting resistance. Field Crops Res 97:188–196. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2005.09.014
Han I, Clancy JA, Jones BL et al (2004) Dissection of a malting quality region on chromosome 1 (7H) of barley. Mol Breed 14:339–347. doi:10.1023/B:MOLB.0000049215.53864.e3
Hedden P, Phillips AL (2000) Gibberellin metabolism: new insights revealed by the genes. Trends Plant Sci 5:523–530. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(00)01790-8
Kato K, Nakamura W, Tabiki T et al (2001) Detection of loci controlling seed dormancy on group 4 chromosomes of wheat and comparative mapping with rye and barley genomes. Theor Appl Genet 102:980–985. doi:10.1007/s001220000494
Kermode AR (2005) Role of abscisic acid in seed dormancy. J Plant Growth Regul 24:319–344. doi:10.1007/s00344-005-0110-2
Kettlewell PS, Lunn GD, Major BJ et al (1996) A possible scheme for pre-harvest prediction of Hagberg falling number and sprouting of wheat in the UK and France. In: Noda K, Mares DJ (eds) Pre-harvest sprouting in cereals 1995. Center for Academic Societies, Japan, Osaka, pp 35–41
Korff M, Wang H, Leon J et al (2008) AB-QTL analysis in spring barley: III. Identification of exotic alleles for the improvement of malting quality in spring barley (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Mol Breed 21:81–93. doi:10.1007/s11032-007-9110-1
Kunert A, Naz AA, Dedeck O et al (2007) AB-QTL analysis in winter wheat: I Synthetic hexaploid wheat (T. turgidum ssp. diciccoides × T. tauschii) as a source of favourable alleles for milling and baking quality traits. Theor Appl Genet 115:683–695. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0600-7
Lazarus CM, Baulcombe DC, Martienssen RA (1985) α-Amylase genes of wheat are two multigene families which are differentially expressed. Plant Mol Biol 5:13–24. doi:10.1007/BF00017869
Li C, Ni P, Francki M et al (2004) Genes controlling seed dormancy and pre-harvest sprouting in a rice–wheat–barley comparison. Funct Integr Genomics 4:84–93. doi:10.1007/s10142-004-0104-3
Mares D, Mrva K (2008) Late-maturity α-amylase: low falling number in wheat in the absence of preharvest sprouting. J Cereal Sci 47:6–17. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2007.01.005
Marquez-Cedillo LA, Hayes PM, Jones BL (2000) QTL analysis of malting quality in barley based on the doubled-haploid progeny of two elite North American varieties representing different germplasm groups. Theor Appl Genet 101:173–184. doi:10.1007/s001220051466
Masojć P (1987) Genetics of α-amylases from rye endosperm. Theor Appl Genet 73:440–444. doi:10.1007/BF00262513
Masojć P, Gale MD (1991) α-Amylase structural genes in rye. Theor Appl Genet 82:771–776. doi:10.1007/BF00227324
Masojć P, Larsson-Raźnikiewicz M (1991) Genetic variation of α-amylase levels among rye kernels, tested by gel diffusion technique. Swed J Agric Res 21:141–145
Masojć P, Milczarski P (2005) Mapping QTLs for alpha-amylase activity in rye grain. J Appl Genet 46:115–123
Masojć P, Banek-Tabor A, Milczarski P et al (2007) QTLs for resistance to preharvest sprouting in rye (Secale cereale L.). J Appl Genet 48:211–217
Milczarski P, Banek-Tabor A, Lebiecka K et al (2007) New genetic map of rye composed of PCR-based molecular markers and its alignment with the reference map of the DS2 × RXL10 intercross. J Appl Genet 48:11–24
Mrva K, Mares DJ (2002) Screening methods and identification of QTLs associated with late maturity alpha-amylase in wheat. Euphytica 126:55–59. doi:10.1023/A:1019667521448
Twardowska M, Masojć P, Milczarski P (2005) Pyramiding genes affecting sprouting resistance in rye by means of marker assisted selection. Euphytica 143:257–260. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-7873-1
Ullrich SE, Clancy JA, Blanco IA et al (2008) Genetic analysis of preharvest sprouting in a six-row barley cross. Mol Breed 21:249–259. doi:10.1007/s11032-007-9125-7
Wang SC, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B (2006) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carol St Univ, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Zanetti S, Winzeler M, Keller M et al (2000) Genetic analysis of pre-harvest sprouting resistance in a wheat × spelt cross. Crop Sci 40:1406–1417
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Center of Scientific Research and Development (grant no PBZ-MNiSW-2/3/2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masojć, P., Milczarski, P. Relationship between QTLs for preharvest sprouting and alpha-amylase activity in rye grain. Mol Breeding 23, 75–84 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9215-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9215-1